Margins- Margins can have different meanings depending on the context in which they are used. Here are a few common interpretations of the term “margins”:
- Financial Margins: In the context of finance and business, margins typically refer to the difference between the cost of producing or acquiring a product or service and the price at which it is sold. There are various types of margins, including gross margin (the difference between the cost of goods sold and the selling price), operating margin (which accounts for operating expenses), and net margin (which considers all expenses, including taxes and interest). Margins are a key indicator of a company’s profitability.
- Document Margins: In document formatting, margins are the blank spaces at the top, bottom, left, and right sides of a page. Margins are used to define the printable area of a page and provide space for binding, notes, or aesthetics. Setting margins can be important for readability and aesthetics in printed or digital documents.
- Political Margins: In a political context, margins can refer to the difference in the number of votes or percentage points between two candidates or parties in an election. A candidate who wins by a large margin secures a significant majority of the votes, while a narrow margin indicates a closely contested race.
- Geographical Margins: Geographically, margins can refer to the outer edges or boundaries of a region, country, or landmass. For example, the “margins of a forest” would refer to the outer areas or edges of the forest.
- Margins in Trading: In the context of trading and investing, margins refer to the collateral that an investor or trader must deposit with their broker to cover potential losses. It allows traders to leverage their investments, potentially amplifying both gains and losses.
- Profit Margin: In business and economics, the profit margin is the percentage difference between the selling price and the cost of producing a product or service. It’s a measure of how efficiently a company operates and generates profit.
- Margin of Error: In statistics and polling, the margin of error indicates the range within which a sample or survey result is likely to fall. It reflects the uncertainty in the measurement and is often expressed as a percentage.
- White Space Margins: In graphic design and layout, margins refer to the white space surrounding text or other elements on a page. Adequate margins are essential for readability and visual appeal.
The specific meaning of “margins” will depend on the context in which it is used. If you have a specific context in mind, please provide more details, and I can offer a more precise explanation.
What is Margins
In the most general sense, “margins” refer to the empty or blank spaces that surround the content in a document, page, or any other medium. Margins are commonly used in various contexts, including document formatting, design, and publishing. Here’s a more detailed explanation of what margins are in different contexts:
- Document Margins: In the context of documents (such as written reports, essays, or printed materials), margins are the blank spaces around the text on a page. These spaces are typically at the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the page. Margins serve several purposes:
- Aesthetics: Margins create a frame around the content, making it visually appealing and easier to read.
- Space for Notes: Margins can be used for handwritten or printed notes, comments, or annotations.
- Binding: In printed materials like books or magazines, larger inner margins (called “gutter” margins) are used to allow for binding without obscuring the content.
- Design Margins: In graphic design and layout, margins play a crucial role in creating a balanced and visually pleasing composition. Designers use margins to establish a clear separation between the content and the edges of a page or canvas. Margins help maintain a sense of order, improve readability, and enhance the overall design aesthetics.
- Printing Margins: When preparing documents for printing, printers often require specific margins to ensure that the content is properly placed on the page and that nothing important is cut off during the printing process. These printer margins may vary depending on the type of document and the printing equipment used.
- Online and Digital Content: In digital content, margins can also be applied for the sake of design and readability. For instance, web designers use CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) to define margins for web pages, creating a consistent and visually appealing online reading experience.
- Margins in Word Processing Software: In word processing software like Microsoft Word or Google Docs, you can set the margins for your documents. This allows you to control the amount of space around your text, ensuring it looks neat and professional when printed or shared electronically.
The specific size and use of margins can vary depending on the purpose of the document, design preferences, and printing requirements. Margins are essential for creating well-organized and visually pleasing content in both print and digital media.
Who is Required Margins
“Required Margins” is not a specific person or entity but rather a term used to describe the minimum or necessary margins in various contexts, particularly in document formatting and printing. Required margins are the minimum amount of empty space that must be left around the content to ensure that the document or page is formatted correctly and can be easily read or printed without cutting off text or other important elements.
