Functions of entrepreneur-
An entrepreneur plays a multifaceted role in the economy, involving various functions crucial to the success of a business. Here are the primary functions of an entrepreneur:
1. Innovation
- Idea Generation: Entrepreneurs create new ideas for products, services, or processes.
- Research and Development: They invest in R&D to improve existing products or develop new ones.
2. Risk Taking
- Financial Risk: Investing personal funds or acquiring loans to start or expand a business.
- Market Risk: Entering new or existing markets with uncertainty about consumer acceptance.
- Operational Risk: Managing daily business operations with the inherent risks of failures and challenges.
3. Resource Allocation
- Capital Management: Securing and allocating financial resources efficiently.
- Human Resources: Recruiting, training, and retaining skilled employees.
- Material Resources: Acquiring and managing the necessary materials and equipment.
4. Organization and Management
- Business Planning: Developing a comprehensive business plan outlining goals, strategies, and operational plans.
- Structuring: Establishing the organizational structure and defining roles and responsibilities.
- Decision Making: Making strategic and operational decisions to steer the business.
5. Market Analysis and Strategy
- Market Research: Conducting market analysis to understand customer needs and market trends.
- Marketing Strategy: Developing marketing strategies to promote and sell products or services.
6. Customer Relations
- Customer Satisfaction: Ensuring customer satisfaction through quality products and services.
- Feedback Mechanism: Implementing feedback systems to improve products and services based on customer input.
7. Leadership
- Vision: Setting a clear vision for the future of the business.
- Motivation: Inspiring and motivating employees to achieve business goals.
- Adaptability: Adapting to changes in the market, technology, and industry.
8. Networking
- Building Relationships: Establishing and maintaining relationships with suppliers, customers, investors, and other stakeholders.
- Collaboration: Collaborating with other businesses, organizations, and individuals to enhance business opportunities.
9. Financial Management
- Budgeting: Preparing budgets and monitoring financial performance.
- Cost Control: Managing expenses to ensure profitability.
- Fundraising: Raising capital through loans, investments, or other means.
10. Compliance and Ethics
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring the business adheres to laws and regulations.
- Ethical Standards: Upholding high ethical standards in business practices.
11. Scaling and Growth
- Expansion Planning: Planning for business growth and expansion.
- Innovation in Growth: Innovating continuously to scale the business.
These functions collectively help entrepreneurs to successfully establish, manage, and grow their businesses, contributing significantly to economic development and innovation.
What is Required Functions of entrepreneur
The required functions of an entrepreneur can be summarized as the essential tasks and responsibilities that entrepreneurs must fulfill to effectively start, manage, and grow a business. These functions are critical for achieving business success and sustainability. Here are the key required functions of an entrepreneur:
1. Opportunity Identification and Innovation
- Identifying Opportunities: Recognizing gaps or needs in the market that can be addressed with a new product, service, or solution.
- Innovation: Generating creative ideas and solutions to capitalize on identified opportunities.
2. Risk Management
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating and understanding the risks associated with business decisions, including financial, market, and operational risks.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing strategies to minimize and manage risks effectively.
3. Resource Acquisition and Management
- Financial Resources: Securing funding through personal investment, loans, or external investment.
- Human Resources: Hiring, training, and managing a skilled workforce.
- Material Resources: Acquiring and managing physical assets, equipment, and materials necessary for operations.
4. Business Planning and Strategy
- Business Plan Development: Creating a detailed roadmap that outlines business goals, objectives, strategies, and action plans.
- Strategic Decision Making: Making informed decisions based on market analysis, financial data, and business objectives.
5. Marketing and Customer Relations
- Market Research: Conducting research to understand customer needs, preferences, and market trends.
- Marketing Strategy: Developing effective marketing campaigns to promote products or services and attract customers.
- Customer Relationship Management: Building and maintaining strong relationships with customers to enhance loyalty and satisfaction.
6. Financial Management
- Financial Planning: Developing budgets, forecasts, and financial projections to manage cash flow and ensure financial stability.
- Financial Monitoring: Monitoring financial performance, analyzing variances, and making adjustments as needed.
- Fundraising: Raising capital through loans, investments, or other financing methods to support business operations and growth.
