Courtesy : Bachelor of Science Microbiology (CBM) – Chemistry, Botany, Microbiology in USA
Fermentation and germ theory of diseases
Pasteur was motivated to investigate fermentation while working at Lille. In 1856 a local wine manufacturer, M. Bigot, whose son was one of Pasteur’s students, sought for his advice on the problems of making beetroot alcohol and souring. Pasteur began his research in the topic by repeating and confirming works of Theodor Schwann, who demonstrated a decade earlier that yeast were alive. # ISO certification in India
According to his son-in-law, René Vallery-Radot, in August 1857 Pasteur sent a paper about lactic acid fermentation to the Société des Sciences de Lille, but the paper was read three months later. A memoire was subsequently published on 30 November 1857. In the memoir, he developed his ideas stating that: “I intend to establish that, just as there is an alcoholic ferment, the yeast of beer, which is found everywhere that sugar is decomposed into alcohol and carbonic acid, so also there is a particular ferment, a lactic yeast, always present when sugar becomes lactic acid.”# ISO certification in India
Pasteur also wrote about alcoholic fermentation. It was published in full form in 1858. Jöns Jacob Berzelius and Justus von Liebig had proposed the theory that fermentation was caused by decomposition. Pasteur demonstrated that this theory was incorrect, and that yeast was responsible for fermentation to produce alcohol from sugar. He also demonstrated that, when a different microorganism contaminated the wine, lactic acid was produced, making the wine sour. In 1861, Pasteur observed that less sugar fermented per part of yeast when the yeast was exposed to air. The lower rate of fermentation aerobically became known as the Pasteur effect.# ISO certification in India

Pasteur experimenting in his laboratory.

Institut Pasteur de Lille
Pasteur’s research also showed that the growth of micro-organisms was responsible for spoiling beverages, such as beer, wine and milk. With this established, he invented a process in which liquids such as milk were heated to a temperature between 60 and 100 °C. This killed most bacteria and moulds already present within them. Pasteur and Claude Bernard completed tests on blood and urine on 20 April 1862. Pasteur patented the process, to fight the “diseases” of wine, in 1865. The method became known as pasteurization, and was soon applied to beer and milk.# ISO certification in India
Beverage contamination led Pasteur to the idea that micro-organisms infecting animals and humans cause disease. He proposed preventing the entry of micro-organisms into the human body, leading Joseph Lister to develop antiseptic methods in surgery.
In 1866, Pasteur published Etudes sur le Vin, about the diseases of wine, and he published Etudes sur la Bière in 1876, concerning the diseases of beer.
In the early 19th century, Agostino Bassi had shown that muscardine was caused by a fungus that infected silkworms. Since 1853, two diseases called pébrine and flacherie had been infecting great numbers of silkworms in southern France, and by 1865 they were causing huge losses to farmers. In 1865, Pasteur went to Alès and worked for five years until 1870.
Silkworms with pébrine were covered in corpuscles. In the first three years, Pasteur thought that the corpuscles were a symptom of the disease. In 1870, he concluded that the corpuscles were the cause of pébrine (it is now known that the cause is a microsporidian). Pasteur also showed that the disease was hereditary. Pasteur developed a system to prevent pébrine: after the female moths laid their eggs, the moths were turned into a pulp. The pulp was examined with a microscope, and if corpuscles were observed, the eggs were destroyed. Pasteur concluded that bacteria caused flacherie. The primary cause is currently thought to be viruses. The spread of flacherie could be accidental or hereditary. Hygiene could be used to prevent accidental flacherie. Moths whose digestive cavities did not contain the microorganisms causing flacherie were used to lay eggs, preventing hereditary flacherie.# ISO certification in India
Spontaneous generation

Bottle en col de cygne (swan-neck bottle) used by Pasteur
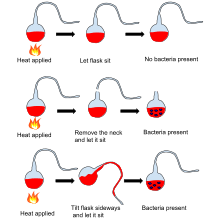
Louis Pasteur’s pasteurization experiment illustrates the fact that the spoilage of liquid was caused by particles in the air rather than the air itself. These experiments were important pieces of evidence supporting the germ theory of disease.
Following his fermentation experiments, Pasteur demonstrated that the skin of grapes was the natural source of yeasts, and that sterilized grapes and grape juice never fermented. He drew grape juice from under the skin with sterilized needles, and also covered grapes with sterilized cloth. Both experiments could not produce wine in sterilized containers.# ISO certification in India
His findings and ideas were against the prevailing notion of spontaneous generation. He received a particularly stern criticism from Félix Archimède Pouchet, who was director of the Rouen Museum of Natural History. To settle the debate between the eminent scientists, the French Academy of Sciences offered the Alhumbert Prize carrying 2,500 francs to whoever could experimentally demonstrate for or against the doctrine.
Pouchet stated that air everywhere could cause spontaneous generation of living organisms in liquids. In the late 1850s, he performed experiments and claimed that they were evidence of spontaneous generation. Francesco Redi and Lazzaro Spallanzani had provided some evidence against spontaneous generation in the 17th and 18th centuries, respectively. Spallanzani’s experiments in 1765 suggested that air contaminated broths with bacteria. In the 1860s, Pasteur repeated Spallanzani’s experiments, but Pouchet reported a different result using a different broth.# ISO certification in India
Pasteur performed several experiments to disprove spontaneous generation. He placed boiled liquid in a flask and let hot air enter the flask. Then he closed the flask, and no organisms grew in it. In another experiment, when he opened flasks containing boiled liquid, dust entered the flasks, causing organisms to grow in some of them. The number of flasks in which organisms grew was lower at higher altitudes, showing that air at high altitudes contained less dust and fewer organisms. Pasteur also used swan neck flasks containing a fermentable liquid. Air was allowed to enter the flask via a long curving tube that made dust particles stick to it. Nothing grew in the broths unless the flasks were tilted, making the liquid touch the contaminated walls of the neck. This showed that the living organisms that grew in such broths came from outside, on dust, rather than spontaneously generating within the liquid or from the action of pure air.# ISO certification in India
These were some of the most important experiments disproving the theory of spontaneous generation. Pasteur gave a series of five presentations of his findings before the French Academy of Sciences in 1881, which were published in 1882 as Mémoire Sur les corpuscules organisés qui existent dans l’atmosphère: Examen de la doctrine des générations spontanées (Account of Organized Corpuscles Existing in the Atmosphere: Examining the Doctrine of Spontaneous Generation). Pasteur won the Alhumbert Prize in 1862. He concluded that:
Never will the doctrine of spontaneous generation recover from the mortal blow of this simple experiment. There is no known circumstance in which it can be confirmed that microscopic beings came into the world without germs, without parents similar to themselves.



