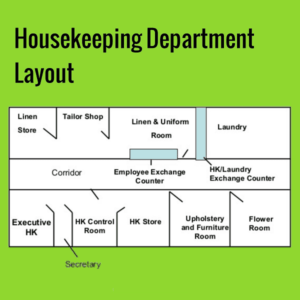
Sentence corrections- There are several types of sentence corrections that can be made to improve the clarity, grammar, and overall quality of a sentence. Here are some common types of sentence corrections:
- Grammar Corrections: These involve fixing errors in sentence structure, verb tense, subject-verb agreement, and other grammatical issues. For example:
- Incorrect: She is goes to the store yesterday.
- Corrected: She went to the store yesterday.
- Punctuation Corrections: These involve adding, removing, or adjusting punctuation marks like commas, periods, semicolons, and apostrophes to ensure proper punctuation. For example:
- Incorrect: Its a beautiful day the sun is shining.
- Corrected: It’s a beautiful day; the sun is shining.
- Spelling Corrections: These involve fixing misspelled words within the sentence. For example:
- Incorrect: He recieved a letter from his freind.
- Corrected: He received a letter from his friend.
- Word Usage Corrections: Sometimes, words may be used incorrectly, and corrections are needed to convey the intended meaning. For example:
- Incorrect: She was complementing his outfit.
- Corrected: She was complimenting his outfit.
- Sentence Structure Corrections: These involve reorganizing or restructuring sentences to improve clarity and readability. For example:
- Incorrect: Tired and hungry after work, my dinner was ready.
- Corrected: Tired and hungry after work, I found my dinner ready.
- Conciseness Corrections: Eliminating unnecessary words or phrases to make the sentence more concise and to the point. For example:
- Incorrect: In my opinion, I think the movie is too long.
- Corrected: I think the movie is too long.
- Subject-Verb Agreement Corrections: Ensuring that the subject and verb agree in number (singular or plural). For example:
- Incorrect: The team are playing well.
- Corrected: The team is playing well.
- Parallel Structure Corrections: Making sure that items in a list or series are grammatically consistent. For example:
- Incorrect: She likes swimming, hiking, and to ride a bike.
- Corrected: She likes swimming, hiking, and riding a bike.
- Modifiers Corrections: Ensuring that modifiers (words or phrases that describe other elements) are properly placed. For example:
- Incorrect: She almost ate all the cake.
- Corrected: She ate almost all the cake.
- Tone and Clarity Improvements: Sometimes, sentences may need adjustments to convey the desired tone or to make the meaning clearer.
These are some of the common types of sentence corrections, but there can be others depending on the specific issues within a sentence. If you have a particular sentence you’d like me to correct or if you’re looking for corrections related to a specific type of issue, please provide the sentence or details, and I’ll be happy to assist you further.
What is Sentence corrections
Sentence corrections refer to the process of identifying and rectifying errors or improving the structure, grammar, punctuation, spelling, and overall clarity of a sentence in written or spoken communication. The goal of sentence corrections is to ensure that a sentence effectively conveys the intended message and adheres to the rules and conventions of the language in which it is written or spoken.
Common types of errors or issues that sentence corrections address include:
- Grammar: Correcting errors related to sentence structure, verb tense, subject-verb agreement, and other grammatical rules.
- Punctuation: Ensuring proper placement and use of punctuation marks such as commas, periods, semicolons, and quotation marks.
- Spelling: Identifying and fixing misspelled words.
- Word Usage: Replacing or rephrasing words to convey the intended meaning more accurately.
- Sentence Structure: Reorganizing or restructuring sentences for clarity and coherence.
- Conciseness: Removing unnecessary words or phrases to make sentences more concise and easier to understand.
- Subject-Verb Agreement: Ensuring that the subject and verb in a sentence agree in terms of number (singular or plural).
- Parallel Structure: Making sure that elements in a list or series are grammatically consistent.
- Modifiers: Proper placement and use of words or phrases that describe other elements in the sentence.
- Tone and Clarity: Making adjustments to sentences to convey the desired tone and ensure clarity of communication.
Sentence corrections are essential in various forms of writing, including essays, reports, emails, academic papers, and more. They help enhance the quality of written communication, making it more effective and professional. Whether for academic, professional, or personal purposes, reviewing and making necessary corrections to sentences is a fundamental aspect of good writing and effective communication.
Who is Required Sentence corrections
The need for sentence corrections can arise for various individuals and in different contexts. Here are some situations and individuals who may require sentence corrections:
- Students: Students often need sentence corrections in their academic assignments, essays, research papers, and exams to ensure that their writing meets the required standards of grammar and clarity. Teachers and professors may provide feedback and corrections to help students improve their writing skills.
