Advantages & disadvantages of computers- Computers have become an indispensable part of modern life, offering numerous advantages but also presenting some disadvantages. Here are some of the key advantages and disadvantages of computers:
Advantages:
- Efficiency: Computers can perform tasks with incredible speed and accuracy, which significantly increases efficiency in various fields such as business, education, and research.
- Automation: They enable automation of repetitive tasks, reducing the need for human intervention and freeing up time for more complex activities.
- Storage: Computers can store vast amounts of data in relatively small physical spaces, making it easy to access, organize, and retrieve information when needed.
- Communication: Computers facilitate communication through email, instant messaging, video conferencing, and social media platforms, allowing people to connect with others globally in real-time.
- Information Access: The internet provides access to a wealth of information, resources, and services, empowering users to learn, research, and stay informed on a wide range of topics.
- Creativity: With software tools for graphic design, music composition, video editing, and more, computers enable users to express their creativity and produce multimedia content.
- Remote Work: Computers support remote work arrangements, allowing employees to work from anywhere with an internet connection, which can enhance work-life balance and reduce commuting time.
Disadvantages:
- Dependency: Excessive reliance on computers can lead to a dependency on technology, making individuals vulnerable to disruptions caused by system failures, cyberattacks, or technical glitches.
- Health Risks: Prolonged use of computers can lead to various health issues such as eye strain, repetitive strain injuries (RSIs), and musculoskeletal problems due to poor ergonomics or sedentary behavior.
- Security Concerns: Computers are susceptible to security breaches, viruses, malware, and hacking, posing risks to personal privacy, sensitive data, and critical infrastructure.
- Social Isolation: Excessive use of computers and online interactions may lead to reduced face-to-face social interactions, potentially contributing to feelings of isolation and loneliness.
- Distraction: Computers can be a source of distraction, with access to entertainment, social media, and online gaming diverting attention from productive tasks and reducing overall focus and concentration.
- Environmental Impact: The manufacturing, usage, and disposal of computers contribute to environmental pollution and resource depletion, particularly concerning electronic waste (e-waste) disposal and energy consumption.
- Job Displacement: Automation driven by computers and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies can lead to job displacement and unemployment in certain industries, as machines replace human labor in routine tasks.
While computers offer numerous benefits, it’s essential to be mindful of their limitations and potential drawbacks to mitigate risks and maximize their positive impact on society.
What is Required Advantages & disadvantages of computers
It seems like you’re asking for a more concise list of required advantages and disadvantages of computers. Here’s a condensed version:
Required Advantages:
- Efficiency: Computers boost productivity by performing tasks quickly and accurately.
- Storage: They enable easy storage and retrieval of large amounts of data.
- Communication: Facilitates seamless communication through various channels.
- Information Access: Provides instant access to a vast array of information via the internet.
- Automation: Streamlines processes through automation, saving time and effort.
- Creativity: Supports creative endeavors through multimedia tools and software.
- Remote Work: Enables flexible work arrangements and remote collaboration.
Required Disadvantages:
- Dependency: Overreliance on computers can lead to vulnerability to disruptions.
- Health Risks: Prolonged use can cause physical health issues such as eye strain and RSIs.
- Security Concerns: Computers are susceptible to cyber threats and breaches.
- Social Isolation: Excessive use may reduce face-to-face interactions and contribute to social isolation.
- Distraction: Access to entertainment can lead to decreased focus on productive tasks.
- Environmental Impact: Manufacturing and disposal contribute to pollution and resource depletion.
- Job Displacement: Automation can lead to unemployment in certain industries.
This summary highlights the essential advantages and disadvantages of computers without delving into exhaustive detail.
Who is Required Advantages & disadvantages of computers
The advantages and disadvantages of computers are not attributed to any single person. Instead, they are general attributes that have been observed and discussed by researchers, technologists, educators, and society at large over many years. These advantages and disadvantages arise from the capabilities and limitations of computer technology itself, as well as its impact on various aspects of human life and society.
Researchers in fields such as computer science, sociology, psychology, and economics study the effects of computers on individuals, organizations, and society as a whole. They identify and analyze the positive and negative aspects of computer technology, which are then widely discussed and understood by people across different sectors.
