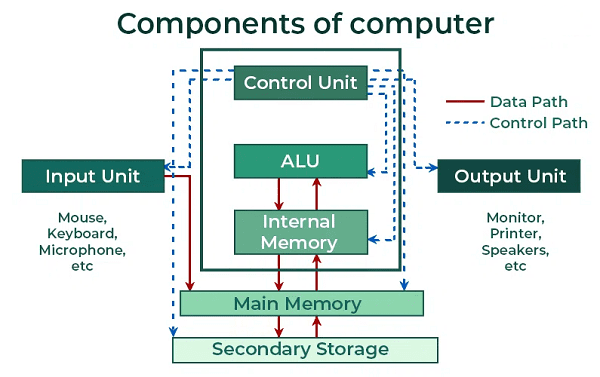
Components of computer- Computers are complex systems composed of various hardware and software components that work together to perform tasks. Here’s an overview of the main components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the brain of the computer, the CPU executes instructions from programs and performs arithmetic, logic, and control operations.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory temporarily stores data and instructions that the CPU needs while a computer is running. It’s volatile, meaning it loses its contents when the power is turned off.
- Storage Devices: These devices store data permanently or semi-permanently. Examples include Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), and Flash Drives. They provide non-volatile storage, meaning data remains even when the power is off.
- Motherboard: The main circuit board in a computer. It holds the CPU, memory, and other essential components and provides connections for other peripherals.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): Converts electrical power from an outlet into usable power for the computer’s components.
- Input Devices: These allow users to interact with the computer. Common input devices include keyboards, mice, touchscreens, and microphones.
- Output Devices: These devices display information processed by the computer. Examples include monitors, printers, speakers, and projectors.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): Specialized electronic circuitry designed to rapidly manipulate and alter memory to accelerate the creation of images in a frame buffer intended for output to a display device.
- Network Interface Card (NIC): This hardware component enables the computer to connect to a network, allowing communication with other computers and devices.
- Expansion Cards: These are optional components that can be added to a computer to enhance its capabilities. Examples include sound cards, network interface cards, and graphics cards.
- Cooling Systems: Components such as fans, heat sinks, and liquid cooling systems are used to dissipate heat generated by the CPU and other components to prevent overheating.
- BIOS/UEFI: Basic Input/Output System or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface initializes and tests hardware components during the boot process and provides basic system management functions.
- Operating System (OS): Software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Examples include Windows, macOS, Linux, and various flavors of Unix.
- Application Software: These are programs designed to perform specific tasks for users. Examples include word processors, web browsers, games, and spreadsheets.
These are the main components, but there are many more specialized components and subsystems within a computer system.
What is Required Components of computer
The required components of a computer system are those necessary for basic operation and functionality. These components are essential for the computer to function properly. Here are the key required components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is the primary component responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory temporarily stores data and instructions that the CPU needs while a computer is running. It provides fast access to data for processing.
- Storage Device: A storage device is necessary to store the operating system, programs, and user data. This can be a Hard Disk Drive (HDD), Solid State Drive (SSD), or any other form of non-volatile memory.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board that houses the CPU, RAM, storage devices, and other essential components. It provides the connections for these components to communicate with each other.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU converts electrical power from an outlet into usable power for the computer’s components.
- Input Device: An input device such as a keyboard or mouse is necessary for users to interact with the computer and input commands or data.
- Output Device: An output device such as a monitor or printer is required to display information or output data processed by the computer.
- Operating System (OS): The operating system is essential software that manages the computer’s hardware resources, provides user interfaces, and enables users to run applications.
These components form the core foundation of a computer system. While other components such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network adapters may enhance the functionality of the system, they are not strictly required for basic operation.
Who is Required Components of computer
When you asked “Who is Required Components of computer,” it seems like you might be asking about individuals or entities related to computer components. If that’s the case, here’s a breakdown:
- Manufacturers and Suppliers: Companies that design, manufacture, and supply computer components such as CPUs, memory modules, storage devices, motherboards, power supply units, input/output devices, and more. Examples include Intel, AMD, Samsung, Western Digital, ASUS, and Corsair.
- Retailers and Distributors: Businesses that sell computer components directly to consumers or distribute them to other retailers. This includes online retailers like Amazon, Newegg, and B&H, as well as brick-and-mortar stores like Best Buy and Micro Center.