7. Legal and Regulatory Compliance
- Compliance: Ensuring the business complies with all applicable laws, regulations, and licensing requirements.
- Ethical Practices: Operating the business with integrity and ethical standards in all dealings with stakeholders.
8. Leadership and Management
- Vision Setting: Establishing a clear vision and direction for the business.
- Team Building: Hiring and developing a competent team capable of achieving business objectives.
- Decision Making: Making timely and effective decisions to drive business growth and success.
9. Networking and Relationship Building
- Networking: Building relationships with industry peers, potential partners, investors, and other stakeholders to create business opportunities.
- Collaboration: Partnering with other businesses or organizations to leverage strengths and resources for mutual benefit.
10. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Learning: Staying informed about industry trends, technological advancements, and market changes.
- Adaptation: Being flexible and agile to adapt business strategies and operations in response to changing market conditions and opportunities.
11. Monitoring and Evaluation
- Performance Monitoring: Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess business performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Evaluation: Conducting periodic reviews and evaluations to measure progress against goals and make adjustments to strategies as necessary.
These required functions collectively enable entrepreneurs to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and build sustainable businesses that contribute to economic growth and innovation.
Who is Required Functions of entrepreneur
However, if you’re asking about the required functions or roles that an entrepreneur must fulfill, I can certainly help with that!
An entrepreneur, regardless of their specific name, is typically expected to fulfill several essential functions or roles to successfully start, manage, and grow a business. These functions include:
- Opportunity Identification: Recognizing opportunities in the market for new products, services, or solutions.
- Innovation: Developing creative ideas and solutions to capitalize on identified opportunities.
- Risk Management: Assessing and managing risks associated with business operations, investments, and decision-making.
- Resource Management: Acquiring and effectively managing financial, human, and material resources necessary for business operations.
- Strategic Planning: Developing a clear vision, mission, and strategic objectives for the business.
- Marketing and Sales: Creating and implementing marketing strategies to attract customers and drive sales.
- Financial Management: Budgeting, managing cash flow, and ensuring financial stability and growth.
- Leadership: Providing leadership and direction to employees and stakeholders.
- Networking and Relationship Building: Building relationships with customers, suppliers, partners, and other stakeholders.
- Continuous Learning and Adaptation: Staying informed about industry trends, technological advancements, and market changes, and adapting strategies accordingly.
These functions collectively contribute to the entrepreneur’s ability to navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and build a successful and sustainable business. Each function is crucial in its own right, and successful entrepreneurs often excel in managing these roles effectively.
When is Required Functions of entrepreneur
The required functions of an entrepreneur are applicable throughout the lifecycle of a business, from its inception to its growth and sustainability phases. Here’s a breakdown of when these functions are typically relevant:
1. Startup Phase
- Opportunity Identification: This is crucial at the beginning when entrepreneurs identify a gap or need in the market.
- Innovation: Creating unique ideas or solutions to address identified opportunities.
- Risk Management: Assessing financial, market, and operational risks associated with starting a new venture.
- Resource Management: Acquiring initial funding, hiring key personnel, and securing necessary resources.
2. Early Growth Phase
- Strategic Planning: Developing a clear business plan and setting strategic goals for growth.
- Marketing and Sales: Implementing marketing strategies to build brand awareness and attract initial customers.
- Financial Management: Managing cash flow and finances to support growth and expansion.
- Networking: Building relationships with investors, partners, and suppliers to support business growth.
3. Expansion Phase
- Leadership: Providing strong leadership to guide the organization through growth stages.
- Scaling Operations: Expanding production, distribution, and infrastructure to meet increasing demand.
- Continuous Learning: Staying updated with industry trends and customer preferences to remain competitive.
- Adaptation: Adjusting strategies and operations in response to market changes and challenges.
4. Maturity Phase
- Optimization: Streamlining operations and improving efficiency to maintain profitability.
- Diversification: Exploring new markets or product/service lines to sustain growth.
- Sustainability: Ensuring long-term viability by managing risks and adapting to economic fluctuations.
- Innovation: Continuing to innovate to stay relevant and meet evolving customer needs.
