Growth of Tourism-
The growth of tourism is influenced by various factors that shape travel patterns and destinations worldwide. Here are some key factors contributing to the growth of tourism:
- Globalization: Improved transportation infrastructure and easier access to information have made travel more convenient and affordable. This has opened up new destinations and increased tourist mobility.
- Economic Growth: Rising incomes and standards of living in many countries have enabled more people to afford leisure travel. This demographic shift has expanded the potential tourist base.
- Technology: The internet and social media play crucial roles in promoting destinations and facilitating travel bookings. Online reviews and recommendations also influence travel decisions.
- Cultural Exchange: There is a growing interest in cultural exchange and experiencing different lifestyles. Tourists seek authentic experiences, local cuisine, and traditions, which drive tourism to culturally rich destinations.
- Government Policies: Governments play a significant role in promoting tourism through policies that facilitate travel, invest in infrastructure, and support tourism-related businesses.
- Environmental Factors: Increased awareness of environmental sustainability has led to the rise of eco-tourism and responsible travel practices. Many travelers now seek destinations that prioritize conservation and environmental protection.
- Events and Festivals: Special events, festivals, and cultural celebrations attract tourists and boost local economies. These events often showcase unique aspects of a destination’s culture and heritage.
- Infrastructure Development: Investments in tourism infrastructure such as hotels, resorts, airports, and transportation networks enhance a destination’s appeal and accessibility.
- Medical Tourism: The globalization of healthcare services has contributed to the growth of medical tourism, where people travel to other countries for medical treatment at lower costs or for specialized procedures.
- Changing Demographics: Aging populations in many countries have led to increased demand for senior travel and wellness tourism, including spa retreats and health-focused vacations.
Overall, the growth of tourism is a complex interplay of economic, social, cultural, and technological factors that continue to evolve with changing global trends and consumer preferences.
What is Required Growth of Tourism
The required growth of tourism can vary depending on the context and goals of different stakeholders such as governments, tourism boards, businesses, and communities. Generally, the required growth of tourism refers to the desired increase in tourist arrivals, expenditures, or other relevant metrics within a specified timeframe. Here are some aspects to consider:
- Economic Objectives: Governments often aim for tourism growth to stimulate economic development, create jobs, and generate revenue through tourist expenditures on accommodation, dining, attractions, and souvenirs.
- Infrastructure Development: Required growth may necessitate investments in tourism infrastructure such as hotels, transportation networks, and tourist attractions to accommodate increasing visitor numbers.
- Sustainability: Growth should be balanced with sustainability considerations to preserve natural resources, protect cultural heritage, and minimize negative impacts on local communities.
- Marketing and Promotion: Tourism growth often requires effective marketing strategies to attract visitors from target markets, raise destination awareness, and differentiate the destination from competitors.
- Regulatory Framework: Clear policies and regulations are essential to manage tourism growth responsibly, ensuring safety, quality standards, and positive visitor experiences.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Stakeholders need to collaborate across sectors (public, private, and community) to achieve sustainable tourism growth and address challenges collectively.
- Diversification: To sustain growth, destinations may need to diversify their tourism offerings, appealing to different market segments and reducing dependency on seasonal or specific types of tourism.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuous monitoring of tourism metrics and visitor satisfaction helps stakeholders assess progress, identify challenges, and adjust strategies as needed to achieve required growth.
In summary, the required growth of tourism involves setting clear objectives aligned with economic, environmental, and social goals, implementing strategies to achieve these objectives, and monitoring outcomes to ensure sustainable and inclusive development of the tourism sector.
Who is Required Growth of Tourism
“Required Growth of Tourism” isn’t a person but rather a concept or a goal that various entities, such as governments, tourism boards, businesses, and communities, might pursue. It refers to the desired increase in tourism activity within a region or destination over a specific period. Here’s how different stakeholders might interpret or pursue the concept of required growth of tourism:
- Governments: Governments often see tourism growth as a means to stimulate economic development, create jobs, and generate revenue through visitor expenditures. They may set targets for increasing tourist arrivals, length of stay, or spending per tourist.