- System Integrators: Companies or individuals who assemble computers using various components to create custom-built systems according to customers’ specifications. Examples include boutique PC builders like Origin PC, CyberPowerPC, and Maingear, as well as local computer shops.
- IT Professionals: Technicians, engineers, and specialists who install, maintain, and troubleshoot computer systems in various settings such as businesses, educational institutions, healthcare facilities, and government organizations.
- End Users: Individuals, organizations, and institutions that use computer systems for personal, professional, educational, or recreational purposes. End users may purchase pre-built computers or assemble their own systems using required components.
These are some of the key players and stakeholders involved in the ecosystem of computer components. Each plays a crucial role in ensuring the availability, accessibility, and functionality of computer hardware.
When is Required Components of computer
The phrase “Required Components of computer” doesn’t inherently refer to a specific time or event. However, if we interpret your question as asking about the timing of when components are needed in the context of building or maintaining a computer, here are some scenarios:
- Building a New Computer: When assembling a new computer, all required components are needed at the outset. This includes the CPU, motherboard, RAM, storage device, power supply unit, input and output devices, and any additional necessary components such as a graphics card or network adapter.
- Upgrading or Repairing a Computer: If upgrading or repairing an existing computer, the timing of component installation depends on the specific task. For example, if upgrading RAM, you would need to install the new RAM before powering on the computer. Similarly, if replacing a faulty hard drive, you would need to install the new drive before booting up the system.
- Routine Maintenance: Components such as cooling systems or power supply units may need to be replaced periodically due to wear and tear. The timing of such replacements depends on factors like the age of the components, usage patterns, and any signs of malfunction or degradation.
- Expansion or Customization: Some users may choose to add new components to their computer systems over time to expand functionality or customize performance. The timing of these additions depends on individual preferences and needs.
In summary, the timing of when required components are needed for a computer depends on the specific context, such as building a new system, upgrading or repairing an existing system, performing routine maintenance, or customizing the system to meet specific requirements.
Where is Required Components of computer
The required components of a computer are typically found within the computer itself, as they are integral to its operation. Here’s where you can typically find these components:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU is housed within the computer’s motherboard, usually protected by a heat sink and fan assembly.
- Memory (RAM): RAM modules are installed onto slots on the motherboard. In desktop computers, these slots are typically located near the CPU. In laptops, RAM modules are often accessible through a compartment on the bottom of the device.
- Storage Device: Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) and Solid State Drives (SSDs) are usually mounted within the computer case. In desktops, they’re often located in drive bays. In laptops, they are typically located beneath a service panel or underneath the keyboard.
- Motherboard: The motherboard is the main circuit board of the computer, where most components are connected or mounted. It’s typically located within the computer case and secured to the chassis.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU is also located within the computer case and is typically mounted at the top or bottom of the case. It connects to the motherboard, providing power to all components.
- Input and Output Devices: Input devices such as keyboards and mice are external peripherals connected to the computer via USB or other ports. Output devices such as monitors, printers, and speakers are also external and connected to the computer.
- Operating System (OS): The operating system is installed on the computer’s storage device (HDD or SSD) and is loaded into memory (RAM) when the computer boots up.
These components come together to form the core functionality of a computer system. While some components, like input and output devices, may be external to the computer case, the primary processing components such as the CPU, RAM, and storage devices are typically housed within the case.
How is Required Components of computer
The required components of a computer work together in a coordinated manner to enable the system to function. Here’s how these components interact:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): The CPU serves as the brain of the computer, executing instructions and performing calculations. It communicates with other components by sending and receiving signals through the motherboard’s data bus.
- Memory (RAM): RAM serves as temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. The CPU fetches data from RAM as needed for processing tasks. When the computer is powered off, the data stored in RAM is lost, unlike data stored in permanent storage devices.
- Storage Device: Storage devices, such as hard disk drives (HDDs) or solid-state drives (SSDs), store the operating system, programs, and user data persistently. The CPU can read and write data to storage devices as necessary, allowing programs to load, save files, and retrieve data.
- Motherboard: The motherboard serves as the central hub that connects all the computer’s components. It provides communication pathways between the CPU, RAM, storage devices, input/output devices, and other peripherals. The motherboard also houses essential circuitry and controllers to manage data flow and system functions.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU converts electrical power from an outlet into the various voltages required by the computer’s components. It supplies power to the motherboard, CPU, storage devices, and other components, ensuring they receive the necessary energy to operate.
