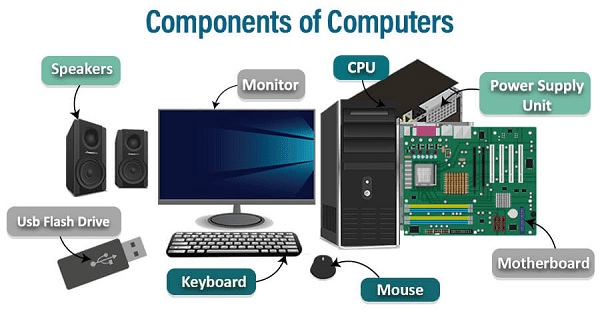
Components of computer- A computer is a complex system composed of various hardware and software components that work together to perform a wide range of tasks. Here are the main components of a typical computer system:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the brain of the computer. It executes instructions from programs and performs calculations. Modern CPUs have multiple cores to handle multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory (RAM) is used to store data and instructions that the CPU is currently working with. It provides fast, temporary storage for data and is essential for a computer’s performance.
- Storage Devices: Computers have various storage devices to store data, including:a. Hard Disk Drive (HDD): A traditional mechanical storage device that stores data on spinning disks. b. Solid-State Drive (SSD): A faster and more durable storage device that uses flash memory. c. Optical Drives: Used for reading and writing optical discs, such as CDs and DVDs. d. USB Drives: Portable flash drives for data storage and transfer.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects and houses the CPU, RAM, and other components. It provides the electrical and data connections between these components.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU supplies electrical power to all the computer components. It converts AC power from an outlet into DC power that the computer’s components can use.
- Input Devices: These devices allow you to input data into the computer, including:a. Keyboard: Used for typing text and issuing commands. b. Mouse: Used for pointing and clicking in graphical user interfaces. c. Touchpad or Trackpad: Commonly found on laptops for mouse-like control. d. Joysticks, Gamepads, and Other Controllers: Used for gaming and specific applications.
- Output Devices: These devices display the computer’s output, including:a. Monitor: Displays visual information and graphics. b. Printer: Produces hard copies of documents and images. c. Speakers: Output audio and sound.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The GPU is responsible for rendering graphics and images, making it essential for gaming and graphic-intensive tasks.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): The NIC enables the computer to connect to networks, including wired Ethernet and wireless Wi-Fi.
- Expansion Cards: These are optional components that can be added to the motherboard to provide additional functionality. Common examples include sound cards and graphics cards.
- BIOS/UEFI: The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is firmware that initializes the hardware during the boot process and manages system settings.
- Operating System (OS): The OS is system software that manages hardware resources and provides a user interface for interacting with the computer. Popular OSs include Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Software: This includes applications and programs that run on the computer, such as web browsers, word processors, and games.
These components work together to process data, run software, and perform a wide range of tasks, making the computer a versatile tool for various applications.
What is Components of computer
The components of a computer system can be broadly categorized into two main categories: hardware and software.
Hardware Components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the core component of a computer. It executes instructions and performs calculations for various tasks. Modern CPUs can have multiple cores for improved multitasking.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory (RAM) provides temporary storage for data and programs that are currently in use. It allows for quick data access by the CPU.
- Storage Devices: Computers use different storage devices to store data, including:
- Hard Disk Drives (HDD): These provide large, non-volatile storage using spinning disks.
- Solid-State Drives (SSD): Faster and more durable than HDDs, SSDs use flash memory for storage.
- Optical Drives: Used for reading and writing optical discs like CDs and DVDs.
- USB Drives: Portable flash drives for data storage and transfer.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board that connects and houses the CPU, RAM, and other hardware components. It provides the necessary electrical and data connections.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU converts electricity from your wall outlet into a form that the computer’s components can use. It supplies power to all hardware components.
- Input Devices: Input devices allow users to interact with the computer. Common examples include:
- Keyboard: Used for typing text and entering commands.
- Mouse: Enables pointing and clicking in graphical user interfaces.
- Touchpad or Trackpad: Found on laptops for mouse-like control.
- Joysticks, Gamepads, and Other Controllers: Used for gaming and specialized applications.
- Output Devices: Output devices display the computer’s results. Common ones include:
- Monitor: Displays visual information and graphics.
- Printer: Produces hard copies of documents and images.
- Speakers: Output audio and sound.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The GPU is responsible for rendering graphics and is essential for gaming and graphic-intensive tasks.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): The NIC allows the computer to connect to networks, including wired Ethernet and wireless Wi-Fi.
- Expansion Cards: These optional components can be added to the motherboard to enhance functionality. Examples include sound cards and graphics cards.
Software Components:
- Operating System (OS): The OS is system software that manages hardware resources and provides a user interface for interacting with the computer. Popular OSs include Windows, macOS, and Linux.
- Application Software: These are the programs and applications that run on the computer. Examples include web browsers, word processors, and games.
- Firmware: Firmware is software embedded in hardware components, such as the BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) or UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface), which initializes the hardware during the boot process.
- Drivers: These software components enable the OS to communicate with and control specific hardware components. They are essential for hardware functionality.