So, the “who” in this context refers to the collective knowledge and understanding of the global community rather than any specific individual or group.
When is Required Advantages & disadvantages of computers
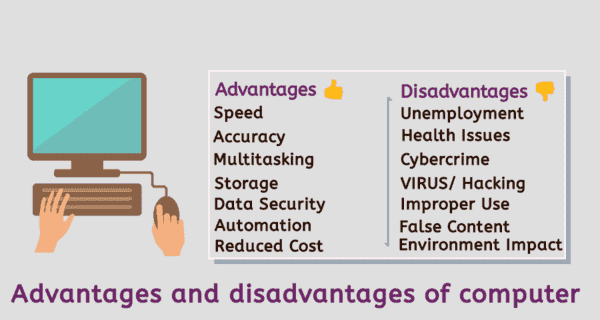
The concept of the advantages and disadvantages of computers has been discussed and understood for several decades since the widespread adoption of computer technology in various fields. The discussion continues to evolve as technology advances and its impact on society changes over time.
Advantages and disadvantages of computers have been recognized and analyzed in academic research, industry reports, and everyday discussions since the mid-to-late 20th century. With the rapid advancement of computing technology, particularly since the advent of personal computers in the 1970s and the internet in the 1990s, the understanding of these advantages and disadvantages has become increasingly nuanced and detailed.
Therefore, there isn’t a specific date associated with when the concept of the advantages and disadvantages of computers emerged, as it has been an ongoing conversation influenced by technological developments and societal changes over many years.
Where is Required Advantages & disadvantages of computers
The discussion and analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of computers occur in various contexts and settings. These conversations take place in:
- Academic Institutions: Researchers in fields such as computer science, sociology, psychology, and economics study the impacts of computers and technology on individuals, organizations, and society. They publish their findings in academic journals and present them at conferences.
- Industry: Professionals in technology companies, businesses, and organizations discuss the advantages and disadvantages of computers in the context of their specific applications and industries. This can include considerations of efficiency, productivity, security, and compliance.
- Media and Publications: Journalists, writers, and bloggers cover topics related to computers and technology, including their benefits and drawbacks. These discussions can be found in newspapers, magazines, online articles, and blogs.
- Education: Teachers, professors, and educators incorporate discussions about the advantages and disadvantages of computers into their curricula, especially in fields related to computer science, information technology, and digital literacy.
- Online Forums and Communities: Discussions about computers and technology take place on various online platforms, including forums, social media platforms, and specialized communities. Here, individuals share their experiences, opinions, and insights regarding the pros and cons of using computers.
- Government and Policy: Policymakers and government agencies may consider the implications of computer technology when formulating regulations and policies related to cybersecurity, privacy, digital access, and employment.
In summary, discussions about the advantages and disadvantages of computers occur in diverse settings, reflecting the broad impact of computer technology on society, economy, culture, and individual lives.
How is Required Advantages & disadvantages of computers
The advantages and disadvantages of computers are analyzed and understood through various methods and approaches. Here’s how they are typically assessed:
Analysis Methods:
- Empirical Research: Researchers conduct studies to gather data on the usage and effects of computers. This can involve surveys, experiments, observations, and data analysis to quantify the benefits and drawbacks.
- Case Studies: Examining specific cases or examples allows for a detailed analysis of how computers impact different contexts, such as businesses, education, healthcare, or government.
- Literature Review: Scholars review existing research and literature to synthesize knowledge about the advantages and disadvantages of computers, identifying trends, patterns, and areas for further investigation.
- Qualitative Analysis: Researchers collect qualitative data through interviews, focus groups, or textual analysis to understand people’s perceptions, attitudes, and experiences related to computer technology.
Assessment Approaches:
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluating the costs and benefits associated with using computers helps decision-makers weigh the advantages against the disadvantages in specific contexts.
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and analyzing potential risks associated with computer use, such as security breaches, data loss, or social impacts, helps mitigate negative consequences.