- Tourism Boards: Tourism boards focus on promoting destinations and enhancing visitor experiences. They set goals for attracting more tourists, improving destination infrastructure, and developing sustainable tourism practices.
- Businesses: Businesses in the tourism sector, such as hotels, restaurants, tour operators, and souvenir shops, seek growth to increase their customer base and revenue. They may align their strategies with broader tourism growth objectives.
- Communities: Local communities benefit from tourism through job creation, business opportunities, and cultural exchange. However, they also seek to manage tourism growth sustainably to preserve their environment, culture, and quality of life.
- International Organizations: Organizations like the UN World Tourism Organization (UNWTO) may provide guidelines and support for sustainable tourism growth globally, focusing on economic, social, and environmental sustainability.
In essence, the concept of required growth of tourism encompasses strategic planning, development initiatives, marketing efforts, and policy decisions aimed at fostering sustainable and inclusive tourism growth to benefit both stakeholders and destinations. Each stakeholder plays a role in shaping and achieving the desired growth of tourism in their respective contexts.
When is Required Growth of Tourism
The “required growth of tourism” is not tied to a specific time or date but rather refers to a goal or objective that stakeholders in the tourism industry aim to achieve over a period. This period can vary based on various factors such as:
- Long-term Strategic Plans: Governments, tourism boards, and businesses often set long-term goals for tourism growth, typically spanning several years (e.g., 5-year plans, 10-year plans). These plans outline targets for increasing tourist arrivals, expenditures, or improving infrastructure.
- Annual Targets: Many destinations and tourism organizations set annual targets for tourism growth. These targets may include metrics such as percentage increases in tourist arrivals, revenue from tourism, or improvements in visitor satisfaction.
- Event-Specific Growth: Tourism growth may also be linked to specific events or occasions, such as hosting international conferences, cultural festivals, or major sporting events. Organizers often set growth targets related to visitor numbers and economic impact during these events.
- Seasonal Variations: In some cases, tourism growth targets may be seasonal, focusing on increasing visitor numbers during peak seasons or promoting off-peak tourism to achieve year-round sustainability.
- Recovery Goals: After economic downturns, natural disasters, or global crises (e.g., pandemics), destinations may set recovery goals for tourism, aiming to return to pre-crisis levels of visitor arrivals, revenues, and employment.
Overall, the timing of required growth of tourism is contextual and depends on the specific objectives and strategies of stakeholders involved. It involves setting realistic and measurable targets over varying timeframes to drive sustainable tourism development and economic benefits for destinations.
Where is Required Growth of Tourism
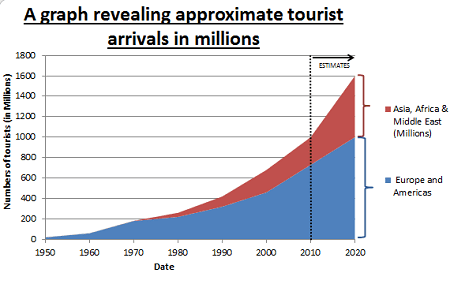
The “required growth of tourism” is not a physical location but rather a strategic objective or goal that is pursued by stakeholders within the tourism industry. However, this goal can be applied to various destinations around the world, depending on the specific context and needs of each location. Here are some examples of where the required growth of tourism may be targeted:
- Countries and Regions: National governments often set targets for increasing tourism arrivals, expenditures, and employment within their countries. They may focus on promoting specific regions or attractions to achieve growth.
- Cities and Urban Areas: Many cities aim to attract more tourists to boost local economies, create jobs, and enhance their global visibility. They may develop tourism infrastructure, promote cultural events, and improve visitor experiences.
- Rural and Remote Areas: Some destinations seek to diversify tourism beyond urban centers by promoting natural landscapes, heritage sites, and unique cultural experiences. This helps distribute economic benefits more broadly.
