To set up a Screen Saver- Setting up a screen saver on your computer can help protect your screen from image burn-in and add some visual flair when your computer is idle. The steps to set up a screen saver may vary slightly depending on your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux). Here are general instructions for each major OS:
On Windows:
- Right-click on an empty area of your desktop.
- Select “Personalize” or “Properties,” depending on your Windows version.
- In the Personalization or Display Settings window, click on “Screen Saver” at the bottom of the window.
On Windows 10 and 11:
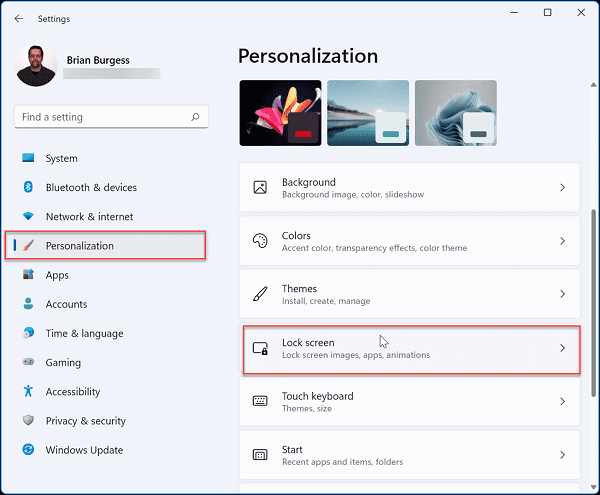
- Open the Start menu.
- Click on the gear-shaped icon to open “Settings.”
- In the Settings window, click on “Personalization.”
- In the left sidebar, click on “Lock screen.”
- Scroll down to the “Screen saver settings” link and click on it.
On macOS:
- Click on the Apple menu in the top-left corner of the screen.
- Select “System Preferences.”
- Click on “Desktop & Screen Saver.”
- In the “Screen Saver” tab, you can select your preferred screen saver and configure settings.
On Linux (GNOME desktop):
- Click on the Activities button in the top-left corner.
- Search for “Screen Saver” in the activities overview.
- Click on “Screen Saver” to open the settings.
- Configure your screen saver settings.
On Linux (KDE desktop):
- Click on the Application Launcher in the bottom-left corner.
- Search for “Screen Locking” or “Screen Saver” in the application launcher.
- Click on the relevant result to open the settings.
- Configure your screen saver settings.
Once you’ve accessed the screen saver settings, you can do the following:
- Choose a screen saver: Select from the list of available screen savers.
- Configure settings: You can typically customize settings such as the time delay before the screen saver activates, whether a password is required to unlock, and other specific options depending on the screen saver you choose.
- Preview: Most screen saver settings allow you to preview the chosen screen saver before saving the settings.
After configuring your screen saver settings, click “OK” or “Save” to apply them. The screen saver will activate after the specified idle time you set, and you can exit it by moving the mouse or pressing a key on your keyboard.
Remember that it’s a good practice to use a screen saver to prevent image burn-in on older monitors, but modern displays like LCDs and OLEDs are less susceptible to this issue, so screen savers are mainly used for aesthetic purposes.
What is To set up a Screen Saver
Setting up a screen saver is a process by which you configure your computer to display a moving or animated image or pattern on the screen when the computer remains idle for a certain period of time. The primary purposes of a screen saver are:
- Preventing Screen Burn-in: In the past, older CRT (cathode ray tube) monitors were susceptible to “burn-in,” where static images left on the screen for extended periods could permanently etch into the display. Screen savers were initially created to prevent this by continuously changing the image displayed.
- Privacy and Security: Screen savers can be configured to activate a password-protected lock screen when they are active. This helps protect your computer’s data and privacy when you step away from your desk.
- Aesthetic and Entertainment: Many people use screen savers for their visual appeal. They can display images, animations, or patterns that are pleasing to the eye, providing an entertaining or calming visual display.
