Pulses & Cereals- Pulses and cereals are two important categories of food items that form the basis of many people’s diets worldwide. They are significant sources of nutrition and are commonly consumed for their high content of carbohydrates, protein, and various essential nutrients. Here’s an overview of both pulses and cereals:
Cereals:
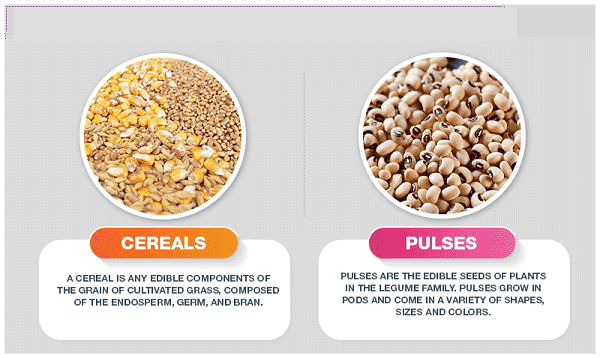
Cereals are a broad category of grass crops that are cultivated for their edible grains or seeds. These grains are often ground into flour to make various food products, such as bread, pasta, and breakfast cereals. Some common cereal crops include:
- Wheat: Wheat is one of the most widely cultivated cereal grains and is used to make products like bread, pasta, and pastries.
- Rice: Rice is a staple food for many people, particularly in Asian countries. It comes in various varieties, including long-grain, short-grain, and basmati rice.
- Maize (Corn): Corn is a versatile cereal used for a wide range of products, including cornmeal, corn syrup, and as animal feed.
- Barley: Barley is often used for making beer and is also used in soups and stews.
- Oats: Oats are used for making oatmeal, granola, and are a source of soluble fiber.
- Rye: Rye is commonly used in bread-making, especially in Northern and Eastern Europe.
- Millet: Millet is a group of small-seeded grasses used in various dishes and as a staple in some regions.
Pulses:
Pulses are the edible seeds of legume plants, which are harvested for their seeds that are high in protein and fiber. They are an essential source of plant-based protein and have numerous health benefits. Some common pulse varieties include:
- Lentils: Lentils are small, lens-shaped pulses that come in various colors, such as brown, green, and red. They are used in soups, stews, and salads.
- Chickpeas: Chickpeas are popular in many cuisines and are used to make dishes like hummus, falafel, and curries.
- Black-eyed Peas: These are small, creamy-white beans with a distinct black spot on their hilum. They are commonly used in Southern U.S. cuisine and other regional dishes.
- Kidney Beans: Kidney beans are large, red or dark red beans often used in chili and other dishes.
- Split Peas: Split peas can be green or yellow and are commonly used in split pea soup.
- Pigeon Peas: Pigeon peas are a staple in some tropical and subtropical regions and are used in various dishes.
- Soybeans: Soybeans are highly versatile and are used to make tofu, soy milk, and various other soy-based products.
Both pulses and cereals are important components of a balanced diet and provide essential nutrients such as carbohydrates, protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They are often consumed as a primary source of energy and are integral to various culinary traditions around the world.
What is Pulses & Cereals
Pulses and cereals are two distinct categories of food items:
Pulses: Pulses are a subgroup of legumes and are primarily the dried seeds of certain plants in the legume family. They are rich in protein and fiber and are a good source of various essential nutrients. Common examples of pulses include lentils, chickpeas, black-eyed peas, kidney beans, and split peas. Pulses are often used in cooking to prepare dishes like soups, stews, curries, and salads. They are an essential part of many diets, particularly for those seeking plant-based sources of protein.
Cereals: Cereals, on the other hand, refer to the edible grains or seeds of grass crops. These grains are typically ground into flour to make various food products, such as bread, pasta, and cereals. Common cereal crops include wheat, rice, maize (corn), barley, oats, and rye. Cereals are a significant source of carbohydrates and provide a staple food source for many cultures around the world. They are used to make a wide variety of foods, from bread and noodles to breakfast cereals and alcoholic beverages like beer.
In summary, pulses are leguminous crops known for their protein and fiber content, while cereals are grains from grass crops that serve as a primary source of carbohydrates in the human diet. Both pulses and cereals are important components of the global food supply and are used in a wide range of culinary traditions.
Who is Required Pulses & Cereals
Pulses and cereals are required and consumed by people all around the world. They are fundamental components of diets in many countries and cultures. Here’s why they are required:
1. Nutritional Value: Pulses and cereals are rich in essential nutrients. Pulses are an excellent source of plant-based protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals, while cereals are a primary source of carbohydrates and various essential nutrients. Consuming a combination of pulses and cereals can help meet a wide range of nutritional needs.