- Developing Destinations: Emerging destinations may prioritize tourism growth as a means to accelerate economic development, reduce poverty, and improve living standards through increased visitor spending.
- Tourist Attractions: Specific tourist attractions, such as national parks, historical sites, or theme parks, may have growth targets to increase visitor numbers while managing environmental impact and preserving cultural heritage.
- Global Tourism Hotspots: Established tourism hotspots, like major cities, beach resorts, or iconic landmarks, continually seek to maintain or grow visitor numbers through marketing campaigns, infrastructure improvements, and sustainability initiatives.
In summary, the required growth of tourism can be pursued in various geographical locations worldwide, each with unique strategies and challenges tailored to their specific tourism offerings and market positioning. It involves setting goals, implementing strategies, and measuring outcomes to achieve sustainable tourism development and economic benefits for the destination and its communities.
How is Required Growth of Tourism
Achieving the required growth of tourism involves a strategic approach that encompasses several key elements and actions. Here’s a breakdown of how tourism growth can be pursued:
- Setting Clear Objectives: Define specific and measurable goals for tourism growth, such as increasing tourist arrivals, extending length of stay, boosting visitor spending, or improving seasonality.
- Market Research and Analysis: Conduct thorough market research to understand current trends, visitor demographics, competitive landscapes, and emerging market opportunities. This helps in identifying target markets and tailoring marketing strategies accordingly.
- Infrastructure Development: Invest in tourism infrastructure such as transportation networks, accommodation options, attractions, and facilities to enhance visitor experiences and accommodate increasing tourist numbers.
- Destination Marketing and Promotion: Develop and implement effective marketing campaigns to raise awareness of the destination, highlight unique selling points, and attract tourists from target markets. This includes digital marketing, social media engagement, partnerships with travel agencies, and participation in trade shows.
- Product Development: Diversify tourism products and experiences to appeal to different market segments. This could include cultural tours, adventure activities, culinary experiences, eco-tourism initiatives, and themed events.
- Sustainability and Responsible Tourism Practices: Implement sustainable tourism practices to preserve natural resources, protect cultural heritage, and support local communities. This includes promoting eco-friendly accommodations, minimizing carbon footprint, and fostering community engagement.
- Policy Support and Regulatory Framework: Create supportive policies and regulations that facilitate tourism growth while ensuring visitor safety, quality standards, and environmental sustainability. This involves collaboration between government agencies, tourism boards, and private sector stakeholders.
- Training and Capacity Building: Provide training and capacity building programs for tourism industry professionals, local communities, and service providers to enhance hospitality skills, customer service standards, and cultural sensitivity.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Continuously monitor tourism performance metrics such as visitor arrivals, expenditure patterns, occupancy rates, and customer satisfaction. Evaluate the effectiveness of strategies and adjust plans as needed to achieve growth targets.
- Collaboration and Stakeholder Engagement: Foster partnerships and collaboration among stakeholders including government agencies, tourism boards, businesses, local communities, academia, and NGOs. This collective effort helps in leveraging resources, sharing expertise, and addressing challenges collectively.
By implementing these strategies and actions systematically, destinations can work towards achieving sustainable and inclusive growth of tourism, maximizing economic benefits while minimizing negative impacts on the environment and local cultures.
Case Study on Growth of Tourism
Let’s consider a case study on the growth of tourism in a specific destination: Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
Background: Dubai has transformed from a small fishing village into a global hub for tourism, trade, and finance. Over the past few decades, it has strategically leveraged its geographic location, infrastructure investments, and visionary leadership to become one of the world’s most visited cities.
Factors Contributing to Tourism Growth:
- Visionary Leadership and Strategic Planning:
- Dubai’s leadership, particularly under the guidance of Sheikh Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum, has played a crucial role. They envisioned Dubai as a global city and invested heavily in infrastructure and tourism development.
- The launch of initiatives like Dubai Tourism Strategy 2020 aimed to attract 20 million visitors per year by 2020, focusing on diversifying tourism offerings and enhancing visitor experiences.
