Methods of marketing research-
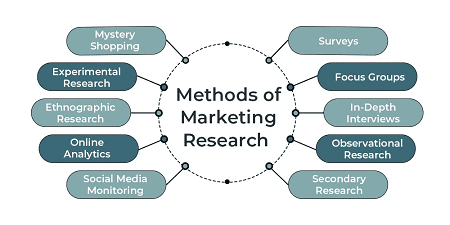
Marketing research employs various methods to gather and analyze information about markets, customers, competitors, and the effectiveness of marketing strategies. Here are some common methods used in marketing research:
- Surveys: Surveys can be conducted through various means such as online surveys, telephone interviews, face-to-face interviews, or mailed questionnaires. They help gather quantitative data and qualitative insights from a large number of respondents.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups involve small groups of individuals discussing a product, service, or concept in-depth. This method provides qualitative insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions, and preferences.
- Interviews: In-depth interviews (IDIs) are one-on-one conversations between a researcher and a respondent. These can be structured (following a set of predetermined questions) or unstructured (allowing for more open-ended responses).
- Observational Research: This involves observing consumers in their natural environment to understand their behavior and decision-making processes. It can be conducted in-store, online, or through ethnographic studies.
- Experimental Research: Controlled experiments are used to test hypotheses about consumer behavior. This could involve A/B testing of marketing campaigns, pricing strategies, or product features.
- Secondary Research: This involves using existing data sources such as industry reports, government publications, and academic journals to gather information relevant to the research objectives.
- Social Media Monitoring: Monitoring social media platforms to gather insights about consumer opinions, trends, and sentiment related to a brand or industry.
- Data Analytics: Utilizing data analytics tools to analyze large sets of data, such as sales data, website traffic, or customer demographics, to uncover patterns and trends.
- Online Communities: Creating online communities or forums where consumers can interact and provide feedback on products or services.
- Neuromarketing: Using neuroscience techniques to measure physiological and neurological responses to marketing stimuli, providing insights into consumer emotions and decision-making processes.
Each method has its strengths and weaknesses, and often a combination of several methods is used to provide a comprehensive understanding of the market and consumer behavior.
What is Required Methods of marketing research
“Required methods of marketing research” typically refers to the essential or fundamental approaches that marketers and researchers use to gather necessary information. These methods are crucial for obtaining insights into market dynamics, consumer behavior, competitive landscape, and other relevant factors influencing business decisions. Here are some key required methods of marketing research:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: These are essential for collecting quantitative data from a large number of respondents. Surveys can be conducted through various channels such as online platforms, telephone interviews, or in-person interactions.
- Focus Groups: Focus groups involve small groups of individuals discussing specific topics or products. They provide qualitative insights into consumer opinions, perceptions, and preferences.
- Interviews (In-depth and Structured): In-depth interviews (IDIs) and structured interviews are conducted to gather detailed qualitative information from individuals. These can be face-to-face, over the phone, or via video conferencing.
- Secondary Research: This involves gathering and analyzing existing data from sources such as industry reports, government publications, and academic studies. Secondary research helps in understanding the broader market context and trends.
- Observational Research: Observing consumers in real-life settings or through online platforms to understand their behavior and decision-making processes.
- Data Analytics and Big Data: Utilizing advanced analytical tools to analyze large datasets, including sales data, customer demographics, and website traffic patterns. This helps in identifying trends and correlations that inform marketing strategies.
- Competitive Analysis: Studying competitors through various methods to understand their strategies, market positioning, strengths, and weaknesses.
- Social Media Monitoring and Online Communities: Monitoring social media platforms and participating in online communities to gather insights into consumer sentiment, trends, and interactions related to products or brands.
- Experimental and A/B Testing: Conducting controlled experiments to test hypotheses and evaluate the effectiveness of marketing strategies, product features, pricing models, etc.