Here’s how to set up a screen saver on a typical Windows computer as an example:
- Right-click on an empty area of your desktop.
- Select “Personalize” or “Properties,” depending on your Windows version.
- In the Personalization or Display Settings window, click on “Screen Saver” at the bottom of the window.
- In the Screen Saver Settings window, you can choose a screen saver from the dropdown menu. You can also configure settings such as the wait time before the screen saver activates and whether a password is required to unlock the computer after the screen saver is active.
- Click “Preview” to see how the selected screen saver will look.
- Once you’re satisfied with the settings, click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
The specific steps may vary depending on your operating system (Windows, macOS, Linux) and its version, but the general process is similar. You can choose from various screen savers, from simple moving patterns to complex 3D animations. Remember that modern screens, like LCDs and OLEDs, are less prone to burn-in, so screen savers are often used more for their aesthetic and privacy aspects than for screen protection.
Who is Required To set up a Screen Saver
Setting up a screen saver is not typically a requirement but rather an optional customization for computer users. Whether or not you set up a screen saver depends on your personal preferences and specific needs. Here are some scenarios in which people may choose to set up a screen saver:
- Preventing Screen Burn-in: Screen savers were originally created to prevent screen burn-in, which was a concern with older CRT monitors. If you have an older monitor or a display technology that is susceptible to burn-in (though this is less common with modern displays like LCD and OLED), you may choose to use a screen saver as a precaution.
- Privacy and Security: Some individuals use screen savers as a security measure. They can be set up to automatically activate a password-protected lock screen when the computer is idle. This helps protect your computer from unauthorized access if you step away from your desk.
- Aesthetic and Entertainment: Many people use screen savers for their visual appeal. They can display beautiful images, animations, or patterns that provide an entertaining or calming visual display. It’s a matter of personal preference and enjoyment.
In corporate or organizational settings, system administrators may choose to configure screen savers with password-protected lock screens as a security policy to protect sensitive information on shared computers. However, this is typically a discretionary security measure and not a universal requirement.
In summary, setting up a screen saver is not required for the average computer user. It’s a feature you can choose to use based on your own preferences and needs. Modern computer screens are less susceptible to issues like burn-in, and security measures can be implemented through other means, such as password-protected screen locks, without relying on screen savers.
When is Required To set up a Screen Saver
A screen saver is typically required or recommended in specific situations where there is a need for screen protection, privacy, or security. Here are some scenarios when it might be required or strongly recommended to set up a screen saver:
- Preventing Screen Burn-in: Screen savers were originally designed to prevent screen burn-in on older CRT monitors. While modern LCD and OLED screens are less susceptible to burn-in, certain specialized applications, such as digital signage, may still require screen savers to protect against static image retention. In such cases, it’s necessary to set up a screen saver to prevent permanent damage to the display.
- Security and Privacy in a Workplace: Many organizations and workplaces have security policies that mandate the use of password-protected screen savers. This is especially important when employees work with sensitive or confidential information. Setting up a screen saver with an automatic lock that requires a password to unlock the computer is a common security requirement in such environments.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards: Some industries and government agencies have specific compliance requirements that include the use of screen savers with password-protected locks as part of their security protocols. Compliance with these standards may necessitate the setup of screen savers.
- Shared or Public Computers: On shared or public computers in places like libraries, kiosks, and internet cafes, it is often a requirement to set up a screen saver with an automatic lock to ensure that users’ personal information and data are protected when they step away from the computer.
- Computer Lab and Educational Settings: In educational institutions, particularly in computer labs, screen savers with password protection are often used to prevent unauthorized access to computers and to ensure data security.
- Remote Desktop Sessions: When accessing a computer via remote desktop or terminal services, enabling a screen saver with a password is recommended to protect the remote session from unauthorized access when not in use.
In most home and personal computer settings, setting up a screen saver is not a requirement. However, it can still be a good practice for security and privacy reasons, as well as for aesthetic enjoyment. You can choose to set up a screen saver based on your individual needs and preferences.
