Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production-
In quantity food production, whether in restaurants, catering operations, or institutional settings, specific equipment plays a crucial role in ensuring efficiency, consistency, and quality. Here are some essential types of equipment commonly used:
- Commercial Ovens: These can include convection ovens for even baking and roasting, deck ovens for pizzas and bread, and combi ovens that offer convection, steam, and combination cooking modes.
- Commercial Range: Typically includes gas or electric stoves with multiple burners and ovens, allowing for simultaneous cooking of various dishes.
- Grills and Griddles: Used for grilling meats, seafood, and vegetables, and for cooking pancakes, eggs, and sandwiches on a large scale.
- Steamers: Vital for cooking vegetables, rice, and seafood quickly while retaining nutrients and flavor.
- Deep Fryers: Used for frying foods like French fries, chicken, and seafood quickly and in large quantities.
- Food Processors and Mixers: Essential for chopping, slicing, grating, and mixing ingredients in bulk.
- Commercial Refrigerators and Freezers: Maintain safe temperatures for storing perishable ingredients and finished dishes.
- Food Holding and Warming Equipment: Such as steam tables, hot holding cabinets, and heat lamps, to keep food at safe temperatures before serving.
- Slicers and dicers: For preparing large quantities of vegetables, cheeses, and meats efficiently.
- Industrial Dishwashers: Ensure quick and sanitary cleaning of large quantities of dishes, utensils, and cookware.
- Food Scales and Measuring Tools: Essential for accurately portioning ingredients in large-scale recipes.
- Cutting Boards and Knives: Heavy-duty equipment for preparing ingredients safely and efficiently.
- Storage Containers and Shelving: To organize and store ingredients and prepared foods safely.
- Specialty Equipment: Depending on the type of cuisine, this may include pasta cookers, tandoors (for Indian cuisine), or woks (for Asian cuisine).
- Safety Equipment: Including fire suppression systems, ventilation hoods, and ergonomic mats for kitchen staff.
These are just a few examples, as the specific equipment needed can vary widely based on the type of food being prepared and the scale of production.
What is Required Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
In quantity food production, whether in commercial kitchens, catering operations, or institutional settings, several specific types of equipment are essential to ensure efficient and high-quality food preparation. Here’s a detailed list of required equipment typically used:
- Commercial Ovens: Including convection ovens for even cooking, deck ovens for baking bread and pizza, and combi ovens for versatile cooking with steam, convection, or a combination of both.
- Commercial Range: Gas or electric ranges with multiple burners and ovens, allowing for simultaneous cooking of different dishes.
- Grills and Griddles: Used for grilling meats, vegetables, and sandwiches, and griddling pancakes, eggs, and meats.
- Steamers: For cooking vegetables, rice, seafood, and other items quickly and retaining nutrients.
- Deep Fryers: Essential for frying foods like French fries, chicken, and seafood quickly and in large batches.
- Food Processors and Mixers: For chopping, slicing, grating, and mixing ingredients in bulk.
- Commercial Refrigerators and Freezers: Maintain safe temperatures for storing perishable ingredients and prepared foods.
- Food Holding and Warming Equipment: Steam tables, hot holding cabinets, heat lamps, and warming drawers to keep food at safe temperatures before serving.
- Slicers and Dicers: For preparing large quantities of vegetables, cheeses, and meats efficiently.
- Industrial Dishwashers: Ensures quick and sanitary cleaning of large volumes of dishes, utensils, and cookware.
- Food Scales and Measuring Tools: Essential for accurately portioning ingredients in large-scale recipes.
- Cutting Boards and Knives: Heavy-duty cutting boards and quality knives for safe and efficient preparation of ingredients.
- Storage Containers and Shelving: To organize and store ingredients, prepared foods, and kitchen equipment.
- Specialty Equipment: Depending on the type of cuisine, this may include pasta cookers, tandoors (for Indian cuisine), woks (for Asian cuisine), and more specialized items.
