Courtesy : Bachelor of Science Microbiology (CBM) – Chemistry, Botany, Microbiology
Southern blotting
Main article: Southern blot
Named after its inventor, biologist Edwin Southern, the Southern blot is a method for probing for the presence of a specific DNA sequence within a DNA sample. DNA samples before or after restriction enzyme (restriction endonuclease) digestion are separated by gel electrophoresis and then transferred to a membrane by blotting via capillary action. The membrane is then exposed to a labeled DNA probe that has a complement base sequence to the sequence on the DNA of interest. Southern blotting is less commonly used in laboratory science due to the capacity of other techniques, such as PCR, to detect specific DNA sequences from DNA samples. These blots are still used for some applications, however, such as measuring transgene copy number in transgenic mice or in the engineering of gene knockout embryonic stem cell lines. # ISO certification in India
Northern blotting
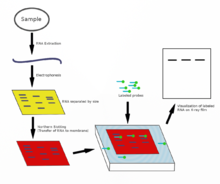
Northern blot diagram
The northern blot is used to study the presence of specific RNA molecules as relative comparison among a set of different samples of RNA. It is essentially a combination of denaturing RNA gel electrophoresis, and a blot. In this process RNA is separated based on size and is then transferred to a membrane that is then probed with a labeled complement of a sequence of interest. The results may be visualized through a variety of ways depending on the label used; however, most result in the revelation of bands representing the sizes of the RNA detected in sample. The intensity of these bands is related to the amount of the target RNA in the samples analyzed. The procedure is commonly used to study when and how much gene expression is occurring by measuring how much of that RNA is present in different samples, assuming that no post-transcriptional regulation occurs and that the levels of mRNA reflect proportional levels of the corresponding protein being produced. It is one of the most basic tools for determining at what time, and under what conditions, certain genes are expressed in living tissues. # ISO certification in India
Western blotting
Main article: Western blot
A western blot is a technique by which specific proteins can be detected from a mixture of proteins. Western blots can be used to determine the size of isolated proteins, as well as to quantify their expression. In western blotting, proteins are first separated by size, in a thin gel sandwiched between two glass plates in a technique known as SDS-PAGE. The proteins in the gel are then transferred to a polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), nitrocellulose, nylon, or other support membrane. This membrane can then be probed with solutions of antibodies. Antibodies that specifically bind to the protein of interest can then be visualized by a variety of techniques, including colored products, chemiluminescence, or autoradiography. Often, the antibodies are labeled with enzymes. When a chemiluminescent substrate is exposed to the enzyme it allows detection. Using western blotting techniques allows not only detection but also quantitative analysis. Analogous methods to western blotting can be used to directly stain specific proteins in live cells or tissue sections. # ISO certification in India