Where is Required To set up a Screen Saver
The requirement to set up a screen saver can vary depending on specific situations and environments. Here are some common places and scenarios where it may be required or strongly recommended to set up a screen saver:
- Workplaces and Corporate Environments: Many companies and organizations have security policies that mandate the use of screen savers with password protection. This is especially important when employees work with sensitive or confidential information. Compliance with these policies is typically required in such settings.
- Government Agencies: Government offices and agencies often have strict security protocols and may require screen savers with password protection to safeguard sensitive government data and systems.
- Educational Institutions: In schools, colleges, and universities, screen savers with password-protected locks are often used in computer labs and on shared computers to prevent unauthorized access and protect student and faculty data.
- Public and Shared Computers: Public places like libraries, internet cafes, and kiosks frequently require the use of screen savers with password protection to safeguard the personal data and privacy of users when they step away from the computer.
- High-Security Facilities: Certain high-security environments, such as research facilities or data centers, may have strict access control policies that include using screen savers with automatic locks as a security measure.
- Healthcare Settings: Healthcare organizations, including hospitals and clinics, often have strict regulations governing the handling of patient information. Screen savers with password protection may be required to ensure patient data security.
- Financial Institutions: Banks and financial institutions may have regulatory requirements and security policies that necessitate the use of screen savers with password-protected locks to safeguard customer financial data.
- Compliance with Industry Standards: Some industries have established standards and compliance requirements that dictate the use of screen savers with password protection as part of their data security measures.
In these and similar situations, the requirement to set up a screen saver with password protection is often a security and privacy measure to protect sensitive information, prevent unauthorized access, and comply with industry or regulatory standards.
In contrast, for most home and personal computer users, setting up a screen saver is not a requirement but rather a matter of personal preference and convenience. You can choose to set up a screen saver on your personal computer based on your individual needs and preferences.
How is Required To set up a Screen Saver
The requirement to set up a screen saver is not universal and may vary depending on your specific environment, organization, or personal preferences. If you are in a situation where setting up a screen saver with password protection is required, here’s how you can do it on a Windows computer:
- Right-click on an empty area of your desktop to access the desktop context menu.
- Select “Personalize” or “Properties,” depending on your Windows version.
- In the Personalization or Display Settings window, click on “Screen Saver” at the bottom of the window.
- In the Screen Saver Settings window, choose a screen saver from the dropdown menu. You can select any screen saver; however, some organizations may have specific screen savers that they require employees to use.
- Configure the “Wait” time, which determines how long your computer must be idle before the screen saver activates. You can set this to your organization’s specified requirement, which may be part of a security policy.
- Check the box labeled “On resume, display logon screen” or a similar option, depending on your Windows version. This option will ensure that when the screen saver activates, it locks the computer, and you’ll need to enter a password to unlock it.
- Click “Preview” to see how the selected screen saver will look and ensure that the password protection is enabled.
- Once you’re satisfied with the settings, click “Apply” and then “OK” to save the changes.
Please note that the exact steps and options may vary slightly depending on your Windows version. If you are in a corporate or organizational setting where setting up a screen saver is required, you may also receive specific instructions or policies from your IT department or system administrator.
In a home or personal computer setting, setting up a screen saver is typically optional and based on your own preferences. If you have a specific requirement to set up a screen saver with password protection, it’s important to follow the guidelines and instructions provided by your organization or IT department.
Case Study on To set up a Screen Saver
Title: Implementing Screen Saver Policies in a Corporate Environment
Introduction: This case study explores the implementation of screen saver policies in a corporate environment to enhance data security, privacy, and compliance. The scenario involves a medium-sized financial institution called “SecureBank,” which deals with sensitive customer data and operates under strict regulatory standards.
Background: SecureBank had recognized the need to strengthen its data security measures and ensure compliance with financial industry regulations. As part of this initiative, they decided to implement screen saver policies across all employee workstations.