- Safety Equipment: Fire suppression systems, ventilation hoods, non-slip mats, and ergonomic tools to ensure a safe working environment.
- Packaging Equipment: For packing and storing prepared food items, including vacuum sealers, food wrappers, and containers.
- Kitchen Utensils: Ladles, spatulas, tongs, and other tools for handling food during preparation and serving.
- Water Filtration Systems: Ensure clean water supply for cooking, cleaning, and sanitation purposes.
- Temperature Monitoring Devices: Thermometers and temperature probes to monitor cooking and storage temperatures for food safety.
- Cleaning and Sanitizing Equipment: Including sinks, sprayers, and cleaning supplies for maintaining hygiene standards.
These equipment types are crucial for efficiently producing large quantities of food while maintaining consistency, quality, and safety in commercial food production environments. Each plays a specific role in different stages of food preparation, storage, and service.
Who is Required Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
In quantity food production, the equipment used is crucial for ensuring efficient operations, maintaining food safety, and producing consistent high-quality meals. Here’s a breakdown of the specific types of equipment and their roles in quantity food production:
- Cooking Equipment:
- Commercial Ovens: Convection ovens, combi ovens, and deck ovens for baking, roasting, and cooking large quantities of food evenly.
- Ranges: Gas or electric ranges with multiple burners and ovens for cooking various dishes simultaneously.
- Grills and Griddles: Used for grilling meats, vegetables, and sandwiches, and griddling pancakes, eggs, and meats.
- Food Preparation Equipment:
- Food Processors and Mixers: Chopping, slicing, grating, and mixing ingredients in bulk.
- Slicers and Dicers: Efficiently preparing large quantities of vegetables, cheeses, and meats.
- Blenders and Immersion Blenders: For blending sauces, soups, and purees.
- Refrigeration and Freezing:
- Commercial Refrigerators and Freezers: To store perishable ingredients and prepared foods at safe temperatures.
- Walk-in Coolers and Freezers: Larger capacity storage for bulk ingredients and prepared foods.
- Food Holding and Warming:
- Steam Tables and Bain Maries: Keeping food warm and ready for service.
- Hot Holding Cabinets and Warming Drawers: Maintaining the temperature of prepared dishes before serving.
- Specialized Cooking Equipment:
- Deep Fryers: For frying foods like French fries, chicken, and seafood.
- Steamers: Cooking vegetables, rice, and seafood quickly with steam.
- Pressure Cookers: Speeding up cooking times for soups, stews, and tougher cuts of meat.
- Cleaning and Sanitation:
- Industrial Dishwashers: Cleaning large volumes of dishes, utensils, and cookware efficiently.
- Sink Stations: For manual washing, rinsing, and sanitizing of equipment and utensils.
- Food Safety and Measurement:
- Food Thermometers: Ensuring food reaches safe internal temperatures.
- Portion Scales and Measuring Cups: Accurate measurement of ingredients for consistency in recipes.
- Storage and Organization:
- Storage Containers and Shelving: Organizing ingredients, prepared foods, and kitchen supplies.
- Labeling and Dating Equipment: Ensuring proper rotation and identification of food items.
- Safety and Ergonomics:
- Ventilation Systems and Hoods: Removing heat, smoke, and odors from the kitchen.
- Non-slip Mats and Safety Shoes: Preventing slips and falls in busy kitchen environments.
- Specialty Equipment:
- Pasta Cookers, Tandoors, Woks, etc.: Depending on the cuisine specialty, specific equipment may be required for authentic preparation methods.
These equipment types are essential for meeting production demands, maintaining food quality, adhering to safety standards, and ensuring efficient workflow in quantity food production settings such as restaurants, catering services, hotels, and institutional kitchens. Each piece serves a specific purpose in the overall process of preparing and serving large volumes of food.