These hardware and software components work together to enable a computer to perform various tasks and functions, from basic word processing to complex data analysis and gaming.
Who is Required Components of computer
The required components of a computer are the fundamental hardware and software components necessary for the computer to function and perform its basic operations. Without these components, a computer cannot operate. Here’s a list of the essential components:
Hardware Components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is essential for processing instructions and performing calculations. It is often referred to as the computer’s “brain.”
- Memory (RAM): RAM provides temporary storage for data and programs that are currently in use. It allows for quick data access by the CPU.
- Storage Device: A basic storage device is required for storing the computer’s operating system, software, and user data. This can be either a Hard Disk Drive (HDD) or a Solid-State Drive (SSD).
- Motherboard: The motherboard serves as the central circuit board that connects and houses the CPU, RAM, and other essential hardware components. It provides the necessary electrical and data connections.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU is needed to supply electrical power to all the computer’s components. It converts AC power from an outlet into DC power that the computer’s components can use.
- Input Device: An input device like a keyboard is necessary for typing text and issuing commands to the computer.
- Output Device: An output device like a monitor or display is essential for viewing the computer’s output and interacting with it visually.
- Operating System (OS): The OS is the system software that manages hardware resources and provides a user interface for interacting with the computer. It is required to boot and operate the computer.
Software Components:
- BIOS/UEFI: The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is firmware embedded in the motherboard that initializes the hardware during the boot process.
- Device Drivers: These are necessary software components that enable the operating system to communicate with and control specific hardware components, ensuring they function properly.
These are the core components required for a computer to function and perform basic operations. Additional hardware and software components can be added for enhanced functionality and to perform specific tasks, but the components listed above are the minimum necessary for a computer to operate.
When is Required Components of computer
It’s possible you’re asking when specific computer components are utilized or required. Computer components are needed throughout the entire lifecycle of a computer, from the moment it’s powered on to when it’s performing tasks and even when it’s idle. Here’s a breakdown of when different computer components come into play:
- CPU (Central Processing Unit): The CPU is active whenever the computer is turned on and running. It processes instructions continuously as long as the computer is in use.
- Memory (RAM): RAM is used to store and access data and programs that the CPU is currently working with. It is required for the computer to function effectively, and it’s used while running applications.
- Storage Devices: These are used to store the operating system, software, and user data. Storage devices are accessed whenever you boot up the computer, launch applications, or save and retrieve files.
- Motherboard: The motherboard connects and facilitates communication between all components and is active whenever the computer is running.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU supplies power continuously as long as the computer is turned on.
- Input and Output Devices: Input devices like the keyboard and mouse are required whenever you want to interact with the computer. Output devices like the monitor and speakers are used to view and hear the computer’s responses.
- Operating System (OS): The OS is essential to start and operate the computer. It’s required for tasks like booting up, launching applications, and managing system resources.
- Device Drivers: Drivers are necessary whenever you use specific hardware components, such as printers, cameras, or graphics cards. They are activated when the corresponding hardware is in use.
Computer components work in conjunction to allow the computer to perform tasks and operations at any time it is powered on and in use. If you have a more specific question or if there’s something else you’d like to know, please provide additional details, and I’ll be happy to help.
Where is Required Components of computer
The required components of a computer are physically located within the computer system. Here’s where you can typically find these components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is mounted on the motherboard, often under a protective heatsink and fan assembly.
- Memory (RAM): RAM modules are inserted into slots on the motherboard. In some cases, they may also be located on graphics cards or other specialized hardware.
- Storage Device: Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid-State Drives (SSDs) are typically located within the computer case, connected to the motherboard via data and power cables.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the central circuit board inside the computer case, with various connectors and slots for components such as the CPU, RAM, and expansion cards.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The power supply unit is typically located at the top or bottom of the computer case and is connected to the electrical outlet.
- Input and Output Devices: Input devices like keyboards and mice are connected to USB or other ports on the computer case. Output devices like monitors and speakers are also connected to specific ports on the computer.
- Operating System (OS): The operating system is typically installed on a storage device, often on a partition of the hard drive or SSD.
- Device Drivers: Device drivers are software components installed on the operating system and can be found in various directories and folders within the OS.
These components work together within the computer case to enable the computer to function. The computer case itself houses many of these components, with various connectors and slots for easy installation and connectivity. The exact location and arrangement may vary depending on the computer’s form factor and design.
How is Required Components of computer
The required components of a computer are interconnected and work together to enable the computer to function. Here’s how these components are typically set up and how they interact:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the core of the computer, responsible for processing instructions. It communicates with other components through the motherboard.
- Memory (RAM): RAM provides fast, temporary storage for data and instructions the CPU is currently working on. The CPU reads and writes data to and from RAM.
- Storage Device: The storage device (HDD or SSD) stores the operating system, software, and user data. The operating system and software are loaded from storage into RAM when needed.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the central circuit board that connects all components. It provides electrical and data connections between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other hardware components.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU supplies power to all components. It converts electricity from the electrical outlet into the correct form for the computer’s components.
- Input and Output Devices: Input devices like the keyboard and mouse allow you to interact with the computer, while output devices like the monitor display the computer’s output.