- Writers and Authors: Professional writers and authors often go through multiple rounds of editing and proofreading to correct and improve their sentences in books, novels, articles, and other written works. They may work with editors or use grammar-checking software.
- Job Applicants: When applying for jobs, individuals may need to submit resumes, cover letters, and job applications that are free from errors and present them in the best possible light. Sentence corrections are crucial to make a positive impression on potential employers.
- Business Professionals: Business professionals frequently communicate through written documents, including emails, reports, proposals, and presentations. Correcting sentences is vital in maintaining professionalism and effective communication in the workplace.
- Academic Researchers: Researchers and scholars need to write academic papers, dissertations, and scholarly articles that adhere to strict language and citation standards. Sentence corrections ensure the accuracy and credibility of their work.
- Translators: Translators may require sentence corrections when converting text from one language to another to ensure that the translated sentences are grammatically correct and convey the intended meaning accurately.
- Non-Native English Speakers: People who are learning English as a second language often seek sentence corrections to improve their language skills, especially when communicating in academic or professional settings.
- Content Creators: Bloggers, social media influencers, and content creators on platforms like YouTube may need sentence corrections to enhance the quality and clarity of their written or spoken content.
- Legal Professionals: Lawyers and legal professionals need to draft contracts, legal briefs, and other legal documents with precision, as sentence errors can have significant legal implications.
- Public Speakers: Public speakers and presenters may need to ensure that their spoken sentences are clear, grammatically correct, and effectively convey their message to the audience.
In summary, sentence corrections are essential for individuals in various fields and situations where effective communication is crucial. Correcting sentences helps maintain professionalism, convey ideas accurately, and ensure that written or spoken content is of high quality.
When is Required Sentence corrections

Sentence corrections are required in various situations and contexts whenever written or spoken communication needs to meet specific standards of accuracy, clarity, and professionalism. Here are some common scenarios and instances when sentence corrections are necessary:
- Academic Writing: In academic settings, students and researchers need to ensure that their essays, research papers, theses, and dissertations are free from grammatical errors and convey their ideas clearly and accurately.
- Job Applications: When applying for jobs, candidates should review and correct their resumes, cover letters, and job applications to make a positive impression on potential employers.
- Professional Communication: In the workplace, business professionals need to write emails, reports, proposals, and other documents that are error-free and maintain a high level of professionalism.
- Legal Documents: Legal professionals, such as lawyers, draft contracts, legal briefs, and other legal documents that must be precise and free from errors to avoid legal complications.
- Creative Writing: Authors and writers often require sentence corrections when writing novels, short stories, poetry, or other creative works to ensure the readability and impact of their writing.
- Content Creation: Bloggers, social media influencers, and content creators on various platforms may need to correct sentences in their written or spoken content to maintain credibility and engagement with their audience.
- Translation: Translators must correct sentences when translating text from one language to another to accurately convey the original meaning.
- Public Speaking: Public speakers and presenters may need to correct their spoken sentences to ensure clarity and effectiveness when delivering speeches, presentations, or lectures.
- Proofreading and Editing: Editors and proofreaders are responsible for reviewing and correcting sentences in written materials, including books, articles, and marketing materials.
- Language Learning: Individuals learning a new language often require sentence corrections to improve their language skills and ensure they are using correct grammar and vocabulary.
- Publication and Printing: Publishers and printing companies employ professionals to review and correct sentences before printing books, magazines, newspapers, and other publications.
- Official Documents: Government agencies and organizations issuing official documents, such as passports, identification cards, and licenses, must ensure that sentences are accurate and free from errors.
In essence, sentence corrections are needed whenever clear, accurate, and effective communication is essential. Correcting sentences helps maintain credibility, prevent misunderstandings, and ensure that the intended message is conveyed appropriately in various personal, academic, professional, and creative contexts.
Where is Required Sentence corrections
Sentence corrections are required in various locations and contexts where written or spoken language is used for communication. Here are some common places and situations where sentence corrections are necessary:
- Academic Institutions: Sentence corrections are often needed in schools, colleges, and universities, where students submit assignments, essays, research papers, and exams that require proper grammar and clarity.
- Workplaces: In professional settings such as offices, businesses, and organizations, sentence corrections are essential for maintaining clear and effective written communication through emails, reports, proposals, and other documents.
- Legal Offices and Courts: Legal professionals, including lawyers and judges, require sentence corrections when drafting legal documents, court orders, briefs, and other legal materials.
- Publishing Houses: Publishing companies employ editors and proofreaders who correct sentences in books, magazines, newspapers, and other printed materials before publication.