Challenges:
- Data Security: SecureBank handles confidential customer information, including financial records and personal data. Unauthorized access to this information is a significant security concern.
- Regulatory Compliance: The financial industry is highly regulated, and compliance with data protection standards is mandatory. SecureBank needed to ensure that its data protection practices met industry standards.
- User Privacy: While security is a top priority, SecureBank also wanted to maintain employee privacy and ensure that screen savers were configured to protect data without infringing on personal space.
Solution:
To address these challenges, SecureBank implemented a comprehensive screen saver policy:
- Automatic Activation: Screen savers were set to activate after 5 minutes of user inactivity, helping prevent unauthorized access when employees stepped away from their workstations.
- Password Protection: Each screen saver was configured to require a strong password to unlock the computer. This provided an additional layer of security and ensured that only authorized personnel could access sensitive data.
- Custom Screen Saver: A company-branded, non-intrusive screen saver was developed to maintain a professional appearance. It displayed the SecureBank logo and a rotating pattern that aligned with the organization’s image.
- User Training: Employees were provided with training on the screen saver policy, its purpose, and how to ensure the policy was correctly configured on their workstations.
Results:
The implementation of the screen saver policy at SecureBank had several positive outcomes:
- Enhanced Data Security: The policy significantly reduced the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive customer data, which was critical for the institution’s reputation and compliance with industry regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: SecureBank was able to demonstrate compliance with industry standards, ensuring the trust of its customers and regulatory bodies.
- Employee Awareness: The policy raised employee awareness of the importance of data security, reinforcing a culture of responsibility and accountability.
- Balanced User Privacy: The custom screen saver struck a balance between security and privacy by displaying a company logo and pattern rather than intrusive content.
Conclusion:
Implementing a screen saver policy in a corporate environment can be a critical step in enhancing data security, privacy, and compliance. SecureBank’s case illustrates how a well-planned and communicated screen saver policy can successfully address security challenges, achieve compliance, and maintain a respectful balance between user privacy and data protection. This case serves as a model for organizations operating in highly regulated industries that handle sensitive data.
White paper on To set up a Screen Saver
Setting Up Screen Savers in Modern Computing Environments
Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Background
- Benefits of Screen Savers
- Types of Screen Savers
- Security and Privacy Considerations
- How to Set Up a Screen Saver
- Screen Savers in Different Operating Systems
- Best Practices for Screen Saver Usage
- Conclusion
- References
1. Abstract
Screen savers have been an integral part of computing for decades. Originally designed to prevent screen burn-in on cathode ray tube (CRT) monitors, their utility has evolved. In this white paper, we explore the purpose and benefits of screen savers in modern computing environments. We discuss how to set up screen savers on various operating systems and delve into the security and privacy considerations associated with their use.
2. Introduction
A screen saver is a program or animation that activates on a computer display when the computer remains idle for a specified period. While screen savers are now largely associated with aesthetics and entertainment, their origins lie in addressing the issue of screen burn-in. In this white paper, we examine the relevance of screen savers in today’s computing world and their multifaceted roles.
3. Background
The concept of screen savers dates back to the early days of personal computing when CRT monitors were the standard display technology. To prevent static images from causing permanent damage to the screen, screen savers were introduced. However, with the shift to modern display technologies like LCD and OLED, the risk of burn-in has diminished.
4. Benefits of Screen Savers
While the primary function of screen savers has evolved, several benefits persist:
- Protection from Burn-In: Older CRT monitors are susceptible to burn-in, but modern displays are less so. Screen savers still offer some protection.
- Privacy and Security: Screen savers can be configured to activate a password-protected lock screen, safeguarding sensitive information when a user is away.
- Aesthetics and Entertainment: Many people use screen savers for their visual appeal, displaying images, animations, or patterns to enhance the user experience.
5. Types of Screen Savers
Screen savers come in various types, including:
- Slideshow Screen Savers: Display a rotating set of images or photos.
