Differentiation and segmentation-
Differentiation and segmentation are two key concepts in marketing and business strategy, often used to effectively target and serve customers in competitive markets.
1. Differentiation: Differentiation refers to the process of distinguishing a product or service from others in the market. The goal of differentiation is to create a perceived uniqueness in the minds of customers. This uniqueness can be based on various factors such as:
- Product features: Highlighting unique features or attributes that set the product apart from competitors.
- Quality: Emphasizing superior quality or reliability compared to alternatives.
- Brand image: Building a strong brand identity that customers associate with specific values or benefits.
- Customer service: Providing exceptional service or support that exceeds customer expectations.
- Technological superiority: Leveraging advanced technology or innovation to offer something competitors do not.
The key to successful differentiation is ensuring that the unique aspects of the product or service are valued by the target market. This can lead to competitive advantage, increased customer loyalty, and potentially higher profitability.
2. Segmentation: Market segmentation involves dividing a broad target market into smaller, more homogeneous groups of consumers who have similar needs, preferences, or characteristics. The rationale behind segmentation is that not all customers are alike, and by identifying and understanding distinct segments, businesses can:
- Target effectively: Tailor marketing efforts and messages to specific segments, addressing their unique needs and preferences.
- Position effectively: Position products or services in a way that resonates with each segment, maximizing relevance and appeal.
- Allocate resources efficiently: Allocate resources such as marketing budgets and sales efforts more effectively by focusing on the most profitable segments.
- Differentiate offerings: Develop products or services that cater to the specific demands of different segments, thereby enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
Segmentation criteria can include demographic factors (age, gender, income), psychographic variables (lifestyle, values), behavioral characteristics (usage patterns, brand loyalty), or geographic factors (location, climate). Effective segmentation requires thorough research and analysis to ensure that the segments identified are actionable and meaningful for the business.
Relationship between Differentiation and Segmentation: While differentiation focuses on making a product or service unique within the market, segmentation helps identify which groups of customers are likely to find that differentiation most appealing. Together, they form a powerful strategy:
- Differentiation informs how a product or service can stand out.
- Segmentation guides where and to whom that differentiated offering should be targeted.
By integrating these concepts, businesses can develop a more precise understanding of their target audience and create compelling value propositions that resonate with specific customer segments, ultimately driving competitive advantage and growth.
What is Required Differentiation and segmentation
“Required differentiation and segmentation” refers to the strategic imperative for businesses to effectively distinguish their offerings in the market and identify distinct groups of customers with specific needs and preferences. Here’s a breakdown of each concept in this context:
Required Differentiation: Required differentiation emphasizes the necessity for businesses to create meaningful distinctions in their products or services that are demanded or expected by customers in the marketplace. This differentiation should address critical factors that influence customer decision-making and satisfaction. Key aspects include:
- Relevance: The differentiation should be relevant to the target market’s needs, preferences, and expectations.
- Value Proposition: It should communicate a clear and compelling value proposition that sets the product or service apart from competitors.
- Sustainability: The differentiation should be sustainable over time, offering a competitive advantage that is not easily replicated by competitors.
- Alignment with Brand: It should align with the brand identity and values, reinforcing the brand’s positioning in the market.
Businesses achieve required differentiation through various means, such as product innovation, superior quality, exceptional customer service, unique features or functionalities, or strong brand reputation. The goal is to create perceived value that justifies why customers should choose their offering over alternatives.
Required Segmentation: Required segmentation refers to the strategic necessity for businesses to divide the overall market into distinct segments or groups of customers that have different needs, preferences, and behaviors. This segmentation is essential for several reasons:
- Targeting Efficiency: By identifying specific customer segments, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts and resources more effectively, focusing on segments that are most likely to respond positively to their differentiated offerings.
- Customization: It allows businesses to customize their products, services, and marketing messages to better meet the specific requirements of each segment.
- Market Understanding: It provides deeper insights into customer behavior and trends within different segments, facilitating better strategic decision-making and market positioning.
- Competitive Advantage: Effective segmentation enables businesses to gain a competitive edge by better understanding and serving niche or underserved markets.
Required segmentation involves careful analysis of demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic factors to identify viable segments that offer growth opportunities and align with the company’s strategic objectives.
Integration and Impact: When required differentiation and segmentation are effectively integrated, businesses can enhance their market competitiveness and profitability. By differentiating their offerings in ways that are valued by specific segments, companies can capture market share, build customer loyalty, and drive sustainable growth. This integration ensures that the differentiation strategy is targeted and relevant, maximizing its impact on customer acquisition and retention within identified segments.