- Ethical Analysis: Considering ethical implications, such as privacy, fairness, and accountability, helps assess the ethical dimensions of computer technology and its effects on individuals and society.
- Longitudinal Studies: Tracking changes over time through longitudinal studies allows researchers to understand how the advantages and disadvantages of computers evolve with technological advancements and societal changes.
Stakeholder Perspectives:
- User Feedback: Gathering feedback from computer users provides insights into their experiences, preferences, and concerns, helping improve usability and address potential drawbacks.
- Expert Opinion: Consulting experts in various fields, such as technology, psychology, economics, or policy, offers valuable perspectives on the advantages and disadvantages of computers from different disciplinary lenses.
- Community Engagement: Engaging with diverse stakeholders, including communities, organizations, and policymakers, fosters dialogue and collaboration in addressing the impacts of computer technology.
By employing these methods and approaches, researchers and practitioners can gain a comprehensive understanding of the advantages and disadvantages of computers and make informed decisions to maximize the benefits while mitigating potential drawbacks.
Case Study on Advantages & disadvantages of computers
Small Business Integration of Computer Technology
Background:
XYZ Consulting is a small business providing management consulting services to local businesses. As the business grows, the owner, Jane, is considering integrating computer technology to improve operations and expand the client base.
Advantages:
- Efficiency: Implementing computers for data management, communication, and project tracking can streamline internal processes, reducing manual tasks and saving time.
- Productivity: With computers, consultants can access resources, research materials, and collaboration tools more efficiently, enhancing productivity and client service delivery.
- Scalability: Computer systems allow for scalability, enabling XYZ Consulting to handle more clients and projects without significantly increasing overhead costs.
- Competitive Advantage: Utilizing computers for data analysis, market research, and client management can give XYZ Consulting a competitive edge by offering more comprehensive and data-driven solutions to clients.
Disadvantages:
- Initial Investment: Integrating computer technology requires upfront investment in hardware, software, training, and infrastructure, which may strain the company’s budget initially.
- Learning Curve: Employees, especially older staff members, may face challenges adapting to new technology, leading to resistance, decreased morale, and temporary drops in productivity during the transition period.
- Security Risks: Storing sensitive client data on computers exposes XYZ Consulting to cybersecurity risks, such as data breaches, hacking, or malware attacks, which could damage the company’s reputation and result in legal liabilities.
- Dependence on Technology: Overreliance on computers may lead to disruptions in case of system failures, software glitches, or internet outages, potentially impacting client deliverables and business operations.
Strategies for Mitigation:
- Investment Planning: Jane should conduct a cost-benefit analysis to determine the optimal level of investment in computer technology, considering both short-term expenses and long-term benefits.
- Training and Support: Providing comprehensive training and ongoing support to employees can mitigate resistance and ensure a smooth transition to computer technology, enhancing employee confidence and competence.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as encryption, firewalls, regular data backups, and employee awareness training, can help protect sensitive information and minimize the risk of cyber threats.
- Contingency Planning: Developing contingency plans and backup procedures for dealing with technology-related disruptions can minimize downtime and ensure continuity of client services in case of emergencies.
By carefully weighing the advantages and disadvantages of integrating computer technology into their business operations and implementing appropriate strategies for mitigation, XYZ Consulting can leverage the benefits of technology while minimizing potential drawbacks, ultimately enhancing their competitiveness and success in the marketplace.