- Infrastructure Development:
- Dubai invested heavily in creating world-class infrastructure, including iconic landmarks like the Burj Khalifa (the world’s tallest building), Palm Jumeirah (a man-made island), and luxury hotels and resorts.
- The expansion of Dubai International Airport and the development of Al Maktoum International Airport (Dubai World Central) increased the city’s connectivity to global markets.
- Marketing and Promotion:
- Dubai aggressively marketed itself as a luxury travel destination through global marketing campaigns, participation in travel trade shows, and partnerships with airlines and tour operators.
- Events like the Dubai Shopping Festival and Dubai Expo 2020 (postponed to 2021 due to COVID-19) attracted millions of visitors, boosting tourism revenues.
- Diversification of Tourism Offerings:
- Dubai diversified its tourism offerings beyond shopping and luxury tourism to include cultural experiences, adventure sports, family attractions (e.g., theme parks like Dubai Parks and Resorts), and eco-tourism initiatives.
- Initiatives like Dubai Food Festival and Dubai Opera aimed to showcase the city’s culinary scene and cultural offerings.
- Business and MICE Tourism:
- Dubai positioned itself as a global hub for business and MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions) tourism. The Dubai International Financial Centre (DIFC) and Dubai World Trade Centre (DWTC) host numerous international conferences and events.
- Government Support and Policies:
- Dubai’s government implemented investor-friendly policies, including tax incentives, visa facilitation, and ease of doing business, attracting global investments in hospitality and tourism infrastructure.
- Dubai Tourism and Commerce Marketing (DTCM) provided support to local businesses and stakeholders, fostering collaboration and sustainable growth.
Impact of Tourism Growth:
- Economic Growth: Tourism has become a significant contributor to Dubai’s economy, generating billions of dollars in revenue and supporting thousands of jobs across various sectors.
- Infrastructure Development: The growth of tourism spurred investments in transportation, hospitality, retail, and entertainment sectors, benefiting the overall economy.
- Cultural Exchange: Dubai’s multicultural environment attracts visitors from diverse backgrounds, promoting cultural exchange and understanding.
- Challenges: Sustainable tourism management, environmental conservation, and balancing economic benefits with cultural preservation remain ongoing challenges.
Conclusion: Dubai’s case illustrates how strategic planning, visionary leadership, infrastructure development, diversification of offerings, effective marketing, and supportive policies can drive rapid and sustainable growth in tourism. By continuously innovating and adapting to global trends, Dubai has positioned itself as a leading global tourism destination, offering unique experiences and opportunities for visitors from around the world.
White paper on Growth of Tourism
Title: Accelerating Tourism Growth: Strategies for Sustainable Development
Abstract: Tourism is a key driver of economic growth, job creation, and cultural exchange globally. This white paper explores the current trends, challenges, and strategies for accelerating tourism growth while ensuring sustainable development. It examines successful case studies and provides recommendations for policymakers, industry stakeholders, and communities to maximize the benefits of tourism while mitigating its negative impacts.
1. Introduction
- Importance of tourism as an economic sector
- Global trends in tourism growth and its impact on economies and societies
2. Key Drivers of Tourism Growth
- Economic factors: rising incomes, affordability of travel
- Technological advancements: digital marketing, online booking platforms
- Cultural exchange and experiential travel
- Government policies and infrastructure development
3. Challenges in Tourism Growth
- Overtourism and carrying capacity
- Environmental impacts: carbon footprint, waste management
- Socio-cultural impacts: preservation of heritage and local communities
- Economic dependency on tourism and seasonality
4. Strategies for Sustainable Tourism Growth
- Diversification of tourism products and experiences
- Infrastructure development: transportation, accommodation, attractions
- Sustainable practices: eco-tourism, responsible tourism initiatives
- Community engagement and capacity building
- Policy frameworks and regulatory measures
5. Case Studies of Successful Tourism Growth
- Example 1: Dubai, UAE – Transformation from desert city to global tourism hub
- Example 2: Costa Rica – Sustainable tourism practices and biodiversity conservation
- Example 3: Barcelona, Spain – Managing overtourism through innovative policies
6. Recommendations
- For governments: fostering supportive policies and regulatory frameworks
- For businesses: adopting sustainable practices and innovation in tourism offerings
- For communities: balancing tourism benefits with cultural and environmental preservation
- For travelers: responsible travel practices and awareness
7. Conclusion
- Summary of key findings and recommendations
- Call to action for stakeholders to collaborate for sustainable tourism growth
8. References
- Citations and sources used in the white paper
This outline provides a structured approach to discussing the growth of tourism, emphasizing sustainability and the importance of balanced development. Each section can be expanded with relevant data, case studies, and actionable recommendations to cater to the interests and needs of policymakers, industry professionals, and academics interested in tourism management and development.