- Ethnographic Research: Immersing researchers in the daily lives and environments of consumers to gain deeper insights into their behaviors, values, and cultural influences.
These required methods of marketing research provide a comprehensive approach to gathering both qualitative and quantitative data essential for making informed marketing decisions. Depending on the specific research objectives and the nature of the market, different combinations of these methods may be employed to obtain a holistic understanding of consumer needs and market trends.
Who is Required Methods of marketing research
In the context of your question, “Methods of marketing research” isn’t a person but rather a collective term referring to the various techniques and approaches used to gather and analyze data in marketing research. These methods include:
- Surveys and Questionnaires: Tools for gathering structured data from a large number of respondents.
- Focus Groups: Small group discussions to gather qualitative insights into consumer opinions and behaviors.
- Interviews: In-depth conversations with individuals to explore topics in detail.
- Observational Research: Studying consumer behavior in natural settings to understand their actions and decisions.
- Secondary Research: Using existing data sources like industry reports and publications for insights.
- Data Analytics: Analyzing large datasets to uncover patterns and trends.
- Social Media Monitoring: Tracking and analyzing social media platforms for consumer insights.
- Experimental Research: Testing hypotheses through controlled experiments.
- Ethnographic Research: Immersing researchers in the lives of consumers to understand behaviors and cultures.
These methods collectively form the toolkit that marketing researchers use to understand markets, consumers, and the effectiveness of marketing strategies. Each method has its strengths and applications depending on the research objectives and context.
When is Required Methods of marketing research
It seems you’re asking about the timing or circumstances when required methods of marketing research are used. The use of these methods can vary depending on several factors:
- Research Objectives: Methods are chosen based on what the researcher aims to achieve. For instance, if the goal is to understand consumer preferences in-depth, focus groups or in-depth interviews may be used. If the objective is to gather quantitative data from a large population, surveys are more appropriate.
- Stage of Product Lifecycle: Different methods may be used at different stages of a product’s lifecycle. In the early stages, qualitative methods like focus groups can help refine product concepts. Later, quantitative surveys may gauge customer satisfaction or market penetration.
- Market Conditions: The competitive landscape, consumer behavior trends, and industry dynamics influence method selection. For example, during market entry or expansion, competitive analysis and observational research may be crucial.
- Budget and Resources: Some methods, like data analytics or large-scale surveys, may require significant resources. Smaller businesses or startups might rely more on cost-effective methods like social media monitoring or secondary research.
- Timing within Decision-Making Process: Methods are often used iteratively throughout the decision-making process. Initial exploratory research might use qualitative methods to generate insights, while later stages may focus on quantitative validation.
In summary, the timing of using required methods of marketing research depends on the specific context, research objectives, stage of product lifecycle, market conditions, available resources, and the overall decision-making timeline. Each method has its strengths and is chosen strategically to maximize insights and inform marketing strategies effectively.
Where is Required Methods of marketing research
The phrase “Required Methods of marketing research” doesn’t refer to a physical location but rather to the essential techniques and approaches used in marketing research. However, if you’re asking about where these methods are applied or conducted, here are some contexts or settings where marketing research methods are commonly used:
- In Organizations: Marketing research is conducted within businesses and organizations to gather insights about their markets, customers, and competitors. This can happen in offices, research labs, or dedicated research departments.
- Field Settings: Some methods, such as observational research or ethnographic studies, require researchers to observe consumers in real-world settings. This could be in retail stores, events, or public spaces.
- Online Platforms: Surveys, social media monitoring, and online communities are often conducted virtually through various online platforms and tools.
- Focus Group Facilities: Focus groups typically take place in specialized facilities equipped with recording equipment and observation rooms where moderators can lead discussions and researchers can observe participants.
- Telephone or Online Interviews: Interviews, whether structured or in-depth, may be conducted over the phone, via video calls, or through online platforms like Zoom or Skype.
- Data Analytics Platforms: Data analytics methods are often performed using specialized software and platforms that analyze large datasets to uncover trends and patterns.