5. Decline or Renewal Phase
- Reevaluation: Assessing market conditions and business performance to determine future strategies.
- Pivot: Considering strategic pivots or diversification to revitalize the business.
- Reinvestment: Investing in new technologies or processes to regain market share or explore new opportunities.
In summary, the required functions of an entrepreneur are continuous and evolve with the business lifecycle. Entrepreneurs must adapt their strategies and actions accordingly to navigate different phases successfully and sustain long-term growth and profitability.
Where is Required Functions of entrepreneur
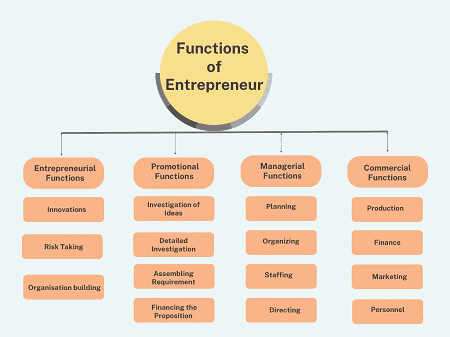
The required functions of an entrepreneur are not confined to a specific physical location but rather encompass a set of responsibilities and activities that entrepreneurs undertake wherever they are conducting business. Here’s how these functions manifest in various contexts:
1. Startup Stage
- Location: Entrepreneurs may work from home, shared workspaces, or small offices depending on their financial resources and needs.
- Functions: They focus on opportunity identification, innovation, and securing initial funding. This stage often involves a lot of networking and relationship building within their local business community.
2. Growth Stage
- Location: As businesses expand, entrepreneurs might move into larger offices or facilities to accommodate increased operations.
- Functions: Strategic planning, marketing, and sales efforts intensify as they aim to scale their business. They may also explore new markets and build partnerships beyond their local area.
3. Expansion Stage
- Location: Entrepreneurs may establish additional branches, open new markets, or engage in international business, necessitating diverse locations.
- Functions: Leadership becomes crucial as they manage multiple locations or operations. Financial management, resource allocation, and regulatory compliance are key as they navigate different jurisdictions and markets.
4. Maturity Stage
- Location: Established businesses may consolidate operations or diversify into new products or services, potentially leading to specialized locations or headquarters.
- Functions: Optimization of operations, sustainability efforts, and ongoing innovation continue to drive the business forward. They may invest in technology and talent to maintain competitiveness.
5. Digital and Remote Settings
- Location: With advancements in technology, many entrepreneurs operate remotely or digitally, managing businesses from anywhere in the world.
- Functions: They leverage digital platforms for marketing, sales, and customer relations. Financial management and networking also take place virtually, often across global networks.
6. Challenges and Adaptation
- Location: During challenging times, such as economic downturns or industry disruptions, entrepreneurs adapt their functions to navigate uncertainties.
- Functions: They may pivot business strategies, seek new funding sources, or restructure operations as needed, regardless of location.
In essence, while the functions of an entrepreneur are not tied to a specific geographical location, they are adaptable and essential across various stages of business development and in different operational contexts. The focus remains on fulfilling key responsibilities to ensure business growth, sustainability, and success, regardless of where the entrepreneur is based or where their business operates.
How is Required Functions of entrepreneur
The required functions of an entrepreneur are executed through a combination of skills, actions, and strategic decisions aimed at building and growing a successful business. Here’s how these functions are typically carried out:
1. Opportunity Identification and Innovation
- Skill: Entrepreneurs possess a knack for spotting gaps or opportunities in the market.
- Action: They actively seek out innovative ideas or solutions to capitalize on these opportunities.
- Decision: They decide which opportunities to pursue based on feasibility, market demand, and potential profitability.
2. Risk Management
- Skill: They assess and manage various risks associated with starting and running a business.
- Action: This involves conducting risk assessments, developing risk mitigation strategies, and making informed decisions to minimize potential negative impacts.
- Decision: They decide on risk tolerance levels and the best course of action to protect the business while pursuing growth.
3. Resource Acquisition and Management
- Skill: Entrepreneurs are adept at securing financial, human, and material resources needed for their business.
- Action: They raise capital through investments, loans, or personal funds and manage resources efficiently to maximize productivity.