For instance, in academic or professional settings, your university or company might have specific guidelines that dictate the required margins for documents such as research papers, reports, or business proposals. These guidelines might specify the width of top, bottom, left, and right margins, as well as other formatting requirements like font size, line spacing, and citation style.
In the context of printing, commercial printers may have their own requirements for required margins to ensure that documents are printed correctly. These requirements can vary depending on the type of printing equipment used and the specific project.
The specific required margins can vary widely depending on the organization or printing service, so it’s essential to consult the relevant guidelines or requirements for the specific project you are working on. In most cases, required margins are set to ensure readability, aesthetics, and compatibility with the chosen medium (print or digital).
When is Required Margins
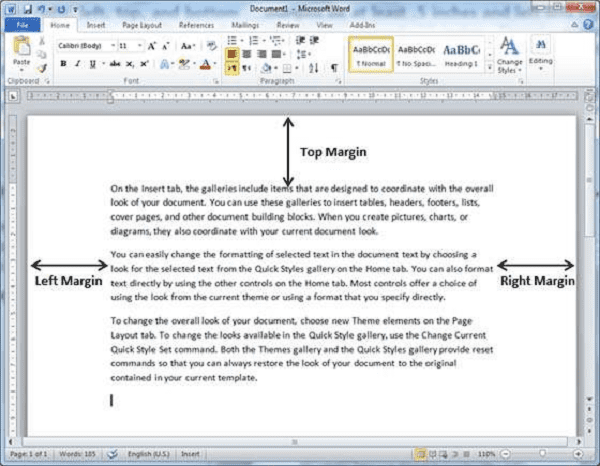
The term “Required Margins” is used in various contexts and can apply at different times, depending on the specific situation. Here are some instances where required margins may be relevant:
- Document Preparation: Required margins are typically set when you’re preparing a document, whether it’s for academic, professional, or personal use. These margins ensure that the document is correctly formatted and complies with any established guidelines or standards. For example, when writing an academic paper, you might be required to set specific margins as part of your document formatting.
- Printing: Required margins are crucial when you’re getting a document professionally printed. Commercial printers often have guidelines for margins to ensure that your content is correctly positioned on the page and that nothing important is cut off during the printing process. These requirements are typically addressed when you submit your document to a printing service.
- Digital Publishing: When creating digital content, such as web pages, e-books, or digital magazines, you may need to consider required margins for online readability and aesthetics. Web designers and digital publishers often set margins for web pages or e-books to ensure content is displayed correctly on various devices and screen sizes.
- Document Templates: In some cases, you might use pre-designed document templates for specific purposes, like resumes, business cards, or brochures. These templates often come with predefined margins, and you should follow these requirements when filling in your content.
- Specific Guidelines: Required margins can be dictated by specific guidelines or standards relevant to your industry or organization. For instance, if you work in a government agency, there may be official document standards that include margin requirements.
- Regulations: In legal and regulatory documents, required margins might be specified by law or governmental regulations to ensure that important legal text is clearly presented and easily recognizable.
The timing of when required margins come into play depends on the nature of your document or project. In most cases, you should determine and set the required margins during the document creation or formatting stage to ensure that your content is properly aligned and presented according to the necessary standards or guidelines. If you’re using a professional printing service, you may need to adhere to their margin requirements when submitting your document for printing.
Where is Required Margins
“Required margins” are not a physical location; rather, they are specific measurements or guidelines regarding the empty space that should surround the content in a document or on a page. These margin requirements are set in the document or page layout, specifying how much space should be left at the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the page.
The location of required margins is within the settings of the document or the design software you are using. Here’s how you can find and set required margins in common applications:
- Word Processing Software (e.g., Microsoft Word, Google Docs):
- Open your document in the word processing software.
- Navigate to the “Page Layout” or “Layout” tab or menu.