- Marketplaces and Trade Shows: Researchers may gather data by participating in or observing interactions at trade shows, industry conferences, or other market events.
- Global and Local Markets: Depending on the scope of the research, methods may be applied locally, nationally, or internationally to understand regional variations and global market trends.
In essence, the application of marketing research methods can occur in various physical and virtual settings, depending on the specific research objectives, target audience, and the nature of the data being collected.
How is Required Methods of marketing research
The phrase “Required Methods of marketing research” implies the essential techniques and approaches used in conducting marketing research. Here’s how these methods are typically implemented:
- Planning and Objective Setting: The research process begins with clearly defining the objectives and goals of the study. This helps in determining which methods will be most effective in achieving those objectives.
- Method Selection: Based on the research objectives, researchers choose appropriate methods such as surveys, focus groups, interviews, observational research, secondary research, data analytics, etc. The selection is guided by whether qualitative or quantitative data is needed, the target audience, and the budget and time constraints.
- Designing Research Instruments: For methods like surveys and questionnaires, researchers design the questions and structure to ensure they gather relevant data that aligns with the research objectives. This includes considerations for question types, scales, and potential biases.
- Data Collection: Methods like surveys, interviews, and observational research involve collecting data from respondents or through direct observation. This stage requires careful execution to ensure data quality and representativeness.
- Data Analysis: Once data is collected, it is analyzed using appropriate techniques. Quantitative data may be analyzed using statistical methods to identify patterns and relationships, while qualitative data may involve thematic analysis or coding.
- Interpretation and Insight Generation: After analysis, researchers interpret the findings in the context of the research objectives. Insights are generated that provide actionable information to inform marketing strategies or decision-making.
- Reporting and Presentation: Finally, the research findings are compiled into a report or presentation. This includes summarizing the methods used, presenting key findings, and providing recommendations based on the insights gained.
- Iterative Process: Marketing research often involves an iterative process where findings may lead to further questions or refinements in methods. This continuous improvement helps in refining marketing strategies over time.
Overall, the execution of required methods of marketing research involves careful planning, methodical implementation, rigorous analysis, and clear communication of findings. Each step is crucial in ensuring that the research objectives are met effectively and that the insights gained contribute to strategic decision-making in marketing.
Case Study on Methods of marketing research
Understanding Customer Preferences for a New Energy Drink
Background: A beverage company is planning to launch a new energy drink targeted at health-conscious consumers. The company aims to gather insights into customer preferences, perceptions, and purchase behavior to inform product development and marketing strategies.
Research Objectives:
- Understand consumer preferences and attitudes towards energy drinks.
- Identify key factors influencing purchase decisions.
- Evaluate potential demand and market positioning for the new product.
Methods Used:
- Surveys:
- Method: Online surveys were conducted among a representative sample of health-conscious individuals aged 18-45.
- Objective: To gather quantitative data on awareness, usage patterns, flavor preferences, and purchase intent related to energy drinks.
- Implementation: Surveys included questions on demographics, current beverage preferences, reasons for consuming energy drinks, preferred packaging, and price sensitivity.
- Focus Groups:
- Method: Conducted several focus group sessions with participants recruited from fitness centers and health food stores.
- Objective: To explore in-depth insights and perceptions about energy drinks, including taste preferences, ingredient preferences (e.g., natural vs. artificial), and perceptions about health benefits.
- Implementation: Moderators led discussions on topics such as taste testing of potential flavors, reactions to product concepts, and reactions to mock-up packaging designs.
- In-depth Interviews:
- Method: Conducted one-on-one interviews with nutritionists, fitness trainers, and health bloggers.
- Objective: To gain expert opinions on consumer trends, health-conscious behaviors, and factors influencing product adoption.
- Implementation: Interviews focused on topics such as consumer education needs, perceptions of energy drinks in relation to overall health, and recommendations for product positioning.