- Input and Output Devices: Input devices, such as keyboards and mice, allow users to interact with the computer by providing input. Output devices, such as monitors and printers, display information or produce output based on the computer’s processing.
- Operating System (OS): The operating system manages the computer’s hardware resources, provides user interfaces, and enables users to run applications. It interacts with the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other components to coordinate system operations, manage processes, and facilitate user interactions.
Overall, the required components of a computer work together through a combination of electrical signals, data transfer, and software instructions to perform various tasks, from simple calculations to complex computations and data processing. Each component plays a crucial role in the overall functionality and performance of the computer system.
Case Study on Components of computer
Tech Innovators Inc.
Background: Tech Innovators Inc. is a software development company specializing in creating custom applications for clients across various industries. The company’s success relies heavily on the efficiency and reliability of its computer systems.
Challenge: Tech Innovators Inc. is experiencing performance issues and system failures that are impacting productivity and customer satisfaction. Upon investigation, it’s discovered that outdated computer components are contributing to these issues.
Solution: The company decides to upgrade its computer systems with modern components to address the challenges and improve overall performance.
Implementation:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU) Upgrade: Tech Innovators Inc. replaces outdated CPUs with newer, more powerful models. The upgraded CPUs provide faster processing speeds, allowing developers to compile code more quickly and run resource-intensive applications with ease.
- Memory (RAM) Expansion: The company increases the amount of RAM in each computer to accommodate the demands of multitasking and running memory-intensive software tools. With more RAM, developers experience smoother performance and reduced slowdowns when working on complex projects.
- Storage Device Enhancement: Tech Innovators Inc. migrates from traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) to solid-state drives (SSDs) for faster data access and improved reliability. The transition to SSDs significantly reduces software loading times and enhances overall system responsiveness.
- Motherboard Replacement: Outdated motherboards are replaced with newer models featuring advanced connectivity options and support for the latest CPU and RAM technologies. The upgraded motherboards provide a stable foundation for the company’s computer systems, ensuring compatibility with future hardware upgrades.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU) Upgrade: Tech Innovators Inc. installs high-efficiency power supply units to deliver clean and reliable power to the upgraded components. The new PSUs improve system stability and energy efficiency while reducing the risk of hardware failures due to power fluctuations.
Results: Following the upgrade of computer components, Tech Innovators Inc. experiences significant improvements in system performance, reliability, and productivity:
- Developers can compile code faster and run software tools more efficiently, leading to shorter development cycles and quicker time-to-market for client projects.
- System crashes and downtime are minimized, allowing employees to work uninterrupted and meet project deadlines more effectively.
- Enhanced hardware capabilities enable Tech Innovators Inc. to take on more demanding projects and deliver innovative solutions to clients, further solidifying its reputation as a leading software development company.
Conclusion: By investing in modern computer components, Tech Innovators Inc. successfully addresses performance challenges and strengthens its competitive position in the software development industry. The company’s commitment to maintaining state-of-the-art computer systems ensures optimal productivity, reliability, and customer satisfaction.
This case study highlights the critical role of computer components in supporting the operations and growth of businesses in technology-driven industries. Upgrading and maintaining hardware infrastructure is essential for maximizing performance, minimizing downtime, and staying ahead of the competition.
White paper on Components of computer
Title: Understanding the Core Components of Computer Systems: A White Paper
Executive Summary: In today’s digital age, computer systems serve as the backbone of virtually every aspect of modern life, from personal computing to large-scale enterprise operations. Understanding the core components of computer systems is essential for both users and professionals in navigating the complexities of technology. This white paper provides an in-depth overview of the fundamental components that make up computer systems, their functions, interactions, and the significance of each component in enabling the seamless operation of computing devices.
Introduction: Computer systems are intricate arrangements of hardware and software components that work together to execute tasks, process data, and facilitate communication. At the heart of every computer lies a set of core components, each playing a crucial role in the overall functionality of the system. This white paper aims to elucidate these components, shedding light on their importance and interdependencies.
Key Components of Computer Systems:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU): Often referred to as the “brain” of the computer, the CPU is responsible for executing instructions, performing calculations, and controlling the flow of data within the system.