When is Required Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
Specific equipment used in quantity food production is employed throughout various stages of the food preparation process. Here’s a breakdown of when and how each type of equipment is typically used:
- Preparation Stage:
- Food Processors and Mixers: Used to chop, slice, grate, and mix ingredients in bulk quantities. This stage includes preparing vegetables, mixing dough, and blending sauces.
- Slicers and Dicers: Efficiently cut large quantities of vegetables, cheeses, and meats for preparation.
- Blenders and Immersion Blenders: Utilized for blending sauces, soups, and purees.
- Cooking Stage:
- Commercial Ovens: Used for baking, roasting, and cooking various dishes. Convection ovens ensure even cooking, while combi ovens offer versatility with steam and convection options.
- Ranges: Gas or electric ranges with multiple burners and ovens allow for simultaneous cooking of different items.
- Grills and Griddles: Utilized for grilling meats, vegetables, and sandwiches, as well as cooking pancakes, eggs, and meats.
- Specialized Cooking Equipment:
- Deep Fryers: Used for frying foods such as French fries, chicken, and seafood.
- Steamers: Cook vegetables, rice, and seafood quickly and healthily with steam.
- Pressure Cookers: Reduce cooking times for soups, stews, and tougher cuts of meat.
- Food Holding and Warming:
- Steam Tables and Bain Maries: Keep food warm and ready for service.
- Hot Holding Cabinets and Warming Drawers: Maintain the temperature of prepared dishes before serving.
- Refrigeration and Freezing:
- Commercial Refrigerators and Freezers: Store perishable ingredients and prepared foods at safe temperatures.
- Walk-in Coolers and Freezers: Larger capacity storage for bulk ingredients and prepared foods.
- Cleaning and Sanitation:
- Industrial Dishwashers: Clean large volumes of dishes, utensils, and cookware efficiently.
- Sink Stations: For manual washing, rinsing, and sanitizing of equipment and utensils.
- Food Safety and Measurement:
- Food Thermometers: Ensure food reaches safe internal temperatures.
- Portion Scales and Measuring Cups: Accurately measure ingredients for consistency in recipes.
- Storage and Organization:
- Storage Containers and Shelving: Organize ingredients, prepared foods, and kitchen supplies.
- Labeling and Dating Equipment: Ensure proper rotation and identification of food items.
- Specialty Equipment:
- Pasta Cookers, Tandoors, Woks, etc.: Depending on the cuisine specialty, specific equipment may be required for authentic preparation methods.
Each piece of equipment plays a critical role at different stages of food production, from preparation and cooking to holding, storing, and cleaning. The timing of their use ensures that food is prepared efficiently, safely, and to high standards of quality in quantity food production environments such as restaurants, catering services, hotels, and institutional kitchens.
Where is Required Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
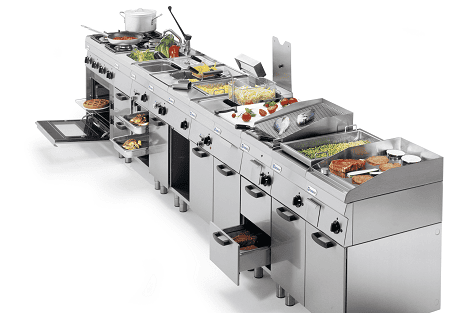
Specific equipment used in quantity food production is typically found in various settings where large volumes of food are prepared and served. Here are the common locations or establishments where such equipment is used:
- Restaurants:
- Full-service restaurants of all types, from casual dining to fine dining, utilize a wide range of equipment for preparing and cooking meals in bulk quantities.
- Catering Companies:
- Caterers require specialized equipment to prepare and transport large quantities of food to events such as weddings, corporate functions, and parties.
- Hotels and Resorts:
- Hotel kitchens are equipped to handle breakfast buffets, banquets, room service orders, and restaurant meals for guests, often requiring equipment capable of high-volume production.