2. Sustenance: Pulses and cereals are often staples in the diets of many communities, providing a significant portion of daily calories. They offer a source of sustained energy and help keep people full and satisfied.
3. Dietary Diversity: The consumption of a variety of foods, including pulses and cereals, is recommended for a well-rounded diet. These foods contribute to dietary diversity, ensuring a broader range of nutrients and flavors in one’s meals.
4. Vegetarian and Vegan Diets: For individuals who follow vegetarian or vegan diets, pulses, such as lentils and chickpeas, are essential sources of protein. Cereals like rice, wheat, and oats provide carbohydrates and are key components of plant-based diets.
5. Global Food Supply: Pulses and cereals are grown in many parts of the world and play a crucial role in the global food supply. They are affordable and accessible sources of nutrition for people in both developed and developing countries.
6. Traditional and Cultural Significance: Many traditional dishes and cultural cuisines are based on the use of pulses and cereals. They are integral to the food heritage of various regions and societies.
In summary, pulses and cereals are required by people of all backgrounds and cultures as they provide essential nutrients, serve as dietary staples, and contribute to the diversity and sustainability of diets. They are fundamental to meeting global food needs and have cultural significance in many societies.
When is Required Pulses & Cereals
Pulses and cereals are required as part of daily diets and meals for people throughout the year. They are not limited to specific seasons and can be consumed year-round. Here are some general occasions and times when pulses and cereals are commonly consumed:
- Daily Meals: Pulses and cereals are typically a part of daily meals. For example, grains like rice, wheat, and corn are commonly consumed as staples in many cultures. Pulses like lentils, beans, and chickpeas are also used regularly in various dishes.
- Breakfast: Cereals, such as oats, cornflakes, and muesli, are often consumed as breakfast options. They can be served with milk or yogurt and topped with fruits and nuts.
- Lunch and Dinner: Pulses and cereals form the basis of many lunch and dinner dishes. They are used to make a wide range of items, including rice dishes, pasta, bread, and legume-based stews or curries.
- Special Occasions: Pulses and cereals are used in traditional dishes for special occasions and festivals. For example, rice is a central component of many celebrations in Asian cultures, and dishes like biryani are prepared for festive gatherings.
- Emergency Food Supplies: In times of emergencies or food shortages, grains and pulses are valuable staples as they can be stored for extended periods and provide essential sustenance.
- Vegetarian and Vegan Diets: People following vegetarian or vegan diets rely on pulses and cereals as primary sources of protein and nutrients in their everyday diets.
- Cultural and Regional Variations: The consumption of pulses and cereals varies by region and culture. Different grains and legumes are prominent in different parts of the world, depending on local agricultural practices and culinary traditions.
In summary, pulses and cereals are not limited to specific times or seasons; they are consumed regularly and are a fundamental part of people’s diets worldwide. Their versatility and nutritional value make them essential for daily nutrition and culinary traditions.
Where is Required Pulses & Cereals
Pulses and cereals are required and consumed in various regions and countries around the world. They are staples of diets in both developed and developing nations. Here’s where pulses and cereals are commonly required:
- Asia: Many Asian countries heavily rely on pulses and cereals as essential components of their diets. Rice, wheat, and various pulses are daily staples in countries like India, China, Japan, and Indonesia.
- Middle East: Pulses like chickpeas and lentils, along with cereals such as wheat and barley, are commonly used in Middle Eastern cuisines. They are found in dishes like hummus, falafel, and various types of bread.
- Africa: Across the African continent, a wide range of pulses and cereals are consumed. For instance, in North Africa, couscous made from wheat is popular, while in Sub-Saharan Africa, millet, sorghum, and maize are common cereals, and legumes like cowpeas and groundnuts are widely used.
- North and South America: Corn (maize), wheat, and rice are major cereal grains in the Americas. Pulses such as black beans and pinto beans are widely used in Latin American cuisines. In the United States, cereals like corn, wheat, and rice are foundational to the diet.
- Europe: Wheat, rye, and barley are important cereals in many European countries. Pulses like lentils and chickpeas are used in Mediterranean dishes, while countries like France and Italy are known for their use of wheat in bread and pasta.
- Oceania: In Australia and New Zealand, wheat is a primary cereal used in bread and other products. Additionally, pulses like chickpeas and lentils are used in various dishes and recipes.
- Global Trade: Pulses and cereals are traded internationally, and they are widely available in most parts of the world, making them accessible to people in regions where they are not traditionally grown.
- Food Aid and Humanitarian Efforts: Pulses and cereals are often distributed as part of food aid and humanitarian assistance programs to regions affected by food shortages or emergencies.
In summary, pulses and cereals are required and consumed across the globe, and their specific use and varieties can vary widely depending on regional and cultural preferences. They are foundational to diets in many parts of the world and serve as important sources of nutrition and sustenance.