In conclusion, required differentiation and segmentation are critical components of strategic marketing and business planning, enabling businesses to create distinctive value propositions and effectively target specific customer segments for long-term success and competitive advantage.
Who is Required Differentiation and segmentation
“Required Differentiation and Segmentation” is not a person or an individual; rather, it’s a strategic concept used in business and marketing.
- Differentiation: This refers to the process of making a product or service distinct from others in the market. Businesses differentiate themselves by highlighting unique features, benefits, or qualities that set them apart and make their offering more attractive to consumers.
- Segmentation: This involves dividing the market into distinct groups of consumers who have similar needs, preferences, or characteristics. By segmenting the market, businesses can tailor their marketing strategies and offerings to better meet the specific needs of each segment.
Together, “Differentiation and Segmentation” form a strategic framework that helps businesses effectively target their offerings to specific groups of consumers while also ensuring that their products or services stand out from competitors. This strategic approach is crucial for achieving competitive advantage, maximizing customer satisfaction, and driving business growth.
When is Required Differentiation and segmentation
“Required Differentiation and Segmentation” is not tied to a specific time or event in a literal sense. Instead, it is a continuous strategic process that businesses engage in to effectively compete in the market. Here’s how these concepts apply across different stages and contexts:
- Market Entry or Launch: When introducing a new product or entering a new market, businesses need to differentiate their offering from existing alternatives. This differentiation helps them carve out a unique position and attract initial customers who resonate with the distinctive features or benefits.
- Growth and Expansion: As businesses grow, they may face increased competition. Continuously evolving and maintaining differentiation is crucial to sustain customer interest and loyalty. Segmenting the market further allows them to identify new opportunities and tailor their offerings to meet the specific needs of different customer groups.
- Product Lifecycle Management: Differentiation and segmentation strategies evolve throughout the product lifecycle. During the growth phase, businesses may expand their product line to appeal to different segments. In the maturity phase, they may innovate or reposition their offerings to maintain relevance and competitiveness. In the decline phase, focusing on profitable segments becomes even more critical to optimize resources.
- Competitive Response: When competitors enter the market or adapt their strategies, businesses may need to adjust their differentiation and segmentation tactics. This could involve refining existing differentiators, exploring new segments, or repositioning their brand to maintain or regain market share.
- Market Dynamics: Changes in consumer preferences, technological advancements, regulatory shifts, or economic conditions can impact differentiation and segmentation strategies. Businesses must stay agile and responsive to these external factors to effectively meet evolving customer needs and maintain competitive advantage.
In summary, “Required Differentiation and Segmentation” is an ongoing strategic imperative rather than a specific point in time. Businesses continuously assess, refine, and adapt their differentiation strategies and segmentation approaches to effectively compete and succeed in dynamic markets.
Where is Required Differentiation and segmentation
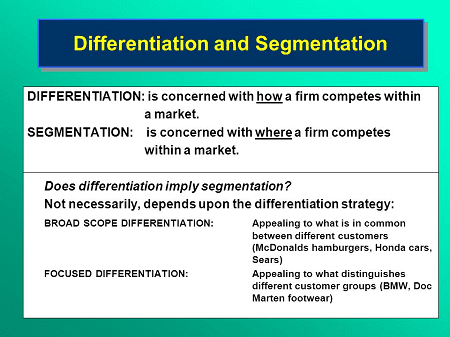
“Required Differentiation and Segmentation” is not a physical location or a specific place. Instead, it refers to strategic concepts and practices that are applied within businesses, typically within their marketing and business development departments. Here’s how these concepts are applied within organizations:
- Strategic Planning: Differentiation and segmentation strategies are developed as part of the overall strategic planning process within a business. This involves analyzing market trends, competitor offerings, and customer insights to identify opportunities for differentiation and to define target segments.
- Product Development: Differentiation begins during the product development phase, where businesses design products or services with unique features or attributes that set them apart from competitors. This process ensures that the offering meets the specific needs and preferences of target market segments.
- Marketing and Branding: Segmentation is used in marketing efforts to identify and target specific customer segments with tailored messages and promotions. Differentiation is communicated through branding and marketing campaigns to highlight the unique value propositions of the products or services.
- Sales and Distribution: Segmentation strategies influence how products or services are distributed and sold. Businesses may use different distribution channels or sales approaches to reach specific segments effectively.