- Government and Administrative Offices: Government agencies and administrative offices use sentence corrections to ensure the accuracy and clarity of official documents, forms, and reports.
- Online Content Platforms: Content creators on websites, blogs, social media platforms, and video-sharing platforms often perform sentence corrections to enhance the quality and readability of their content.
- Language Learning Centers: Language schools and language learning apps may provide sentence corrections to help students improve their language skills, particularly when learning a new language.
- Translation Services: Translation agencies and professionals offer sentence corrections to ensure accurate translations from one language to another.
- Public Speaking Events: Public speakers and presenters may require sentence corrections for their speeches, lectures, and presentations to ensure that their message is clear and impactful.
- Personal Correspondence: When writing personal letters, emails, or messages, individuals may choose to perform sentence corrections to improve their communication with friends and family.
- Publication Companies: Magazines, newspapers, and journals employ editors to perform sentence corrections on articles, columns, and editorial content.
- Advertising and Marketing Agencies: Advertisers and marketers correct sentences in advertising copy, promotional materials, and marketing campaigns to maintain professionalism and appeal.
- Customer Service: Customer service representatives may use sentence corrections in their written responses to customer inquiries and complaints to provide clear and accurate information.
- Academic Conferences and Seminars: Presenters and researchers often correct sentences in their conference papers and presentations to ensure the quality and impact of their work.
In summary, sentence corrections are necessary in a wide range of locations and scenarios where written or spoken language is used for communication. The specific need for sentence corrections can vary depending on the context and the importance of clear, accurate, and effective communication in that context.
How is Required Sentence corrections
The process of conducting sentence corrections involves several steps to ensure that written or spoken sentences are clear, grammatically correct, and effectively convey the intended message. Here’s how sentence corrections are typically performed:
- Review and Identify Errors:
- Carefully read or listen to the sentence to identify any errors or issues. This includes grammar mistakes, punctuation errors, spelling errors, word usage problems, and clarity issues.
- Grammar and Syntax:
- Check the sentence for proper grammar, including subject-verb agreement, verb tense, and sentence structure. Correct any grammatical errors.
- Punctuation:
- Verify that punctuation marks such as commas, periods, semicolons, colons, quotation marks, and apostrophes are correctly used. Make adjustments as needed.
- Spelling:
- Look for misspelled words and correct them. Use spell-check tools if available, but be cautious, as they may not catch all errors.
- Word Usage and Clarity:
- Ensure that words are used correctly, and that the sentence is clear and concise. Replace or rephrase words or phrases that may be ambiguous or unclear.
- Sentence Structure:
- Review the sentence structure to ensure that it flows smoothly and logically. Adjust the sentence structure if it hinders comprehension or readability.
- Conciseness:
- Eliminate unnecessary words or phrases to make the sentence more concise without losing its intended meaning.
- Subject-Verb Agreement:
- Check that the subject and verb agree in terms of number (singular or plural).
- Parallel Structure:
- Ensure that items in lists or series are grammatically consistent in terms of structure and format.
- Modifiers:
- Confirm that modifiers (words or phrases that describe other elements in the sentence) are correctly placed and do not lead to ambiguity.
- Tone and Clarity:
- Adjust the sentence to convey the desired tone and maintain clarity. Consider the context and audience when making these adjustments.
- Proofreading:
- Carefully proofread the sentence to catch any remaining errors or issues. It’s often helpful to read the sentence aloud or ask someone else to review it.
- Use of Tools:
- Utilize grammar and spell-checking software or online tools to assist with corrections, but remember that these tools may not catch all errors, so human review is essential.
- Final Review:
- Give the sentence one final review to ensure that all corrections have been made and that it meets the required standards for accuracy and clarity.
The specific process of sentence corrections may vary depending on the context and purpose of the writing or speech. Additionally, it’s essential to consider the audience and the style guide or language conventions relevant to the situation. Ultimately, the goal of sentence corrections is to produce well-structured, error-free sentences that effectively convey the intended message.
Case Study on Sentence corrections
Improving Business Communication
Background: ABC Corporation is a medium-sized company that specializes in IT services. They were experiencing communication challenges, particularly in written communication such as emails, reports, and client proposals. Many employees lacked strong writing skills, leading to misunderstandings, errors, and a negative impression on clients.
Objective: To improve the quality of written communication within the company, enhance professionalism, and ensure that all written materials meet high standards of clarity, grammar, and correctness.
Process:
- Assessment and Training:
- ABC Corporation began by assessing the writing skills of its employees. They identified common errors, such as grammar mistakes, punctuation issues, and unclear sentences.