Industrial Application of Growth of Tourism
The industrial application of tourism growth refers to how various industries and sectors can benefit and contribute to the expansion and sustainability of tourism. Here’s how different industries can leverage and support the growth of tourism:
- Hospitality Industry:
- Hotels and Accommodation: As tourism grows, there is an increased demand for diverse and high-quality accommodation options. The hospitality industry can benefit from tourism by expanding hotel capacities, offering unique experiences, and adapting to the preferences of different traveler segments (luxury, budget, eco-friendly, etc.).
- Restaurants and Food Services: Tourists often seek authentic culinary experiences. The restaurant sector can capitalize on tourism growth by offering local cuisine, dining experiences, food tours, and catering services for events and conferences.
- Transportation Industry:
- Airlines and Airports: Tourism growth drives demand for air travel, leading to increased routes, frequencies, and passenger numbers. Airports can expand infrastructure to accommodate more international flights and improve connectivity.
- Ground Transportation: Tourists need efficient ground transportation options such as taxis, buses, rental cars, and rideshare services to explore destinations. The transportation sector can innovate with eco-friendly vehicles and services tailored to tourist needs.
- Retail and Shopping:
- Souvenirs and Local Products: Tourists often purchase souvenirs and local products as mementos of their travel experiences. Retailers can cater to tourists by offering unique and culturally significant items, thus boosting local economies.
- Luxury Brands: Popular tourist destinations attract high-net-worth individuals who may indulge in luxury shopping. Retail sectors can benefit from tourism by offering luxury goods and creating exclusive shopping experiences.
- Entertainment and Leisure:
- Attractions and Theme Parks: Tourists visit attractions, theme parks, museums, and cultural sites. These venues can expand offerings, introduce new experiences, and host events to attract visitors and extend their stay.
- Entertainment Venues: The entertainment industry can benefit from tourism by hosting concerts, festivals, sports events, and theater productions that draw local and international audiences.
- Tour Operators and Travel Agencies:
- Tourism Packages: Tour operators and travel agencies create and sell tourism packages that include accommodation, transportation, guided tours, and activities. They play a crucial role in promoting destinations and curating travel experiences.
- Adventure and Eco-Tourism: Specialized tour operators cater to adventure seekers and eco-conscious travelers, offering activities like hiking, wildlife safaris, diving, and sustainable tourism experiences.
- Technology and Innovation:
- Digital Platforms: Technology facilitates online bookings, reviews, and personalized travel recommendations. Tourism industries can leverage digital platforms for marketing, customer engagement, and enhancing visitor experiences.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): Innovative technologies like VR and AR can offer virtual tours of destinations, historical sites, and attractions, enticing potential tourists and enhancing pre-travel planning experiences.
- Healthcare and Wellness:
- Medical Tourism: Healthcare facilities can attract international patients seeking medical treatments, surgeries, and wellness services at competitive prices. This niche market supports local economies and healthcare infrastructure development.
In conclusion, the industrial application of tourism growth involves collaboration and innovation across various sectors to capitalize on opportunities, address challenges, and ensure sustainable development. By aligning strategies with tourism trends and traveler preferences, industries can maximize economic benefits while preserving cultural heritage and natural resources for future generations.