- Observational Research:
- Method: Researchers visited health food stores and fitness centers to observe consumer behavior and purchasing patterns related to energy drinks.
- Objective: To understand real-world decision-making processes, interactions with product displays, and product choices.
- Implementation: Researchers noted which brands were popular, observed interactions between consumers and promotional materials, and recorded any conversations related to energy drinks.
Data Analysis and Insights:
- Quantitative Analysis: Survey data was analyzed using statistical methods to identify correlations between demographics and preferences, determine market segment sizes, and gauge overall market potential.
- Qualitative Analysis: Insights from focus groups, interviews, and observational research were analyzed thematically to identify recurring themes, consumer concerns, and preferences that informed product development decisions.
Findings and Recommendations:
- Consumers expressed a preference for natural ingredients and sugar-free options.
- Convenience and portability were crucial factors influencing purchase decisions.
- There was a demand for flavors that offered both taste and functional benefits, such as improved focus or hydration.
Conclusion: Based on the comprehensive research findings, the beverage company decided to launch a natural, sugar-free energy drink with targeted marketing campaigns emphasizing health benefits, convenience, and appealing flavors. The insights gathered from the various methods of marketing research provided a solid foundation for strategic decision-making, ensuring the new product would resonate with its intended market segment.
This case study demonstrates how a combination of surveying, focus groups, interviews, and observational research can be effectively utilized to gather comprehensive insights and inform product development and marketing strategies in the beverage industry.
White paper on Methods of marketing research
Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of business and consumer behavior, effective marketing research is essential for organizations to understand market trends, consumer preferences, and competitive dynamics. This white paper explores the various methods used in marketing research, highlighting their applications, advantages, and considerations for implementation.
Methods of Marketing Research
1. Surveys and Questionnaires
- Description: Surveys and questionnaires are structured tools used to collect quantitative data from a large sample of respondents.
- Application: Ideal for gathering insights on customer preferences, satisfaction levels, brand awareness, and demographic information.
- Advantages: Scalable, cost-effective, and efficient in reaching a broad audience. Provides statistical validity through quantitative analysis.
- Considerations: Designing unbiased questions, ensuring adequate sample size, and managing response rates are critical factors for success.
2. Focus Groups
- Description: Focus groups involve facilitated discussions with a small group of individuals to explore attitudes, perceptions, and opinions.
- Application: Valuable for exploring complex topics, generating qualitative insights, and testing new product concepts or marketing messages.
- Advantages: Depth of qualitative data, real-time interaction, and the ability to probe participant responses.
- Considerations: Group dynamics can influence outcomes, necessitating skilled moderation and careful selection of participants to ensure diversity.
3. Interviews
- Description: In-depth interviews (IDIs) involve one-on-one conversations between a researcher and a participant to delve deeply into specific topics.
- Application: Useful for exploring nuanced perspectives, gathering detailed qualitative data, and understanding individual motivations.
- Advantages: Allows for personalized insights, flexibility in questioning, and building rapport with participants.
- Considerations: Time-consuming and resource-intensive. Interviewer bias and respondent bias should be minimized through structured protocols.
4. Observational Research
- Description: Observational research involves direct observation of individuals, behaviors, and environments in natural settings.
- Application: Provides insights into actual behavior, product usage, and decision-making processes without relying on self-reported data.
- Advantages: Captures real-time behaviors, identifies discrepancies between stated and actual behavior, and informs contextual insights.
- Considerations: Ethical considerations, observer bias, and logistical challenges in maintaining objectivity and privacy.
5. Secondary Research
- Description: Secondary research involves gathering and synthesizing existing data from sources such as industry reports, academic literature, and databases.
- Application: Provides a foundational understanding of market trends, competitor strategies, and consumer demographics.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, time-efficient, and provides historical context and industry benchmarks.
- Considerations: Quality and relevance of data sources, potential biases in data interpretation, and the need for updated information.