- The company organized training sessions and workshops on business writing and sentence structure. They brought in professional trainers to conduct these sessions.
- Style Guide and Resources:
- ABC Corporation developed an internal style guide to provide employees with clear guidelines on grammar, punctuation, and writing conventions.
- They provided employees with access to grammar-checking software and writing resources to support their efforts.
- Peer Review and Feedback:
- The company encouraged employees to engage in peer review of written materials before submission. Colleagues would review each other’s work and provide constructive feedback.
- Managers and team leaders were trained to provide feedback and corrections in a constructive and helpful manner.
- Editing Team:
- ABC Corporation established a small in-house editing team responsible for reviewing and correcting important documents, proposals, and reports before they were sent to clients.
- Continuous Improvement:
- The company implemented a system for ongoing improvement. They regularly reviewed and updated their style guide and conducted refresher training sessions.
- They encouraged employees to share examples of well-written communication as positive models for others to follow.
Results:
- The implementation of sentence corrections and improved writing practices led to several positive outcomes for ABC Corporation:
- Enhanced Professionalism: The company’s written materials exhibited a higher level of professionalism, which improved its image in the eyes of clients and partners.
- Fewer Errors: The number of grammatical errors, spelling mistakes, and punctuation errors in emails, reports, and proposals significantly decreased.
- Clearer Communication: Clients reported a better understanding of the company’s proposals and project updates, resulting in fewer misunderstandings and disputes.
- Increased Client Satisfaction: Clients were more satisfied with the quality of communication and the accuracy of delivered work, leading to improved client relationships and repeat business.
- Employee Confidence: Employees gained confidence in their writing skills, and the training and feedback helped them become more effective communicators.
- Efficiency: The editing team’s work reduced the time spent on revisions and rework, allowing the company to be more efficient in its operations.
Conclusion:
The case study of ABC Corporation demonstrates the significant impact that sentence corrections and improved writing practices can have on a business. By investing in training, resources, and a culture of continuous improvement, the company was able to enhance its professionalism, reduce errors, and ultimately improve client satisfaction and employee confidence in written communication. This case study underscores the importance of effective sentence corrections in a professional context.
White paper on Sentence corrections
Title: Sentence Corrections: Enhancing Clarity and Professionalism in Written Communication
Abstract:
A brief summary of the white paper’s key findings and contributions.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- A brief overview of the importance of sentence corrections in written communication.
- The scope and objectives of the white paper.
- The Significance of Sentence Corrections
- Why sentence corrections matter in various contexts (academic, professional, personal).
- The impact of clear and error-free communication on perception and comprehension.
- Common Sentence Errors
- An examination of the most frequent sentence errors, including grammatical, punctuation, and spelling errors.
- Real-world examples illustrating these errors.
- Tools and Resources for Sentence Corrections
- A review of available tools and resources, both manual (style guides) and technological (grammar-checking software).
- Pros and cons of different correction methods.
- Best Practices for Sentence Corrections
- A comprehensive guide to best practices for correcting sentences, including step-by-step processes.
- Advice on maintaining tone, clarity, and coherence during corrections.
- Challenges in Sentence Corrections
- An exploration of challenges faced during sentence corrections, such as idiosyncrasies in language, context-specific corrections, and readability concerns.
- The Role of Professionals in Sentence Corrections
- How professional editors, proofreaders, and language experts contribute to improving written communication.
- When and why to seek professional help with corrections.
- Impact on Various Sectors
- Case studies and examples showcasing the impact of sentence corrections in academia, business, legal, and other fields.
- Quantitative and qualitative data on improved communication after corrections.
- Technological Advances in Sentence Corrections
- A look at emerging technologies (e.g., AI-driven language tools) and their role in automating and enhancing the correction process.
- The balance between automated and human corrections.
- Conclusion
- Summary of key takeaways and findings from the white paper.
- A reaffirmation of the significance of sentence corrections in achieving effective communication.
- References
- A comprehensive list of academic sources, books, articles, and other references used in the white paper.
- Appendices
- Supplementary materials, such as additional case studies, correction examples, and practical guides for readers.
Additional Considerations:
- Include visuals, such as charts, graphs, and illustrations, to support key points and findings.
- Incorporate quotes and testimonials from experts, educators, or professionals who emphasize the importance of sentence corrections.
- Include practical exercises or checklists that readers can use to practice and improve their sentence correction skills.
- Ensure that the white paper is well-organized, logically structured, and easy to navigate for readers.
Remember to conduct thorough research and consult relevant experts to provide a comprehensive and authoritative perspective on the topic of sentence corrections.