- Customer Relationship Management: Differentiation strategies also extend to how businesses manage customer relationships and provide ongoing support and services. This helps in enhancing customer satisfaction and loyalty within targeted segments.
- Competitive Analysis: Continuous monitoring of competitors and market dynamics allows businesses to adjust their differentiation and segmentation strategies as needed to maintain or gain competitive advantage.
Therefore, “Required Differentiation and Segmentation” are implemented throughout various functions and departments within a business, with the goal of effectively positioning products or services in the market and meeting the needs of different customer segments. These concepts are integral to overall business strategy and contribute to sustainable growth and profitability.
How is Required Differentiation and segmentation
“Required Differentiation and Segmentation” are implemented through strategic actions that businesses take to effectively position themselves in the market and target specific customer segments. Here’s how each concept is executed:
Differentiation:
- Identifying Unique Value Propositions: Businesses analyze their strengths, market research, and customer feedback to identify what makes their products or services unique. This could be in terms of features, quality, performance, design, customer service, or brand reputation.
- Developing Unique Products or Services: Based on the identified unique value propositions, businesses develop products or services that stand out from competitors. This may involve innovation, technology advancements, or leveraging core competencies that competitors find hard to replicate.
- Communicating Differentiation: Once the unique value propositions are defined, businesses communicate them clearly to their target audience through marketing and branding efforts. This helps in building a strong brand identity and perception among consumers.
- Consistently Delivering on Promises: To maintain differentiation, businesses must consistently deliver on the promises made through their unique value propositions. This involves ensuring product quality, reliability, and customer service excellence.
- Evaluating and Adjusting: In a dynamic market environment, businesses continuously evaluate their differentiation strategies. They monitor competitor actions, customer feedback, and market trends to make adjustments and innovations as necessary to stay ahead.
Segmentation:
- Market Research: Businesses conduct thorough market research to identify different customer segments based on demographics, psychographics, behavior, and geographic factors. This helps in understanding the specific needs, preferences, and buying behaviors of each segment.
- Segmentation Criteria: Using the insights from market research, businesses develop segmentation criteria to divide the overall market into meaningful segments. This could include factors such as age, income level, lifestyle, purchasing behavior, or geographic location.
- Targeting Strategies: Once segments are identified, businesses develop targeted marketing strategies for each segment. This involves tailoring products, services, pricing, promotions, and distribution channels to meet the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
- Customization and Personalization: Segmentation enables businesses to offer customized and personalized experiences to different customer groups. This enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty by demonstrating that the business understands and values their unique requirements.
- Monitoring and Adapting: Similar to differentiation, segmentation strategies require ongoing monitoring and adaptation. Businesses track the performance of each segment, assess changes in customer preferences or market conditions, and adjust their strategies accordingly to optimize results.
Integration:
Effective implementation of differentiation and segmentation often involves integrating these strategies seamlessly. Businesses align their differentiation efforts with the needs and characteristics of each targeted segment. By doing so, they create compelling value propositions that resonate with specific customer groups, driving competitive advantage and sustainable growth.
In summary, businesses execute required differentiation and segmentation by understanding their market, identifying unique strengths, tailoring their offerings to specific customer needs, and continuously adapting to changes in the competitive landscape and consumer behavior. These strategic practices are essential for achieving market success and maintaining relevance in dynamic markets.
Case Study on Differentiation and segmentation
XYZ Fitness Wear
Background: XYZ Fitness Wear is a new entrant in the activewear market, aiming to compete with established brands by offering unique products tailored to specific customer segments.
Differentiation Strategy:
- Product Innovation: XYZ Fitness Wear differentiates itself through innovative product features. They develop activewear using advanced moisture-wicking fabrics that are eco-friendly, catering to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Brand Positioning: The brand positions itself as a premium activewear option with a focus on performance and sustainability. Their messaging emphasizes quality, durability, and ethical manufacturing practices, appealing to health-conscious and socially responsible consumers.
- Customer Experience: XYZ Fitness Wear provides exceptional customer service, including personalized fitting consultations in-store and online. They also offer a seamless shopping experience with easy returns and exchanges, reinforcing their commitment to customer satisfaction.
- Marketing: In their marketing campaigns, XYZ Fitness Wear showcases real-life testimonials from athletes and fitness enthusiasts who value the performance and sustainability features of their activewear. They utilize social media platforms to engage with their target audience and promote their unique selling propositions effectively.
Segmentation Strategy:
- Market Research: XYZ Fitness Wear conducts extensive market research to identify distinct customer segments. They analyze demographics, lifestyle choices, fitness preferences, and purchasing behaviors to understand their target audience.