- Decision: They allocate resources strategically to support business operations, growth initiatives, and day-to-day activities.
4. Business Planning and Strategy
- Skill: They develop clear business plans and strategic goals to guide their business.
- Action: This involves setting objectives, outlining strategies, and creating action plans to achieve business milestones.
- Decision: They make critical decisions regarding business direction, market positioning, and resource allocation based on strategic planning.
5. Marketing and Customer Relations
- Skill: Entrepreneurs understand the importance of marketing and building strong customer relationships.
- Action: They develop marketing strategies, promote their products or services, and engage with customers to understand their needs.
- Decision: They make decisions on marketing channels, messaging, pricing strategies, and customer service initiatives to attract and retain customers.
6. Financial Management
- Skill: They possess financial acumen and the ability to manage finances effectively.
- Action: This includes budgeting, cash flow management, financial forecasting, and monitoring financial performance.
- Decision: They make decisions on investments, cost control measures, pricing strategies, and financing options to ensure financial health and sustainability.
7. Leadership and Team Building
- Skill: Entrepreneurs demonstrate strong leadership qualities and the ability to inspire and motivate their team.
- Action: They build and lead a talented team, delegate responsibilities, and foster a positive work environment.
- Decision: They make decisions on hiring, training, managing performance, and creating a cohesive organizational culture that supports business goals.
8. Networking and Relationship Building
- Skill: They excel in building relationships with stakeholders, including investors, customers, suppliers, and industry peers.
- Action: They network actively, attend industry events, and engage in community activities to expand their professional network.
- Decision: They make decisions on partnerships, collaborations, and alliances that can benefit their business and enhance market presence.
9. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Skill: Entrepreneurs are committed to lifelong learning and staying updated with industry trends and best practices.
- Action: They seek knowledge, attend workshops, and stay informed about technological advancements and market changes.
- Decision: They make decisions on adopting new technologies, adjusting strategies, and innovating to stay competitive and relevant in the market.
10. Monitoring and Evaluation
- Skill: They have a keen eye for detail and a commitment to monitoring business performance.
- Action: They track key performance indicators (KPIs), analyze data, and evaluate business outcomes against goals.
- Decision: They make decisions on refining strategies, making improvements, and seizing new opportunities based on performance insights.
In summary, the required functions of an entrepreneur are executed through a combination of skills, actions, and decisions that collectively drive business growth, innovation, and success. Entrepreneurs leverage their expertise and strategic thinking to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and build sustainable businesses in dynamic and competitive environments.
Case Study on Functions of entrepreneur
Launching a Sustainable Fashion Startup
Entrepreneur: Emma Smith
1. Opportunity Identification and Innovation
- Challenge: Emma, a passionate advocate for sustainable fashion, notices a growing trend among consumers towards eco-friendly and ethical clothing choices.
- Action: She identifies an opportunity to create a sustainable fashion brand that offers stylish, high-quality garments made from organic materials and using ethical production practices.
- Decision: Emma decides to launch “Green Threads,” targeting environmentally conscious consumers seeking fashionable and sustainable alternatives.
2. Risk Management
- Challenge: Starting a new fashion brand involves financial risks, market uncertainties, and challenges in establishing supplier relationships.
- Action: Emma conducts thorough market research to understand consumer preferences, competitive landscape, and potential risks such as supply chain disruptions and fluctuating material costs.
- Decision: She develops a risk management plan that includes securing initial funding through a combination of personal savings and a small business loan. Emma also establishes backup suppliers and negotiates contracts to ensure reliable sourcing of materials.
3. Resource Acquisition and Management
- Challenge: Acquiring sufficient resources, including capital, skilled labor, and sustainable materials, is critical for launching and scaling the business.
- Action: Emma raises capital from a mix of personal savings, a crowdfunding campaign emphasizing sustainability, and a loan from a socially responsible investment fund.
- Decision: She hires experienced designers and garment makers committed to ethical production practices. Emma also sources organic cotton and recycled fabrics from certified suppliers, ensuring adherence to sustainability standards.
4. Business Planning and Strategy
- Challenge: Developing a clear business plan and strategy is essential to guide the startup through its initial stages and long-term growth.