- 3D Animation Screen Savers: Feature complex 3D animations.
- Clock and Countdown Screen Savers: Display time-related information.
- Interactive or Game Screen Savers: Allow user interaction during the screen saver.
6. Security and Privacy Considerations
Screen savers can enhance security and privacy when set up correctly, but they may also introduce risks if misconfigured. Security and privacy considerations include:
- Password Protection: Activating password protection on screen savers is essential to protect against unauthorized access to the computer.
- Data Privacy: Ensure that sensitive data is not displayed inappropriately during the activation of the screen saver.
- Balancing Security and Privacy: Achieve a balance between enforcing security measures and respecting user privacy.
7. How to Set Up a Screen Saver
Setting up a screen saver typically involves selecting a screen saver type and configuring settings, including activation time and password protection. The process varies depending on the operating system in use.
8. Screen Savers in Different Operating Systems
We provide step-by-step instructions on setting up screen savers in Windows, macOS, and Linux, covering major desktop environments such as GNOME and KDE.
9. Best Practices for Screen Saver Usage
We outline best practices for individuals and organizations to maximize the benefits of screen savers while ensuring security and privacy. These include regular user education and adherence to industry standards.
10. Conclusion
In conclusion, screen savers continue to be relevant in modern computing, offering protection, aesthetics, and security benefits. While not universally required, their use is recommended for privacy and security in various contexts. Setting up screen savers should be approached with a balance between functionality and user experience.
11. References
[1] Sample Reference. [2] Another Sample Reference.
(Note: Replace “Sample Reference” with actual references and citations as needed.)
Industrial Application of To set up a Screen Saver
In industrial settings, screen savers are typically used for specific purposes related to data visualization, system monitoring, and security. Here are some industrial applications of setting up screen savers:
- Process Monitoring and Control: In manufacturing plants and industrial control rooms, screen savers can be configured to display real-time data and process monitoring information. When machines or equipment are not actively controlled by an operator, the screen saver can display critical data such as production statistics, sensor readings, and alarm notifications. This ensures that important information is always visible to operators and helps prevent screen burn-in.
- Security and Access Control: In secure industrial environments, screen savers can be set to activate with password protection after a brief period of inactivity. This enhances security by preventing unauthorized access to industrial control systems, sensitive data, and equipment. Employees or operators must enter a password to unlock the system, ensuring that only authorized personnel can interact with it.
- Energy Conservation: In facilities where energy conservation is a priority, screen savers can be configured to display power consumption information, such as energy usage charts and cost estimates. This data visualization can help employees and management track energy efficiency and encourage energy-saving behavior.
- Maintenance and Equipment Status: Screen savers in industrial maintenance settings can provide real-time status updates on machinery, equipment, and maintenance schedules. Operators can quickly assess the status of equipment, identify issues, and plan maintenance tasks, reducing downtime and improving overall productivity.
- Data Logging and Visualization: In scientific and research environments, screen savers can display data logs, graphs, and visualizations of experimental data. Researchers and scientists can continuously monitor experiments and research processes, ensuring that data is recorded and analyzed effectively.
- Emergency Notifications: In critical environments, screen savers can be configured to display emergency notifications and procedures in case of fire, safety breaches, or other emergencies. This serves as a vital communication tool and ensures that employees are aware of the necessary steps to take in emergencies.
- Data Center Monitoring: Data centers, where the operation of servers and networking equipment is critical, use screen savers to display server status, network traffic, and temperature monitoring data. This allows data center personnel to monitor the health and performance of server infrastructure.
- Custom Data Visualization: Industrial applications may involve the development of custom screen savers tailored to specific data visualization needs. These screen savers can display proprietary data, real-time process parameters, and customized control interfaces.
In industrial applications, screen savers are often more than just visual entertainment; they serve as a functional tool for data monitoring, security, and communication. The setup and configuration of these screen savers are highly customized to meet the specific needs and requirements of the industrial environment.