- Segment Identification: Based on their research, XYZ Fitness Wear identifies two primary customer segments:
- Active Professionals: Busy professionals who prioritize comfort and performance during workouts. They value high-quality materials and stylish designs that seamlessly transition from the gym to everyday activities.
- Eco-Conscious Consumers: Environmentally conscious consumers who seek activewear made from sustainable materials. They are willing to pay a premium for products that align with their values of sustainability and ethical sourcing.
- Targeted Marketing Campaigns: XYZ Fitness Wear tailors their marketing strategies to each segment. For active professionals, they highlight the versatility and performance of their activewear in various settings. For eco-conscious consumers, they emphasize the sustainability features and eco-friendly production processes.
- Product Customization: The company offers customization options such as color choices and fit preferences, catering to the specific tastes and needs of each segment. This customization enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Integration and Impact:
By effectively implementing differentiation and segmentation strategies, XYZ Fitness Wear achieves several outcomes:
- Competitive Advantage: They differentiate themselves from competitors by offering unique, high-performance activewear with eco-friendly credentials.
- Market Penetration: By targeting specific customer segments, XYZ Fitness Wear captures niche markets that value their unique product offerings.
- Brand Loyalty: Their focus on quality, sustainability, and personalized customer experiences fosters strong brand loyalty among their target segments.
- Revenue Growth: Through targeted marketing efforts and product customization, XYZ Fitness Wear drives sales growth and increases profitability.
In conclusion, XYZ Fitness Wear’s success demonstrates how a strategic approach to differentiation and segmentation can effectively position a new brand in a competitive market. By understanding their customers’ needs and preferences and delivering tailored solutions, they create value, build brand equity, and drive sustainable business growth.
White paper on Differentiation and segmentation
Introduction
In today’s competitive business landscape, differentiation and segmentation are critical strategies that businesses must leverage to effectively position themselves in the market and cater to diverse customer needs. This white paper explores the importance of differentiation and segmentation, provides insights into their strategic implementation, and offers practical recommendations for businesses seeking to achieve sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Why Differentiation and Segmentation Matter
Differentiation and segmentation are fundamental concepts that help businesses stand out in crowded markets and target specific customer segments effectively. Here’s why they are crucial:
- Competitive Advantage: Differentiation allows businesses to create unique value propositions that set them apart from competitors. This can be through product innovation, superior quality, exceptional customer service, or brand reputation.
- Market Relevance: Segmentation enables businesses to identify distinct groups of customers with similar needs and preferences. By understanding these segments, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts and offerings to better meet the specific requirements of each group.
- Enhanced Customer Satisfaction: When businesses differentiate their products or services based on what matters most to their target segments, they enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty. Customers feel understood and valued, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth.
Strategies for Differentiation
Effective differentiation strategies involve several key steps:
- Identify Unique Value Propositions: Conduct market research to understand customer pain points, preferences, and unmet needs. Use this insight to develop unique features or benefits that address these aspects better than competitors.
- Focus on Quality and Innovation: Invest in product development and innovation to create offerings that are superior in quality, functionality, or design. Continuously improve and iterate based on customer feedback and market trends.
- Build a Strong Brand Identity: Develop a compelling brand story and identity that resonates with your target audience. Communicate your unique value propositions consistently through branding, marketing campaigns, and customer interactions.
- Provide Exceptional Customer Service: Offer personalized customer experiences and exceptional service that exceed customer expectations. This can be a significant differentiator in industries where service quality is crucial.
Strategies for Segmentation
Effective segmentation strategies involve the following steps:
- Segmentation Criteria: Identify relevant segmentation criteria such as demographics (age, gender, income), psychographics (lifestyle, values), behavioral (usage patterns, purchasing behavior), and geographic factors (location, climate).
- Segment Identification: Analyze data to identify distinct customer segments within your target market. Group customers who share similar characteristics and needs into segments that are meaningful and actionable.
- Targeted Marketing and Positioning: Develop targeted marketing strategies and positioning statements for each segment. Tailor your messaging, promotions, and product offerings to resonate with the specific needs and preferences of each segment.
- Customization and Personalization: Offer customization options or personalized recommendations based on customer preferences. Use data analytics and technology to deliver targeted messages and experiences across various touchpoints.