- Operating System (OS): The OS manages hardware resources and provides a user interface for interacting with the computer. It is loaded from storage into RAM during the boot process.
- Device Drivers: Device drivers are software programs that facilitate communication between the OS and specific hardware components. They allow the OS to control and interact with these components effectively.
The interaction among these components can be summarized as follows:
- When you power on the computer, the PSU provides power to all components.
- The BIOS or UEFI (firmware) on the motherboard initializes the hardware, performs a power-on self-test (POST), and loads the operating system.
- The OS is loaded from storage into RAM, and it manages the hardware resources, allowing you to run software and interact with the computer.
- When you use input devices like the keyboard and mouse, the CPU processes your input.
- Software applications are loaded from storage into RAM, where the CPU can execute them.
- Output devices like the monitor display the results of the computer’s operations.
- Device drivers help the OS communicate with and control specific hardware components.
This process occurs continually as you use the computer for various tasks and operations, creating a seamless and interactive computing experience.
Case Study on Components of computer
Upgrading a Home Office Computer
Background: John is a freelance graphic designer who works from a home office. He has been using the same computer for the past five years, and it’s starting to show signs of slowing down. His work involves running graphic design software and handling large image files, so he needs a computer that can handle the demands of his profession. He is considering upgrading his computer to improve its performance.
Challenges: John’s computer is outdated and struggles to run the latest design software efficiently. He faces the following challenges:
- Slow Performance: The computer’s CPU and RAM are no longer sufficient for his graphic design work. Running design software is slow and often results in crashes.
- Insufficient Storage: John’s current hard drive is nearly full, and he needs more storage space for his large design files.
- Compatibility: John must ensure that any new components he purchases are compatible with his existing hardware and software.
Solution: To address these challenges, John decides to upgrade his computer by replacing and adding several components:
- CPU and RAM Upgrade:
- He selects a more powerful CPU with multiple cores to handle multi-threaded tasks efficiently.
- He also increases the RAM capacity to a higher amount, ensuring that he has enough memory to run large design projects smoothly.
- SSD Installation:
- To improve system responsiveness and reduce loading times, John replaces his old HDD with a high-capacity SSD. This provides faster data access and faster boot times.
- Additional Hard Drive:
- John adds an additional large-capacity HDD for storing his design files, ensuring he has ample space for his projects.
- GPU Upgrade:
- Since graphic design software can benefit from a powerful GPU, he upgrades to a more advanced graphics card to enhance his workflow.
- Operating System and Software Updates:
- John updates his operating system and design software to the latest versions to take advantage of performance improvements and new features.
Results: After upgrading his computer with these components, John experiences significant improvements in his work efficiency:
- The computer now runs graphic design software smoothly, allowing John to work on complex projects without slowdowns or crashes.
- The SSD and additional HDD provide ample storage and fast data access for his design files.
- The upgraded GPU enhances the rendering and display of graphic elements, further improving his design work.
Conclusion: This case study illustrates how understanding the components of a computer and making strategic upgrades can have a positive impact on a professional’s work and productivity. By addressing the specific challenges he faced and upgrading his computer, John was able to create a more efficient and effective home office setup for his graphic design work.
White paper on Components of computer
Title: An Overview of Computer Components
Abstract: This white paper offers a comprehensive overview of the key components that make up a modern computer system. It covers the fundamental hardware and software components that enable a computer to perform various tasks, ranging from basic operations to complex applications. Understanding these components is essential for users, enthusiasts, and professionals in the world of computing.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- The Role of Computers in Our Lives
- The Importance of Understanding Computer Components
- Hardware Components
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)
- Memory (RAM)
- Storage Devices (HDD and SSD)
- Motherboard
- Power Supply Unit (PSU)
- Input Devices (Keyboard, Mouse)
- Output Devices (Monitor, Printer)
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Expansion Cards
- BIOS/UEFI
- Software Components
- Operating System (OS)
- Application Software
- Firmware
- Device Drivers
- The Interaction of Hardware and Software
- How Hardware and Software Work Together
- Boot Process: BIOS/UEFI and OS Initialization
- Upgrading and Maintaining Computer Components
- Reasons for Upgrading
- Considerations for Component Upgrades
- Maintaining a Computer for Longevity
- The Evolution of Computer Components
- Historical Overview of Key Components
- Recent Advancements in Hardware and Software
- Security Implications
- The Role of Hardware and Software in Computer Security
- Protecting Computer Components from Threats
- Conclusion
- The Ongoing Relevance of Computer Components
- The Impact of Future Technological Advancements
Conclusion: Understanding the components of a computer is essential in today’s digitally driven world. This white paper provides a thorough exploration of the hardware and software components that make up a computer system. It outlines their significance, evolution, and interactions, emphasizing the importance of maintaining, upgrading, and securing these components. With technological advancements continually shaping the computing landscape, this knowledge is crucial for making informed decisions about computer use, maintenance, and future investments.
Please note that this is a concise white paper outline. To create a full white paper, each section would need to be elaborated upon in detail, providing explanations, examples, and supporting information as needed.