6. Data Analytics
- Description: Data analytics involves the use of statistical techniques and algorithms to analyze large datasets for patterns, correlations, and insights.
- Application: Utilized for predictive modeling, customer segmentation, sentiment analysis, and optimization of marketing campaigns.
- Advantages: Enables data-driven decision-making, identifies actionable insights, and supports personalized marketing strategies.
- Considerations: Requires expertise in data handling and analysis tools, ensuring data accuracy, and addressing privacy concerns.
Conclusion
Effective marketing research employs a blend of these methods to uncover actionable insights that drive strategic decisions. By understanding the strengths, applications, and considerations of each method, organizations can navigate complexities in consumer behavior, market dynamics, and competitive landscapes with greater precision and confidence.
For further guidance on implementing these methods in your organization’s marketing research strategy, consult with our team of experts who specialize in leveraging data-driven insights for business success.
This white paper provides a comprehensive overview of the methods of marketing research, emphasizing their practical applications and considerations. It serves as a foundational resource for businesses seeking to enhance their understanding of customers and markets through systematic research approaches.
Industrial Application of Methods of marketing research
Industrial applications of marketing research methods are crucial for businesses operating in industrial markets, where products and services are typically sold to other businesses rather than directly to consumers. Here are some key methods of marketing research and how they can be applied in industrial settings:
- Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Application: Surveys can be used to gather feedback from industrial buyers regarding their satisfaction with products, preferences for features, pricing sensitivity, and supplier perceptions.
- Example: A manufacturing company may conduct surveys among its B2B customers to understand their needs for customized product features or their satisfaction with delivery times.
- Focus Groups:
- Application: Focus groups can bring together key decision-makers from industrial companies to discuss industry trends, product requirements, and pain points.
- Example: A supplier of industrial machinery may host focus groups with engineers and procurement managers to gather insights into the usability and performance expectations of their equipment.
- In-depth Interviews:
- Application: In-depth interviews with industrial customers allow for deeper exploration of specific issues such as service quality, technical support needs, and long-term partnership expectations.
- Example: A software development company may conduct interviews with IT managers in industrial firms to understand their challenges in implementing new technology solutions.
- Observational Research:
- Application: Observing industrial buyers in their operational environment can provide insights into workflow processes, product usage patterns, and decision-making dynamics.
- Example: A supplier of industrial chemicals might observe how their products are integrated into manufacturing processes to identify opportunities for efficiency improvements.
- Secondary Research:
- Application: Secondary research in industrial markets involves analyzing industry reports, trade publications, and economic data to understand market trends, competitive landscapes, and regulatory changes.
- Example: An industrial equipment manufacturer may use secondary research to track competitor product launches, market share trends, and industry forecasts to inform strategic planning.
- Data Analytics:
- Application: Advanced analytics techniques can analyze large datasets in industrial markets to identify patterns in customer behavior, forecast demand, and optimize pricing strategies.
- Example: A logistics company might use predictive analytics to forecast shipping volumes based on historical data and seasonal trends to optimize fleet operations.
- Competitive Analysis:
- Application: Studying competitors in industrial markets helps businesses understand their strengths, weaknesses, and market positioning to identify gaps and opportunities.
- Example: An industrial components manufacturer may analyze competitor pricing strategies, distribution channels, and product innovations to differentiate its offerings effectively.
- Market Segmentation and Targeting:
- Application: Segmenting industrial markets based on factors such as company size, industry vertical, geographic location, and buying behavior helps tailor marketing strategies and sales approaches.
- Example: A provider of industrial automation solutions may segment its market to target specific industries with customized solutions that meet unique operational needs.
In summary, industrial applications of marketing research methods enable businesses to gain actionable insights into customer needs, market dynamics, and competitive landscapes. By leveraging these methods effectively, industrial firms can make informed decisions that enhance customer satisfaction, drive growth, and maintain competitive advantage in their respective markets.