Integration of Differentiation and Segmentation
Successful businesses integrate differentiation and segmentation strategies seamlessly to maximize their impact:
- Alignment with Business Goals: Ensure that differentiation and segmentation strategies align with overall business objectives and growth targets. Continuously evaluate and adjust strategies based on market dynamics and competitive landscape.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor customer feedback, market trends, and competitor actions to identify opportunities for improvement and innovation. Stay agile and responsive to changes in customer preferences and industry trends.
- Cross-functional Collaboration: Foster collaboration between marketing, product development, sales, and customer service teams to ensure a cohesive approach to differentiation and segmentation. Share insights and best practices across departments to drive collective success.
Conclusion
In conclusion, differentiation and segmentation are indispensable strategies that businesses must leverage to achieve sustainable growth, competitive advantage, and customer satisfaction. By understanding their target market segments and delivering differentiated value propositions, businesses can position themselves effectively in the market and foster long-term success.
For businesses looking to implement or enhance their differentiation and segmentation strategies, it is essential to conduct thorough market research, invest in innovation, build strong brand identities, and tailor marketing efforts to meet the specific needs of diverse customer segments. By doing so, businesses can differentiate themselves effectively and build lasting relationships with their customers.
This white paper provides a comprehensive overview of differentiation and segmentation strategies, outlining their significance, implementation strategies, and integration within business operations.
Industrial Application of Differentiation and segmentation
Differentiation and segmentation strategies are crucial in industrial settings as they help businesses optimize their operations, target specific markets effectively, and maintain competitive advantage. Here’s how these concepts are applied in industrial applications:
1. Product Differentiation:
In industrial manufacturing, differentiation focuses on creating unique products or solutions that stand out in the market. This can include:
- Technological Innovation: Developing products with advanced features or capabilities that improve efficiency, performance, or reliability.
- Customization: Offering configurable products that meet specific customer requirements or industry standards.
- Quality and Reliability: Emphasizing superior product quality, durability, and adherence to industry regulations or certifications.
- Service Differentiation: Providing value-added services such as installation, training, maintenance, or technical support.
Example: A manufacturer of industrial machinery differentiates itself by incorporating IoT technology into its equipment, enabling predictive maintenance and remote monitoring capabilities that reduce downtime and improve operational efficiency for customers.
2. Market Segmentation:
Segmentation in industrial markets involves categorizing customers based on factors such as industry type, company size, geographic location, and specific operational needs. This allows businesses to:
- Targeted Marketing: Develop tailored marketing campaigns and messaging that resonate with the unique challenges and priorities of each segment.
- Product Development: Customize product offerings to address the specific requirements and use cases of different industries or applications.
- Sales Strategy: Allocate sales resources effectively by focusing efforts on high-potential segments that are likely to benefit most from the company’s products or services.
- Customer Service: Provide specialized support and solutions that cater to the technical and operational demands of each segment.
Example: A supplier of industrial chemicals segments its market into pharmaceutical, food processing, and automotive industries. Each segment receives customized product formulations and technical support tailored to their unique regulatory requirements and operational processes.
3. Supply Chain Optimization:
Differentiation and segmentation strategies also extend to supply chain management in industrial settings:
- Supplier Differentiation: Establishing strategic partnerships with suppliers that offer unique materials, components, or services that enhance product differentiation.
- Logistics and Distribution: Segmenting logistics operations to prioritize timely delivery and cost-efficient distribution channels based on customer location and order size.
- Inventory Management: Implementing differentiated inventory strategies to meet varying demand patterns across different customer segments or product lines.
Example: An industrial equipment manufacturer optimizes its supply chain by differentiating between critical components sourced from premium suppliers for high-end products and standard components for budget-conscious segments, ensuring cost-effectiveness and product quality.
4. Competitive Strategy and Positioning:
In industrial markets, differentiation and segmentation are essential for maintaining competitive advantage and positioning:
- Brand Positioning: Communicating a clear value proposition and brand identity that resonates with target segments, reinforcing the company’s position as a leader in specific industry niches.
- Competitive Pricing: Setting pricing strategies based on value perception and differentiation factors relative to competitors within each segment.
- Market Expansion: Using segmentation insights to identify new market opportunities and develop strategies for entering or expanding into new geographic regions or industrial sectors.
Example: A manufacturer of industrial automation systems differentiates itself by focusing on precision engineering and reliability, positioning itself as a premium solution provider in the automotive manufacturing segment while offering scalable solutions for other industrial applications.
In conclusion, differentiation and segmentation strategies are integral to industrial applications as they enable businesses to tailor their products, services, and operations to meet the specific needs of diverse customer segments, enhance competitive advantage, and drive sustainable growth in dynamic and competitive markets.