How is Required Pulses & Cereals
The consumption of required pulses and cereals varies widely based on individual dietary choices, cultural traditions, and regional preferences. These food items can be prepared and consumed in various ways to provide essential nutrition and sustenance. Here’s how pulses and cereals are commonly used:
1. Pulses:
- Boiling: Pulses like lentils and chickpeas are often boiled until they become soft and can be used in soups, stews, and salads.
- Roasting: Some pulses, such as roasted chickpeas, are enjoyed as crunchy snacks.
- Grinding: Pulses like chickpeas can be ground into flour and used to make dishes like hummus or falafel.
- Sprouting: Certain pulses can be sprouted, enhancing their nutritional value and making them suitable for salads or as garnishes.
- Fermentation: In some cultures, pulses like soybeans are fermented to create products like soy sauce, miso, and tempeh.
2. Cereals:
- Cooking: Cereals like rice, pasta, and oats are typically cooked by boiling or steaming until they are soft and ready to be served as the main component of a meal.
- Baking: Cereals, particularly wheat, are used to make a wide range of baked goods, such as bread, pastries, cakes, and cookies.
- Milling: Cereals are often milled to produce flour, which is a key ingredient in making various food items, including bread, pasta, and pastries.
- Fermentation: Some cereals are used in the fermentation process to create alcoholic beverages like beer and whiskey.
- Breakfast Cereals: Cereals like cornflakes, oats, and bran are commonly used as the base for breakfast cereals, which are often served with milk or yogurt.
- Snacking: Cereals are used to make snacks like popcorn and rice cakes, which can be flavored and consumed as a quick, convenient food.
Both pulses and cereals are versatile and can be incorporated into a wide range of dishes and culinary traditions. Their methods of preparation and consumption can vary greatly depending on the culture and preferences of the people consuming them. They serve as essential sources of carbohydrates, protein, and other vital nutrients in the human diet.
Case Study on Pulses & Cereals
A case study on pulses and cereals could focus on various aspects, from their role in global food security to their impact on health and nutrition. Here, I’ll outline a hypothetical case study on the use of pulses and cereals in addressing food security in a specific region.
Title: “Promoting Food Security through Pulses and Cereals: A Case Study of the XYZ Region”
Introduction: Food security is a pressing issue in the XYZ region, where a significant portion of the population faces challenges in accessing nutritious and affordable food. This case study aims to explore the potential of pulses and cereals in addressing food security issues in this region, considering their nutritional value, affordability, and local agricultural practices.
Methodology:
- Data Collection: Data is collected on the current state of food security, local dietary patterns, and agricultural practices in the XYZ region.
- Survey and Interviews: Surveys and interviews are conducted with local communities, farmers, and key stakeholders to understand their perspectives and challenges.
- Nutritional Analysis: The nutritional content of locally grown pulses and cereals is analyzed to assess their potential for improving diets in the region.
- Market Analysis: A market analysis is conducted to understand the availability, accessibility, and affordability of pulses and cereals in the local markets.
Findings:
- Local Consumption Patterns: Pulses and cereals, particularly rice, wheat, and chickpeas, are already staples in the local diet. However, dietary diversity is limited, and there is room for improvement in terms of nutritional intake.
- Local Agriculture: The XYZ region has a favorable climate for growing various pulses and cereals. However, traditional farming practices may need to be modernized to increase production and efficiency.
- Nutritional Value: Pulses, in particular, are found to be rich in protein and fiber, addressing the protein deficiency prevalent in the region. Cereals provide essential carbohydrates.
- Market Accessibility: While pulses and cereals are readily available in the local markets, affordability is a concern for some vulnerable populations.
Recommendations:
- Promote Local Agriculture: Encourage and support local farmers to diversify their crops by promoting the cultivation of pulses and cereals alongside traditional crops.
- Nutrition Education: Launch awareness campaigns and nutrition education programs to inform the local population about the nutritional benefits of pulses and cereals and how to incorporate them into their daily meals.
- Subsidies and Incentives: Government initiatives could provide subsidies or incentives to both farmers and consumers to make pulses and cereals more affordable.
- Community Programs: Establish community-based initiatives to create awareness and support the production and distribution of pulses and cereals, particularly among marginalized communities.
Conclusion: Pulses and cereals have the potential to address food security issues in the XYZ region by providing affordable, nutritious food options that align with local dietary habits and agricultural practices. Promoting these crops can contribute to improved food security, better nutrition, and a more sustainable local food system.
This case study serves as a model for how pulses and cereals can be leveraged to enhance food security in a specific region, while similar studies can be adapted to address food security challenges in different parts of the world.