- Institutional Settings:
- Schools, universities, hospitals, and other institutions have kitchens that must cater to hundreds or even thousands of people daily. Equipment here is essential for meeting nutritional guidelines and dietary needs.
- Corporate Cafeterias:
- Large companies with on-site dining facilities use equipment to prepare meals for employees, often serving breakfast, lunch, and sometimes dinner.
- Food Manufacturing Facilities:
- Facilities producing pre-packaged meals, frozen foods, or other food products in bulk quantities rely on specialized equipment for processing, cooking, and packaging.
- Prisons and Military Bases:
- These facilities have kitchens equipped to prepare meals for large numbers of inmates or personnel, adhering to strict dietary and safety standards.
- Event Venues:
- Locations hosting weddings, conventions, and other large events often have kitchens or catering facilities equipped with the necessary tools to serve large numbers of guests efficiently.
- Food Trucks and Mobile Catering:
- Mobile food vendors require compact yet efficient equipment for preparing and serving food on the go, often using specialized equipment adapted for mobile use.
- Industrial Kitchens and Food Service Providers:
- Companies providing meals for airlines, railways, cruise ships, and similar transport sectors need equipment that can handle the unique challenges of producing meals in confined spaces with specific logistical requirements.
In each of these settings, the specific equipment used may vary based on the type of food being prepared, the scale of production, and the operational needs. The key is that each location relies on specialized equipment tailored to efficiently handle the demands of producing large quantities of food while maintaining quality, safety, and consistency.
How is Required Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
The specific equipment used in quantity food production is utilized in various ways to ensure efficient and effective preparation, cooking, storage, and serving of large volumes of food. Here’s how each type of equipment is typically used:
- Preparation Equipment:
- Food Processors and Mixers: Used to chop, slice, grate, and mix ingredients in bulk quantities. For example, food processors can quickly chop vegetables for soups or mix dough for bread.
- Slicers and Dicers: Efficiently prepare large quantities of vegetables, cheeses, and meats. Slicers are used to create consistent slices for sandwiches or salads, while dicers are used for cubing vegetables for soups or stews.
- Blenders and Immersion Blenders: Blend sauces, soups, and purees to a smooth consistency, essential for creating bases for various dishes.
- Cooking Equipment:
- Commercial Ovens: Used for baking, roasting, and cooking large quantities of food evenly. Convection ovens circulate hot air for even cooking, while combi ovens offer versatility with steam and convection cooking options.
- Ranges: Gas or electric ranges with multiple burners and ovens allow simultaneous cooking of different items, crucial for preparing main courses and sides concurrently.
- Grills and Griddles: Grill meats, vegetables, and sandwiches, or griddle pancakes, eggs, and meats quickly and evenly.
- Specialized Cooking Equipment:
- Deep Fryers: Fry foods such as French fries, chicken, and seafood quickly and to a crispy texture.
- Steamers: Steam vegetables, rice, and seafood quickly while preserving nutrients and flavor.
- Pressure Cookers: Cook soups, stews, and tough cuts of meat rapidly, reducing cooking times while tenderizing ingredients.
- Food Holding and Warming Equipment:
- Steam Tables and Bain Maries: Keep prepared food warm and ready for service, ideal for buffet-style or catered events.
- Hot Holding Cabinets and Warming Drawers: Maintain the temperature of cooked dishes before serving, ensuring food stays hot and safe.
- Refrigeration and Freezing:
- Commercial Refrigerators and Freezers: Store perishable ingredients and prepared foods at safe temperatures, preventing spoilage and ensuring food safety.
- Walk-in Coolers and Freezers: Larger storage spaces for bulk ingredients, prepared foods, and perishable items requiring extended storage.
- Cleaning and Sanitation:
- Industrial Dishwashers: Clean large volumes of dishes, utensils, and cookware efficiently, maintaining hygiene and sanitation standards.
- Sink Stations: Provide manual washing, rinsing, and sanitizing of equipment and utensils, crucial for preventing cross-contamination.