- Memory (RAM): Random Access Memory serves as temporary storage for data and instructions that the CPU needs to access quickly. It enables fast access to data and contributes significantly to system performance.
- Storage Devices: Storage devices such as Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), Solid State Drives (SSDs), and Flash Drives provide non-volatile storage for the operating system, programs, and user data. They store data persistently even when the power is turned off.
- Motherboard: The motherboard acts as the central hub that connects all components of the computer system. It provides the infrastructure for communication between the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other peripherals.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU): The PSU converts electrical power from an outlet into usable power for the computer’s components. It ensures stable and reliable power distribution throughout the system.
- Input and Output Devices: Input devices such as keyboards, mice, and touchscreens allow users to interact with the computer, while output devices such as monitors, printers, and speakers display information or produce output based on the computer’s processing.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU): The GPU is a specialized processor designed to accelerate the rendering of images and graphics. It is particularly important for tasks such as gaming, video editing, and graphical design.
Conclusion: Understanding the core components of computer systems is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the world of technology effectively. By grasping the functions, interactions, and significance of these components, users and professionals alike can make informed decisions regarding hardware upgrades, troubleshooting, and system optimization. As technology continues to evolve, a solid understanding of computer components remains invaluable in harnessing the power of computing to drive innovation and progress in various domains.
References:
- Tanenbaum, A. S., & Bos, H. (2014). Modern operating systems (4th ed.). Pearson.
- Patterson, D. A., & Hennessy, J. L. (2017). Computer organization and design: The hardware/software interface (5th ed.). Morgan Kaufmann.
Industrial Application of Components of computer
The industrial application of computer components spans across various sectors, enhancing productivity, efficiency, and automation. Here are some examples of how different components are utilized in industrial settings:
- Central Processing Unit (CPU):
- Industrial control systems: CPUs are used in programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and industrial PCs to monitor and control manufacturing processes, machinery, and equipment.
- Real-time data processing: CPUs handle real-time data acquisition, analysis, and decision-making in industrial environments, enabling predictive maintenance, quality control, and process optimization.
- Memory (RAM):
- Data buffering: RAM is utilized for temporary storage of data in industrial applications, such as buffering sensor data, storing control variables, and caching instructions for rapid execution.
- Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs): RAM is integral to PLCs for storing program instructions, data tables, and temporary variables used in controlling industrial processes.
- Storage Devices:
- Industrial Data Logging: Hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) are used to store large volumes of historical data generated by industrial sensors, machinery, and processes for analysis, compliance, and troubleshooting.
- Embedded Systems: Flash memory is commonly used in embedded systems deployed in industrial environments due to its durability, fast access times, and resistance to shock and vibration.
- Motherboard:
- Industrial PCs (IPCs): Motherboards form the backbone of IPCs used for industrial automation, process control, and data acquisition. They provide connectivity for various components, including CPUs, RAM, storage devices, and expansion cards.
- Customized Industrial Systems: Motherboards are integrated into custom-built industrial systems designed for specific applications such as manufacturing automation, robotics, and control systems.
- Power Supply Unit (PSU):
- Reliable Power Distribution: Industrial-grade PSUs are designed to withstand harsh environmental conditions, voltage fluctuations, and electromagnetic interference commonly encountered in industrial settings.
- Redundant Power Systems: Redundant PSUs ensure continuous operation of critical industrial equipment by providing backup power in the event of a primary PSU failure.
- Input and Output Devices:
- Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Industrial-grade keyboards, touchscreens, and control panels serve as HMIs for operators to interact with and monitor industrial processes in real-time.
- Sensor Interfaces: Input devices interface with sensors, actuators, and other industrial peripherals to capture data, trigger control actions, and provide feedback to the control system.
- Graphics Processing Unit (GPU):
- Industrial Visualization: GPUs are used for rendering 3D graphics, simulations, and virtual environments in industrial applications such as process visualization, training simulators, and digital twin models.
- Machine Vision Systems: GPUs accelerate image processing tasks in machine vision systems used for quality inspection, object recognition, and defect detection in manufacturing processes.
In summary, computer components play vital roles in industrial automation, control systems, data acquisition, and visualization, driving efficiency, reliability, and innovation across various industrial sectors.