White paper on Pulses & Cereals
Writing a white paper on pulses and cereals involves providing a comprehensive overview of these essential food items, covering various aspects, from their nutritional value to their significance in global agriculture and nutrition. Below is an outline for a white paper on pulses and cereals:
Title: White Paper on Pulses and Cereals: Nutrition, Agriculture, and Sustainability
Abstract:
- A concise summary of the paper’s key points and findings.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Briefly introduce the importance of pulses and cereals in the context of global food security and nutrition.
- Pulses and Cereals: An Overview
- Define what pulses and cereals are and provide examples of common varieties.
- Explain their significance as staple foods in various regions.
- Nutritional Value
- Detail the nutritional composition of pulses and cereals, emphasizing their protein, fiber, and micronutrient content.
- Discuss their role in balanced diets, including their value in vegetarian and vegan nutrition.
- Health Benefits
- Explore the health benefits associated with the consumption of pulses and cereals, including their impact on heart health, weight management, and digestive health.
- Global Agriculture and Production
- Provide insights into the worldwide production of pulses and cereals, highlighting major producing countries and regions.
- Discuss the environmental impact of their cultivation, including water usage and sustainability considerations.
- Culinary Uses
- Describe common culinary preparations of pulses and cereals around the world.
- Include recipes and examples of dishes from various cultures.
- Challenges and Constraints
- Address challenges in the production, distribution, and consumption of pulses and cereals, such as post-harvest losses and market access issues.
- Food Security
- Discuss the role of pulses and cereals in addressing food security issues, particularly in regions where access to nutritious food is limited.
- Sustainability and Agroecology
- Explore sustainable agricultural practices related to pulses and cereals, including crop rotation and agroecological approaches.
- Consider the potential for pulses and cereals to contribute to sustainable food systems.
- Policy Recommendations
- Propose policy recommendations for governments and international organizations to promote the cultivation and consumption of pulses and cereals.
- Conclusion
- Summarize the key takeaways from the white paper.
- Emphasize the importance of pulses and cereals in achieving global food security, nutrition, and sustainability goals.
- References
- Cite sources, studies, and references used in the paper.
Appendices:
- Include additional resources, charts, tables, or data to support the white paper.
Acknowledgments:
- Acknowledge contributions from individuals or organizations that provided insights and data for the white paper.
This white paper aims to serve as a comprehensive resource for policymakers, agricultural stakeholders, nutritionists, and anyone interested in the role of pulses and cereals in global food systems and nutrition.
Industrial Application of Pulses & Cereals
Pulses and cereals have a wide range of industrial applications beyond their use as food. Their versatility and properties make them valuable in various industries. Here are some notable industrial applications of pulses and cereals:
1. Food Processing:
- Pulses and cereals are used in the production of numerous processed food products, including pasta, bread, cereal bars, and snacks.
- Cereals are the primary source for flour production, which is used in baked goods, pastries, and other food items.
2. Brewing and Distilling:
- Cereals, particularly barley and corn, are essential ingredients in brewing beer and producing whiskey and other distilled spirits.
3. Animal Feed:
- Cereals such as maize, barley, and wheat are commonly used in the formulation of animal feed for livestock, poultry, and aquaculture.
4. Starch and Sweeteners:
- Corn and wheat are used in the production of starch, which has applications in the food industry for thickening and stabilizing products.
- High-fructose corn syrup is derived from corn and is widely used as a sweetener in the food and beverage industry.
5. Paper and Textile Industry:
- Starch from cereals is used in the paper industry to improve paper strength and smoothness.
- Cereals like cotton are used in the textile industry for the production of fabric and clothing.
6. Ethanol Production:
- Cereals, especially corn and wheat, are used to produce ethanol, which serves as a biofuel for vehicles and industrial purposes.
7. Biodegradable Plastics:
- Starch from cereals is used in the production of biodegradable plastics, reducing environmental impact.
8. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Pulses and cereals are sources of starch used in pharmaceuticals to create tablets and capsules.
9. Cosmetics and Personal Care Products:
- Cereals are used in the formulation of cosmetics and personal care products like lotions, creams, and scrubs.
10. Textile Sizing:
- Starch from cereals is used in textile sizing to provide stiffness and smoothness to fabrics.
11. Biomaterials:
- Cereals and pulses can be used in the production of biodegradable and sustainable materials, including packaging and construction materials.
12. Industrial Enzymes:
- Pulses and cereals can be sources of enzymes used in various industrial processes, such as in the textile and paper industries.
13. Adhesives:
- Starch from cereals can be used in adhesive formulations for paper, packaging, and woodworking applications.
The industrial applications of pulses and cereals are diverse and continue to evolve as new technologies and sustainable practices are developed. Their versatility and availability make them valuable resources in many different sectors, contributing to various products and processes beyond their role as essential food sources.