White paper on Advantages & disadvantages of computers
Title: Understanding the Advantages and Disadvantages of Computer Technology: A Comprehensive White Paper
Abstract: This white paper aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the advantages and disadvantages associated with computer technology in various domains. Through an in-depth analysis of current research, industry trends, and real-world examples, this document seeks to inform stakeholders about the multifaceted impacts of computer technology on individuals, organizations, and society. By understanding the nuanced benefits and drawbacks of computers, stakeholders can make informed decisions to harness the potential of technology while mitigating its potential risks.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Background and Context
- Purpose and Scope
- Advantages of Computer Technology
- Efficiency and Productivity Enhancement
- Access to Information and Resources
- Communication and Collaboration Facilitation
- Automation of Tasks and Processes
- Innovation and Creativity Enablement
- Flexibility and Adaptability in Work Practices
- Scalability and Growth Opportunities
- Disadvantages of Computer Technology
- Cybersecurity Vulnerabilities and Data Breaches
- Technological Dependence and Disruptions
- Health and Wellness Implications
- Social Isolation and Disconnection
- Environmental Impact and Sustainability Concerns
- Economic and Employment Displacement Effects
- Ethical and Privacy Dilemmas
- Case Studies and Examples
- Small Business Integration of Computer Technology
- Educational Institution Adoption of Digital Learning Platforms
- Healthcare Sector Implementation of Electronic Health Records
- Governmental Use of Data Analytics for Policy Making
- Strategies for Maximizing Benefits and Mitigating Risks
- Investment Planning and Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Training and Education Initiatives
- Cybersecurity Measures and Best Practices
- Regulatory Compliance and Ethical Guidelines
- Environmental Sustainability Practices
- Social and Cultural Integration Efforts
- Conclusion
- Recapitulation of Key Points
- Future Outlook and Recommendations
Conclusion: In conclusion, computer technology offers numerous advantages in terms of efficiency, productivity, innovation, and connectivity. However, it also presents significant challenges related to cybersecurity, health, environmental sustainability, and societal impacts. By adopting a holistic approach that considers both the benefits and drawbacks of computer technology, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of the digital age more effectively and realize the full potential of technology in shaping a better future for individuals and communities alike.
Industrial Application of Advantages & disadvantages of computers
The industrial application of the advantages and disadvantages of computers is prevalent across various sectors. Here’s how these aspects manifest in industrial settings:
Advantages:
- Automation and Robotics: Computers enable the automation of manufacturing processes through robotics and programmable systems. This leads to increased efficiency, precision, and consistency in production, reducing labor costs and enhancing output quality.
- Data Analysis and Optimization: Industrial computers process vast amounts of data generated by sensors and machinery to optimize production processes. Through data analysis techniques such as machine learning and predictive analytics, manufacturers can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and make data-driven decisions to improve operational efficiency and product quality.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Industrial computers facilitate remote monitoring and control of machinery and equipment. This allows operators and engineers to monitor production processes in real-time, identify issues proactively, and make adjustments remotely, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Inventory Management: Computerized inventory management systems track inventory levels, monitor stock movement, and automate reorder processes. This ensures optimal inventory levels, minimizes stockouts, and streamlines supply chain operations, leading to cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
- Quality Control: Computers are used for automated quality control processes, such as computer vision systems and sensor-based inspection technologies. These systems detect defects, deviations, and inconsistencies in products, enabling manufacturers to maintain high-quality standards and reduce waste.
Disadvantages:
- Cybersecurity Risks: Industrial computers are vulnerable to cyber threats such as malware, ransomware, and hacking. A cyber-attack on industrial systems can disrupt production, compromise sensitive data, and pose safety risks to workers, equipment, and the environment.
- Dependency on Technology: Overreliance on computerized systems can lead to disruptions in case of system failures, software bugs, or power outages. This dependency may result in production downtime, lost revenue, and decreased productivity if backup systems and contingency plans are not in place.
- Skill Requirements: Operating and maintaining industrial computers require specialized skills and training. The rapid pace of technological advancements necessitates ongoing education and professional development for industrial workers to keep up with evolving technologies and best practices.
- Initial Investment and Integration Challenges: Implementing computerized systems in industrial environments involves significant upfront costs for hardware, software, and infrastructure. Additionally, integrating new technologies with existing legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and coordination.
- Ethical and Social Implications: The automation of industrial processes through computers raises ethical concerns related to job displacement, worker safety, and societal impacts. Automation may lead to job loss or shifts in employment opportunities, requiring thoughtful consideration of workforce implications and societal responsibilities.
In summary, while industrial computers offer significant advantages in terms of automation, data analysis, and efficiency, they also present challenges related to cybersecurity, dependency, skill requirements, integration, and ethical considerations. By understanding and addressing these advantages and disadvantages, industrial organizations can harness the transformative power of computer technology while mitigating potential risks and maximizing benefits.