- Food Safety and Measurement:
- Food Thermometers: Ensure food reaches safe internal temperatures, essential for preventing foodborne illnesses.
- Portion Scales and Measuring Cups: Accurately measure ingredients to maintain consistency and adhere to recipes, crucial in batch cooking.
- Storage and Organization:
- Storage Containers and Shelving: Organize ingredients, prepared foods, and kitchen supplies efficiently, maximizing space and accessibility.
- Labeling and Dating Equipment: Ensure proper rotation of food items to minimize waste and maintain freshness.
- Specialty Equipment:
- Pasta Cookers, Tandoors, Woks, etc.: Depending on cuisine requirements, specialty equipment is used to prepare specific dishes authentically and efficiently.
In summary, each piece of specific equipment in quantity food production serves a vital role in different stages of food preparation, from initial ingredient handling and processing to cooking, holding, and serving. The efficient use of this equipment ensures that large quantities of food can be produced consistently, safely, and to high standards of quality in various food service environments.
Case Study on Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
Let’s consider a case study to illustrate how specific equipment is used in quantity food production, focusing on a fictional catering company called “Gourmet Delights Catering.”
Company Overview: Gourmet Delights Catering specializes in providing high-quality catering services for weddings, corporate events, and private parties in a metropolitan area. They are known for their diverse menu offerings and ability to accommodate various dietary preferences and cultural cuisines.
Scenario: Gourmet Delights Catering has been commissioned to cater a wedding reception for 300 guests. The menu includes a variety of dishes ranging from hors d’oeuvres to main courses and desserts.
Equipment Used and Their Roles:
- Food Preparation:
- Food Processors and Mixers: The kitchen staff uses commercial food processors and mixers to prepare large batches of sauces, dips, and salad dressings efficiently. For example, they use food processors to chop vegetables for crudité platters and mixers to blend marinades for grilled meats.
- Slicers and Dicers: To ensure uniformity in food presentation, slicers are used to cut cured meats and cheeses for charcuterie boards. Dicers are employed to prepare vegetables for salads and stir-fries.
- Cooking Equipment:
- Combi Ovens: The combi ovens are essential for cooking a variety of dishes simultaneously. They use steam to prepare delicate seafood dishes and convection heat for roasting meats and vegetables.
- Commercial Ranges: Gas ranges with multiple burners are used to sauté and sear ingredients for main courses. Electric ovens in the range are used for baking bread and desserts.
- Specialized Cooking Equipment:
- Deep Fryers: Used to prepare crispy appetizers such as spring rolls and tempura shrimp.
- Steamers: Large steamers are employed to cook rice and steam vegetables in bulk quantities, ensuring that side dishes are prepared efficiently and healthily.
- Food Holding and Warming:
- Hot Holding Cabinets: These cabinets are crucial for maintaining the temperature of prepared dishes before they are served. They ensure that all items, from appetizers to desserts, are ready to be served at the optimal temperature.
- Refrigeration and Freezing:
- Walk-in Coolers: To store perishable ingredients such as dairy products, fresh produce, and marinated meats at safe temperatures. This ensures that ingredients remain fresh until they are ready to be used.
- Cleaning and Sanitation:
- Industrial Dishwashers: These dishwashers are used to clean large volumes of dishes, utensils, and cookware efficiently. They operate on a continuous cycle to keep up with the demand generated by a busy catering operation.
- Safety and Measurement:
- Food Thermometers: Used to monitor the internal temperatures of cooked meats and seafood to ensure they reach safe levels, preventing foodborne illnesses.
Workflow and Efficiency: Throughout the event preparation, Gourmet Delights Catering’s kitchen staff follows a structured workflow to maximize efficiency:
- Prep Stations: Ingredients are prepped using food processors, slicers, and dicers in dedicated prep stations. This allows the team to work simultaneously on different components of the menu.