- Action: Emma creates a comprehensive business plan outlining Green Threads’ mission, vision, target market segments, product offerings, pricing strategy, and distribution channels.
- Decision: She decides to focus on direct-to-consumer sales through an e-commerce platform initially, with plans to expand into select retail partnerships and pop-up stores in sustainable fashion hubs.
5. Marketing and Customer Relations
- Challenge: Building brand awareness and fostering customer loyalty in a competitive fashion market requires effective marketing and strong customer relations.
- Action: Emma develops a marketing strategy emphasizing Green Threads’ sustainability credentials, engaging storytelling through social media, content marketing, and collaborations with eco-influencers.
- Decision: She decides to prioritize transparency and customer engagement, launching a blog discussing sustainable fashion tips, behind-the-scenes production stories, and customer testimonials to build trust and a loyal customer base.
6. Financial Management
- Challenge: Managing cash flow, budgeting effectively, and ensuring financial sustainability are crucial for the startup’s viability and growth.
- Action: Emma implements financial management practices, including meticulous budgeting, cash flow forecasting, and monitoring expenses against revenue projections.
- Decision: She makes strategic investments in digital marketing campaigns, product development, and operational efficiencies while prioritizing sustainability practices to minimize environmental impact and operational costs.
7. Leadership and Team Building
- Challenge: Leading a diverse team of creative professionals and ensuring alignment with Green Threads’ mission and values requires strong leadership.
- Action: Emma fosters a collaborative and supportive work environment, emphasizing open communication, creativity, and a shared commitment to sustainability.
- Decision: She hires employees who share her passion for sustainable fashion, empowering them to contribute ideas, innovate, and take ownership of their roles to drive business growth and customer satisfaction.
8. Networking and Relationship Building
- Challenge: Establishing partnerships with suppliers, influencers, industry experts, and sustainability advocates is essential for Green Threads’ growth and credibility.
- Action: Emma attends sustainable fashion conferences, networking events, and collaborates with like-minded organizations and influencers to amplify Green Threads’ brand presence.
- Decision: She forms strategic partnerships with eco-conscious suppliers, collaborates with sustainability influencers for product endorsements, and participates in community initiatives promoting ethical fashion practices.
9. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
- Challenge: Staying abreast of evolving consumer trends, technological advancements, and sustainability innovations is vital for maintaining Green Threads’ competitive edge.
- Action: Emma invests time in continuous learning, attending workshops, webinars, and industry conferences focused on sustainable fashion, consumer behavior, and e-commerce trends.
- Decision: She integrates new technologies such as sustainable fabric innovations and eco-friendly packaging solutions into Green Threads’ product offerings. Emma also adapts marketing strategies based on customer feedback and market insights to optimize brand positioning and customer engagement.
10. Monitoring and Evaluation
- Challenge: Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs), analyzing business metrics, and evaluating the effectiveness of strategies are essential for making informed decisions.
- Action: Emma establishes KPIs related to sales growth, customer acquisition and retention, sustainability metrics (e.g., carbon footprint reduction), and operational efficiency.
- Decision: She regularly reviews performance reports, conducts customer surveys, and gathers feedback from employees to identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. Based on data analysis, Emma adjusts marketing campaigns, operational processes, and product offerings to optimize performance and achieve sustainable business growth.
Conclusion
Through diligent application of the functions of an entrepreneur, Emma successfully launches and grows Green Threads into a reputable sustainable fashion brand. Her strategic decisions, coupled with a strong commitment to sustainability, innovation, and customer engagement, position Green Threads as a leader in the eco-friendly fashion industry, contributing positively to both environmental stewardship and business profitability. This case study illustrates how entrepreneurial functions are integrated and applied in a real-world context to achieve business success and societal impact.
White paper on Functions of entrepreneur
Introduction
Entrepreneurship is a dynamic process driven by individuals who identify opportunities, innovate solutions, and take calculated risks to create value in the marketplace. This white paper explores the fundamental functions that entrepreneurs perform to launch, manage, and grow successful ventures. It examines how these functions contribute to economic development, innovation, and societal impact.