- Look for options related to margins. You can usually set specific margin measurements for the top, bottom, left, and right sides.
- Adjust the margin values as needed to meet the required margins for your specific project.
- Graphic Design Software (e.g., Adobe InDesign, Adobe Illustrator):
- Open your document or create a new one in the design software.
- Access the document setup or page layout settings. This may be found under “File,” “Document Setup,” or a similar menu option.
- In the setup options, you should find settings for margins. You can set the required margins for your project here.
- Web Design (HTML/CSS):
- If you’re working on web design, you can set margins using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS).
- Within your CSS code, you can define margins for different elements using properties like
margin-top,margin-bottom,margin-left, andmargin-right.
- Printing Services:
- If you’re preparing a document for professional printing, the printing service may have specific guidelines for margin requirements. These requirements are typically communicated to you when you submit your document for printing.
- You can also contact the printing service directly or visit their website for information on margin specifications.
The location of required margins is within the settings or options of the software or platform you are using to create your document. Keep in mind that the specific steps and options may vary depending on the software or platform you are using. Always follow the guidelines provided by your organization, academic institution, or printing service to ensure that your document meets the required margin specifications.
How is Required Margins
“Required margins” refer to specific measurements or guidelines regarding the amount of empty space that should be left around the content in a document or on a page. The precise measurements and how you set these required margins can vary depending on the specific guidelines or standards you need to follow. Here’s how you typically set required margins in common applications:
- Word Processing Software (e.g., Microsoft Word, Google Docs):
- Open your document in the word processing software.
- Navigate to the “Page Layout” or “Layout” tab or menu.
- Look for options related to margins. In these options, you can set specific margin measurements for the top, bottom, left, and right sides of the page.
- Enter the required margin measurements according to the guidelines you need to follow.
- Graphic Design Software (e.g., Adobe InDesign, Adobe Illustrator):
- Open your document or create a new one in the design software.
- Access the document setup or page layout settings. This may be found under “File,” “Document Setup,” or a similar menu option.
- In the setup options, you should find settings for margins. Set the required margin measurements for your project according to the provided guidelines.
- Web Design (HTML/CSS):
- If you’re working on web design, you can set margins using Cascading Style Sheets (CSS).
- Within your CSS code, define margins for different elements using properties like
margin-top,margin-bottom,margin-left, andmargin-right. Specify the required margin measurements in pixels, em, or other units as needed.
- Printing Services:
- When preparing a document for professional printing, the printing service may provide specific guidelines for margin requirements. These guidelines could include a minimum margin width.
- Ensure your document layout adheres to these margin specifications before submitting it for printing.
- Custom Templates: If you’re using a template provided by an organization, academic institution, or design service, it may already have predefined margin settings. In such cases, ensure that you don’t adjust the margins beyond what is already set in the template.
The precise measurements for required margins depend on the project’s requirements, which can vary widely based on your organization, academic institution, or specific design standards. Always follow the guidelines and margin measurements provided to you to ensure that your document or design complies with the required margin specifications.
In summary, setting required margins is typically done within the page layout or document setup options of your chosen software, and the measurements should match the specific guidelines for your project.
Case Study on Margins
Margin Planning for ABC Electronics Smartphone Brochure
Background: ABC Electronics is a well-established technology company known for its innovative smartphones. They are planning to create a product brochure for their latest smartphone model, the “ABC Stellar X5,” to promote its features and specifications.
Objective: The objective is to design a visually appealing and informative product brochure that effectively highlights the key features and benefits of the ABC Stellar X5. Proper margin planning is crucial to ensure that the content is presented neatly and that no essential information is lost during printing.
Challenges:
- The brochure design must be aesthetically pleasing and maintain a consistent branding style.
- The brochure will be professionally printed, so proper margin planning is essential to meet printing requirements.
- The document must be visually engaging and easy to read.
Solution:
1. Determine Margin Requirements:
- Consult with the chosen professional printing service to understand their margin requirements and any specific guidelines.