- Cooking Stations: Combi ovens and ranges are strategically utilized to ensure that all dishes are cooked to perfection and ready for plating at the right time.
- Assembly and Holding: Once cooked, dishes are transferred to hot holding cabinets to maintain their temperature until they are plated and served to guests.
- Cleaning and Resetting: Throughout the event, the dishwashing station operates continuously to clean and sanitize used dishes and utensils, ensuring that the kitchen remains organized and efficient.
Conclusion: In this case study, Gourmet Delights Catering demonstrates how specific equipment in quantity food production plays a pivotal role in delivering a seamless catering experience. By leveraging commercial-grade equipment tailored to their operational needs, they maintain high standards of food quality, safety, and efficiency, ultimately satisfying their clients’ expectations for a memorable dining experience.
White paper on Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
Title: Enhancing Efficiency and Quality in Quantity Food Production: A Comprehensive Guide to Specific Equipment
Abstract: In the dynamic world of food service, efficient and high-quality production is paramount to success. This white paper explores the pivotal role of specific equipment in quantity food production. It highlights how various types of equipment—from preparation and cooking to holding and sanitation—contribute to streamlining operations, ensuring consistency, and meeting stringent food safety standards.
Introduction: Quantity food production encompasses diverse settings such as restaurants, catering services, institutional kitchens, and more. The demand for efficiently preparing large volumes of food without compromising quality necessitates the strategic deployment of specialized equipment. This paper delves into the essential equipment categories and their functionalities throughout the production process.
Key Equipment Categories:
- Food Preparation:
- Food Processors and Mixers: These are indispensable for chopping, slicing, grating, and mixing ingredients in bulk, enhancing efficiency in preparing sauces, dips, and doughs.
- Slicers and Dicers: Ensure uniformity and speed in ingredient preparation, crucial for salads, sandwiches, and garnishes.
- Blenders and Immersion Blenders: Ideal for creating smooth textures in soups, sauces, and purees, contributing to culinary consistency.
- Cooking Equipment:
- Commercial Ovens: From convection to combi ovens, these cater to baking, roasting, and multi-modal cooking needs, maintaining flavor and texture integrity.
- Ranges and Grills: Gas or electric, these support versatile cooking methods from searing and sautéing to grilling and frying, pivotal for diverse menu offerings.
- Specialized Cooking Equipment:
- Deep Fryers: Essential for achieving crispy textures in fried foods, ensuring consistent results across batches.
- Steamers and Pressure Cookers: Facilitate rapid, nutritious cooking of vegetables, grains, and meats, preserving nutrients and flavors.
- Food Holding and Warming:
- Hot Holding Cabinets and Steam Tables: Maintain optimal serving temperatures for prepared dishes, crucial for buffet-style service and event catering.
- Heat Lamps and Warming Drawers: Ensure food remains warm and appetizing during service, enhancing guest satisfaction.
- Refrigeration and Freezing:
- Commercial Refrigerators and Walk-in Coolers: Safeguard perishable ingredients and prepared foods, adhering to food safety guidelines and minimizing waste.
- Cleaning and Sanitation:
- Industrial Dishwashers and Sink Stations: Efficiently clean and sanitize kitchenware, supporting continuous workflow and hygiene standards.
- Safety and Measurement:
- Food Thermometers and Portion Scales: Ensure food safety and consistency in portioning, essential for compliance with health regulations and recipe precision.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the effective utilization of specific equipment in quantity food production not only optimizes operational efficiency but also elevates culinary standards and customer satisfaction. By investing in appropriate equipment tailored to their unique needs, food service establishments can enhance productivity, maintain food quality, and uphold rigorous hygiene standards. This white paper serves as a comprehensive resource for decision-makers seeking to enhance their food production capabilities through strategic equipment investments.
References:
- National Restaurant Association (NRA) Guidelines on Commercial Kitchen Equipment.
- Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Regulations on Food Safety and Handling.
- Insights from industry experts and experienced chefs in quantity food production.