1. Opportunity Identification and Innovation
Entrepreneurs are adept at identifying gaps, needs, or inefficiencies in the market. This function involves:
- Market Research: Conducting thorough analysis to understand consumer preferences, industry trends, and competitive landscape.
- Innovation: Developing new products, services, or business models that meet identified needs or capitalize on emerging trends.
- Decision Making: Evaluating opportunities based on feasibility, market demand, and potential profitability to determine which ventures to pursue.
2. Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial for entrepreneurial success:
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and assessing financial, market, operational, and strategic risks associated with business ventures.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing strategies to minimize risks through diversification, contingency planning, and proactive decision-making.
- Adaptability: Adjusting strategies and operations in response to changing market conditions or unexpected challenges.
3. Resource Acquisition and Management
Entrepreneurs must acquire and allocate resources effectively:
- Financial Resources: Securing funding through personal savings, loans, investments, or crowdfunding.
- Human Resources: Recruiting, training, and retaining skilled employees who contribute to the organization’s growth and success.
- Material Resources: Sourcing and managing physical assets, equipment, and raw materials essential for business operations.
4. Business Planning and Strategy
Strategic planning provides a roadmap for achieving long-term goals:
- Business Plan Development: Creating a comprehensive plan that outlines the venture’s mission, vision, objectives, strategies, and operational tactics.
- Strategic Decision Making: Making informed decisions on market entry, product development, pricing, distribution channels, and growth strategies based on market insights and competitive analysis.
5. Marketing and Customer Relations
Successful entrepreneurs understand the importance of marketing and building strong customer relationships:
- Market Segmentation: Identifying target markets and tailoring marketing strategies to meet specific customer needs and preferences.
- Brand Building: Establishing a unique brand identity and positioning that resonates with target customers.
- Customer Engagement: Implementing effective communication and feedback mechanisms to enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
6. Financial Management
Sound financial management is critical for sustainable growth and profitability:
- Budgeting and Forecasting: Developing and monitoring budgets, cash flow projections, and financial performance metrics.
- Cost Control: Implementing strategies to manage expenses and optimize operational efficiency.
- Financial Reporting: Providing transparent and accurate financial reporting to stakeholders, investors, and regulatory authorities.
7. Leadership and Team Building
Effective leadership fosters a motivated and productive workforce:
- Visionary Leadership: Inspiring and guiding employees towards achieving organizational goals and objectives.
- Team Development: Hiring, training, and empowering a diverse team of talented individuals who contribute to innovation and operational excellence.
- Organizational Culture: Cultivating a positive work environment based on trust, collaboration, and continuous learning.
8. Networking and Relationship Building
Entrepreneurs leverage networks to access resources and opportunities:
- Stakeholder Engagement: Building relationships with investors, suppliers, customers, industry peers, and community stakeholders.
- Partnerships and Alliances: Collaborating with strategic partners to leverage complementary strengths and enhance market reach.
- Industry Involvement: Participating in industry events, conferences, and associations to stay informed about industry trends and developments.
9. Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Entrepreneurs embrace lifelong learning to stay competitive and innovative:
- Market Intelligence: Monitoring market trends, technological advancements, and consumer behavior to identify emerging opportunities and threats.
- Adaptability: Responding to changes in the business environment by adjusting strategies, products, and operational processes.
- Innovation: Promoting a culture of innovation that encourages creativity, experimentation, and the pursuit of new ideas.
10. Monitoring and Evaluation
Regular monitoring and evaluation ensure performance optimization:
- Performance Metrics: Establishing key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress towards business objectives.
- Performance Analysis: Analyzing KPIs, financial metrics, and customer feedback to assess business performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: Implementing corrective actions, refining strategies, and making informed decisions based on performance insights.
Conclusion
Entrepreneurs play a pivotal role in driving economic growth, fostering innovation, and creating employment opportunities. By performing these essential functions effectively, entrepreneurs not only build successful ventures but also contribute to societal development and sustainable prosperity. This white paper highlights the multifaceted nature of entrepreneurship and underscores the importance of entrepreneurial skills, actions, and decisions in navigating challenges and seizing opportunities in today’s dynamic business environment.