2. Select a Design Software:
- Choose a professional graphic design software like Adobe InDesign for brochure design.
3. Set Margins:
- Access the document setup in the design software and set the required margins. Typically, the professional printing service specifies that a minimum margin of 0.25 inches (6.35 mm) should be maintained on all sides of the brochure.
- Ensure that there’s a larger inner margin on the side where the brochure will be bound, typically 0.5 inches (12.7 mm).
4. Layout and Content:
- Design the layout with consistent branding, using the company’s colors, fonts, and style guidelines.
- Use the margins to frame the content, keeping text, images, and other elements within these boundaries.
5. Text and Images:
- Ensure that text and images are positioned away from the margins to prevent any risk of cropping during printing.
6. Proofreading and Review:
- Carefully proofread and review the entire brochure to check for any content that might be too close to the margins or any design inconsistencies.
7. Export for Printing:
- When the design is finalized, export the brochure in the required file format (e.g., PDF) for high-quality printing.
8. Printing and Quality Control:
- Submit the brochure to the chosen professional printing service, ensuring that they are aware of the margin requirements.
- Perform a final quality control check to ensure that the printed brochures meet the required margins and have maintained the intended design.
Results: The ABC Electronics brochure for the Stellar X5 smartphone is successfully designed and printed with proper margins. It is visually appealing, easy to read, and meets the company’s branding standards. The brochure effectively promotes the smartphone’s features and specifications, and the content is neatly presented without any cropping or layout issues.
Lessons Learned: Proper margin planning is critical when designing and printing promotional materials like brochures. It ensures that the content is well-organized and maintains the desired aesthetics, ultimately helping the company effectively convey its message to its target audience. Additionally, close collaboration with the printing service and attention to design details are essential for a successful project.
White paper on Margins
Understanding Their Significance and Application
Abstract: Margins, often overlooked, play a crucial role in document design, financial analysis, and various other domains. This white paper explores the concept of margins, their significance, and practical applications in different areas, shedding light on their role in creating well-organized and aesthetically pleasing content.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Document Margins
- Financial Margins
- Political Margins
- Design Margins
- Conclusion
1. Introduction
Margins are the often-underestimated blank spaces that frame content, whether on a page, in financial statements, or within the boundaries of a political landscape. Understanding margins and their importance is vital in ensuring readability, aesthetics, and effective communication.
2. Document Margins
Document margins are the empty spaces at the top, bottom, left, and right sides of a page. They serve several functions:
- Aesthetics: Margins enhance the visual appeal of documents by creating a clean frame around content.
- Readability: Adequate margins ensure text isn’t cramped and can be easily read.
- Annotations: Margins provide space for handwritten or printed notes.
3. Financial Margins
In finance, margins represent the difference between the cost and selling price of a product or service. Key types of financial margins include:
- Gross Margin: The difference between the cost of goods sold and the selling price.
- Operating Margin: Accounting for operating expenses, it reveals operational efficiency.
- Net Margin: Accounting for all expenses, including taxes and interest, it gauges overall profitability.
4. Political Margins
In politics, margins refer to the difference in votes or percentage points between candidates or parties in elections. A wide margin signifies a decisive victory, while a narrow margin indicates a closely contested race.
5. Design Margins
Design margins are essential in creating visually pleasing and balanced compositions. They provide space around content, maintaining order and improving readability in printed and digital media.
6. Conclusion
Margins are an often-underappreciated aspect of document design, finance, politics, and design. Their significance is evident in enhancing aesthetics, enabling effective communication, and facilitating profitability. Recognizing the value of margins and applying them correctly can lead to well-organized, visually appealing content.
This white paper provides an overview of the concept of margins and their importance in various domains. Please note that real white papers on margins may delve deeper into each specific context, provide detailed examples, and offer statistical analysis. The provided content is for illustrative purposes.