Acknowledgments: Special thanks to culinary professionals, equipment manufacturers, and industry experts who contributed insights and expertise to this white paper.
This white paper aims to provide a detailed overview of the role and importance of specific equipment in quantity food production, offering practical insights and recommendations for stakeholders in the food service industry.
Industrial Application of Specific Equipment used in Quantity food Production
The industrial application of specific equipment in quantity food production is crucial for maintaining efficiency, consistency, and quality across large-scale operations. Here’s a detailed exploration of how various types of equipment are applied in industrial settings:
- Food Preparation Equipment:
- Food Processors and Mixers: Industrial-grade processors and mixers handle large volumes of ingredients efficiently. They are used to chop, blend, and mix ingredients for sauces, dressings, and doughs.
- Slicers and Dicers: These machines ensure uniformity and speed in slicing vegetables, meats, and cheeses, essential for large-scale preparation of salads, sandwiches, and garnishes.
- Industrial Blenders: Used for blending large batches of soups, sauces, and purees, ensuring consistent texture and flavor.
- Cooking Equipment:
- Combi Ovens: Industrial combi ovens offer versatility with steam, convection, and combination cooking modes. They handle diverse cooking tasks from baking and roasting to steaming and sous vide, accommodating large batches of food.
- Steam Kettles: These large-capacity kettles use steam for cooking soups, stews, sauces, and pasta in bulk quantities, providing precise temperature control and even cooking.
- Industrial Fryers: Deep fryers designed for industrial use handle large volumes of fried foods efficiently, maintaining consistent frying temperatures and ensuring crispy textures.
- Food Holding and Warming Equipment:
- Hot Holding Cabinets: Industrial cabinets keep prepared food at safe serving temperatures before distribution, crucial for buffet service and large events.
- Heat Lamps and Warming Drawers: These units maintain food warmth and presentation integrity during service, ideal for plated meals and banquet settings.
- Refrigeration and Freezing Solutions:
- Walk-in Refrigerators and Freezers: Industrial walk-ins provide ample storage space for perishable ingredients, prepared foods, and bulk items, ensuring food safety and freshness.
- Blast Chillers and Freezers: Rapidly chill or freeze cooked foods to safe temperatures, preserving quality and extending shelf life.
- Cleaning and Sanitation Systems:
- Industrial Dishwashers: These machines efficiently clean and sanitize large volumes of dishes, utensils, and cookware, maintaining hygiene standards and supporting continuous workflow.
- Sanitizing Stations: Dedicated areas for manual washing, rinsing, and sanitizing equipment ensure thorough cleaning and prevent cross-contamination.
- Safety and Measurement Tools:
- Food Thermometers and Probes: Industrial-grade thermometers verify food safety by measuring internal temperatures, critical for compliance with health regulations.
- Portion Scales and Measuring Tools: Ensure accurate portioning and recipe consistency in mass production, minimizing waste and optimizing ingredient use.
- Specialty Equipment:
- Rotisseries and Smokers: Used for large-scale roasting and smoking of meats, adding unique flavors and textures to dishes.
- Continuous Batch Cooking Systems: Automated systems for continuous cooking of soups, sauces, and gravies, optimizing production efficiency and consistency.
Benefits of Industrial Equipment in Quantity Food Production:
- Scalability: Equipment is designed to handle high volumes of food production, meeting the demands of large-scale operations.
- Efficiency: Automation and specialized features reduce labor costs and production time, improving overall efficiency.
- Consistency: Precise control over cooking processes ensures consistent quality and flavor across batches.
- Safety and Compliance: Equipment meets stringent health and safety standards, ensuring food safety and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion: Industrial application of specific equipment in quantity food production is essential for achieving operational excellence in large-scale food service environments. By investing in reliable and efficient equipment, food manufacturers, caterers, and institutional kitchens can enhance productivity, maintain high food quality, and meet the diverse needs of their clientele effectively.