Industrial Application of Functions of entrepreneur
The functions of an entrepreneur find diverse applications across various industrial sectors, where they contribute to innovation, growth, and competitiveness. Here are some industrial applications illustrating how entrepreneurial functions are applied:
1. Technology and Software Development
- Opportunity Identification: Entrepreneurs identify gaps in technology or software solutions that can streamline processes or meet specific market needs.
- Innovation: They innovate by developing new algorithms, software platforms, or applications that improve efficiency, enhance user experience, or introduce novel functionalities.
- Risk Management: Entrepreneurs manage risks associated with technological advancements, such as cybersecurity threats, intellectual property issues, and rapid technological obsolescence.
- Resource Management: They secure funding for research and development, hire skilled developers, and manage technological infrastructure effectively.
2. Healthcare and Biotechnology
- Opportunity Identification: Entrepreneurs recognize opportunities in healthcare for innovative treatments, diagnostic tools, or medical devices.
- Innovation: They innovate by developing new pharmaceuticals, biotechnological advancements, medical equipment, or digital health solutions.
- Risk Management: Entrepreneurs navigate regulatory hurdles, clinical trial risks, and market adoption challenges inherent in the healthcare industry.
- Resource Management: They secure funding for research, clinical trials, and manufacturing, as well as recruit specialized talent in medical research and development.
3. Renewable Energy and Sustainability
- Opportunity Identification: Entrepreneurs identify opportunities in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or biomass energy, as well as sustainability solutions.
- Innovation: They innovate by developing new technologies for energy generation, energy storage solutions, or sustainable practices for industries.
- Risk Management: Entrepreneurs manage risks associated with project financing, technological feasibility, and regulatory compliance in the renewable energy sector.
- Resource Management: They secure funding for large-scale projects, acquire land or infrastructure for energy installations, and manage resources like raw materials and skilled labor.
4. Manufacturing and Industrial Automation
- Opportunity Identification: Entrepreneurs identify opportunities in manufacturing processes for automation, robotics, or smart factory solutions.
- Innovation: They innovate by developing advanced manufacturing technologies, robotics for assembly lines, or IoT (Internet of Things) solutions for predictive maintenance.
- Risk Management: Entrepreneurs manage risks related to technology integration, workforce adaptation, and cybersecurity in industrial automation.
- Resource Management: They secure funding for capital-intensive projects, acquire state-of-the-art machinery and technology, and manage resources like skilled technicians and engineers.
5. Food and Agriculture
- Opportunity Identification: Entrepreneurs identify opportunities in sustainable agriculture, organic food production, or innovative food processing techniques.
- Innovation: They innovate by developing new agricultural technologies, sustainable farming practices, or food products tailored to consumer trends.
- Risk Management: Entrepreneurs manage risks related to crop failures, food safety regulations, and market volatility in the food and agriculture sector.
- Resource Management: They secure funding for agricultural research, invest in modern farming equipment, and manage resources like land, water, and agricultural inputs.
6. Retail and E-commerce
- Opportunity Identification: Entrepreneurs identify opportunities in online retail, niche markets, or personalized consumer experiences.
- Innovation: They innovate by developing new e-commerce platforms, digital marketing strategies, or customer engagement tools.
- Risk Management: Entrepreneurs manage risks related to cyber threats, logistical challenges, and changing consumer preferences in the retail sector.
- Resource Management: They secure funding for digital marketing campaigns, invest in e-commerce infrastructure, and manage resources like inventory and supply chain logistics.
7. Financial Services and Fintech
- Opportunity Identification: Entrepreneurs identify opportunities in financial technology (fintech), digital banking, or blockchain applications.
- Innovation: They innovate by developing new payment solutions, digital currencies, or AI-driven financial analytics platforms.
- Risk Management: Entrepreneurs manage risks related to cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, and market volatility in the financial services industry.
- Resource Management: They secure funding for fintech startups, recruit data scientists and software engineers, and manage resources like computing infrastructure and financial data.
Conclusion
In each of these industrial applications, entrepreneurial functions are pivotal in driving innovation, managing risks, acquiring and allocating resources effectively, and navigating complex market dynamics. Entrepreneurs play a crucial role in advancing industries, addressing societal challenges, and shaping the future of global economies through their entrepreneurial endeavors.





