Courtesy : Bachelor of Science Biotechnology (CBT) – Chemistry, Botany, Biotechnology Syllabus
History
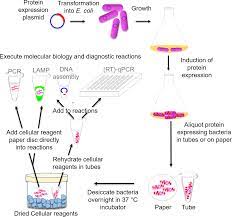
In 1972, the earliest report of the insertion of a foreign sequence into a viral genome was published, when Paul Berg used the EcoRI restriction enzyme and DNA ligases to create the first ever recombinant DNA molecules. This was achieved by joining DNA from the monkey SV40 virus with that of the lambda virus. However, it was not established that either of the two viruses were capable of infection or replication. # ISO certification in India
In 1974, the first report of a genetically modified virus that could also replicate and infect was submitted for publication by Noreen Murray and Kenneth Murray. Just two months later in August 1974, Marjorie Thomas, John Cameron and Ronald W. Davis submitted a report for publication of a similar achievement.# ISO certification in India
Collectively, these experiments represented the very start of the development of what would eventually become known as biotechnology or recombinant DNA methods.# ISO certification in India

Health applications
Gene therapy
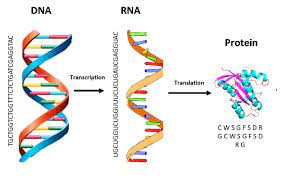
Gene therapy uses genetically modified viruses to deliver genes that can cure diseases in human cells.These viruses can deliver DNA or RNA genetic material to the targeted cells. Gene therapy is also used by inactivating mutated genes that are causing the disease using viruses.
Viruses that have been used for gene therapy are, adenovirus, lentivirus, retrovirus and the herpes simplex virus. The most common virus used for gene delivery come from adenoviruses as they can carry up to 7.5 kb of foreign DNA and infect a relatively broad range of host cells, although they have been known to elicit immune responses in the host and only provide short term expression. Other common vectors are adeno-associated viruses, which have lower toxicity and longer term expression, but can only carry about 4kb of DNA. Herpes simplex viruses is a promising vector, have a carrying capacity of over 30kb and provide long term expression, although it is less efficient at gene delivery than other vectors. The best vectors for long term integration of the gene into the host genome are retroviruses, but their propensity for random integration is problematic. Lentiviruses are a part of the same family as retroviruses with the advantage of infecting both dividing and non-dividing cells, whereas retroviruses only target dividing cells. Other viruses that have been used as vectors include alphaviruses, flaviviruses, measles viruses, rhabdoviruses, Newcastle disease virus, poxviruses, and picornaviruses. # ISO certification in India
Although primarily still at trial stages, it has had some successes. It has been used to treat inherited genetic disorders such as severe combined immunodeficiency rising from adenosine deaminase deficiency (ADA-SCID), although the development of leukemia in some ADA-SCID patients along with the death of Jesse Gelsinger in another trial set back the development of this approach for many years.[16] In 2009 another breakthrough was achieved when an eight year old boy with Leber’s congenital amaurosis regained normal eyesight and in 2016 GlaxoSmithKline gained approval to commercialise a gene therapy treatment for ADA-SCID. As of 2018, there are a substantial number of clinical trials underway, including treatments for hemophilia, glioblastoma, chronic granulomatous disease, cystic fibrosis and various cancers. Although some successes, gene therapy is still considered a risky technique and studies are still undergoing to ensure safety and effectiveness.# ISO certification in India
Cancer treatment
Another potential use of genetically modified viruses is to alter them so they can directly treat diseases. This can be through expression of protective proteins or by directly targeting infected cells. In 2004, researchers reported that a genetically modified virus that exploits the selfish behaviour of cancer cells might offer an alternative way of killing tumours. Since then, several researchers have developed genetically modified oncolytic viruses that show promise as treatments for various types of cancer. # ISO certification in India
Vaccines
Most vaccines consist of viruses that have been attenuated, disabled, weakened or killed in some way so that their virulent properties are no longer effective. Genetic engineering could theoretically be used to create viruses with the virulent genes removed. In 2001, it was reported that genetically modified viruses can possibly be used to develop vaccines against diseases such as, AIDS, herpes, dengue fever and viral hepatitis by using a proven safe vaccine virus, such as adenovirus, and modify its genome to have genes that code for immunogenic proteins that can spike the immune systems response to then be able to fight the virus. Genetic engineered viruses should not have reduced infectivity, invoke a natural immune response and there is no chance that they will regain their virulence function, which can occur with some other vaccines. As such they are generally considered safer and more efficient than conventional vaccines, although concerns remain over non-target infection, potential side effects and horizontal gene transfer to other viruses. Another approach is to use vectors to create novel vaccines for diseases that have no vaccines available or the vaccines that are do not work effectively, such as AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis. Vector-based vaccines have already been approved and many more are being developed.# ISO certification in India



