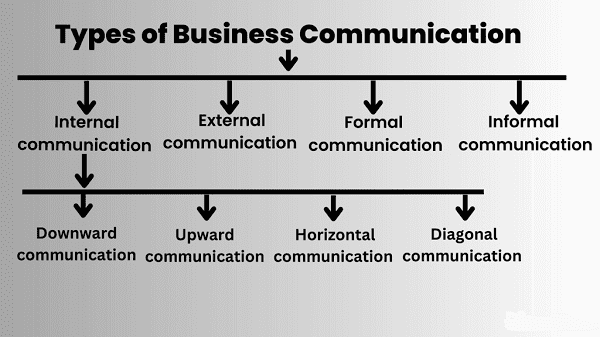
Types Business Communication- Business communication encompasses various types of communication methods and channels used within organizations for conveying information, ideas, and messages. These communication types can be broadly categorized into several categories:
- Verbal Communication:
- Face-to-Face Meetings: In-person discussions, presentations, and negotiations.
- Phone Calls: Conversations over the telephone, including conference calls.
- Video Conferencing: Virtual meetings with the use of video technology.
- Written Communication:
- Email: Electronic messages used for quick written communication.
- Memorandums (Memos): Formal internal documents for conveying information within an organization.
- Letters: Formal written communication with external parties.
- Reports: Detailed documents presenting information, research, or analysis.
- Proposals: Documents outlining plans, projects, or offers.
- Business Plans: Comprehensive documents outlining an organization’s goals, strategies, and financial projections.
- Policy Documents: Documents outlining organizational policies and procedures.
- Minutes of Meetings: Official records of discussions and decisions during meetings.
- Digital Communication:
- Instant Messaging: Real-time text-based communication platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or WhatsApp.
- Social Media: Platforms like LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook used for branding and customer engagement.
- Blogs: Informal written communication for sharing insights and updates.
- Forums and Discussion Boards: Online platforms for discussions and knowledge-sharing.
- Intranet: Internal networks for sharing information within an organization.
- Non-Verbal Communication:
- Body Language: Gestures, postures, and facial expressions used during face-to-face meetings.
- Visual Communication: The use of visuals, such as graphs, charts, and images to convey information.
- Symbols and Icons: Simple graphics that convey specific meanings.
- Formal Communication:
- Official Documents: Contracts, agreements, legal notices, and other formal documents.
- Company Policies and Procedures: Formal guidelines and regulations within an organization.
- Presentations: Structured, often visual, presentations to convey information.
- Informal Communication:
- Watercooler Conversations: Casual discussions among colleagues.
- Gossip: Informal sharing of information and rumors.
- Texting and Personal Messaging: Informal text communication.
- Interpersonal Communication:
- Negotiations: Discussions aimed at reaching agreements or compromises.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing and resolving conflicts within the organization.
- Feedback: Providing and receiving constructive feedback.
- Cross-Cultural Communication:
- Communication Across Cultures: Adapting communication styles for different cultural contexts.
- Mass Communication:
- Public Relations (PR): Managing an organization’s image and reputation through press releases, media communication, and events.
- Advertising: Promotional messages delivered through various media channels.
- Internal Communication:
- Employee Communication: Information dissemination within the organization, including updates, policies, and news.
- Leadership Communication: Communication from top management to the rest of the organization.
- External Communication:
- Customer Communication: Engaging with customers through various channels.
- Supplier Communication: Interaction with suppliers and vendors.
- Investor Communication: Providing information to shareholders and potential investors.
Effective business communication involves choosing the most appropriate type of communication for a specific situation, audience, and purpose. It is essential for achieving organizational goals, building relationships, and ensuring clarity and understanding among stakeholders.
What is Types Business Communication
Types of business communication refer to the various ways and methods through which organizations and individuals exchange information, ideas, and messages in a business context. These types can be categorized into several major forms:
- Internal Communication:
- Vertical Communication: Communication between different levels of hierarchy within an organization, such as from management to employees or vice versa.
- Horizontal Communication: Communication that occurs between individuals or departments at the same organizational level.
- External Communication:
- Customer Communication: Interactions with customers through various channels like emails, phone calls, or in-person meetings.
- Supplier Communication: Communication with suppliers and vendors regarding orders, deliveries, and negotiations.
- Investor Communication: Communication with shareholders and potential investors, often through annual reports, meetings, and financial updates.
- Public Relations (PR): Managing an organization’s image and reputation through media relations, press releases, and events.
- Marketing Communication: Communication with the market to promote products or services, including advertising, social media, and content marketing.
- Written Communication:
- Email: Common for quick written exchanges within and outside an organization.
- Business Letters: Formal written communication for external parties, often used for legal or official matters.
- Memos: Internal documents used for communication within an organization.
- Reports: Comprehensive documents presenting information, research, or analysis.
- Proposals: Documents outlining plans, projects, or offers.
- Verbal Communication:
- Meetings: In-person or virtual gatherings for discussions, decision-making, and presentations.
- Phone Calls: Conversations with stakeholders over the phone, including conference calls.
- Video Conferencing: Virtual meetings using video technology.
- Presentations: Communicating ideas, proposals, or information to an audience through visual and verbal means.
- Non-Verbal Communication:
- Body Language: Gestures, facial expressions, and postures that convey unspoken messages.
- Visual Aids: The use of charts, graphs, images, and other visuals to enhance understanding during presentations.
- Symbols and Icons: Simple graphics and symbols that convey specific meanings.
- Digital Communication:
- Instant Messaging: Real-time text-based communication through platforms like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or WhatsApp.
- Social Media: Utilizing platforms such as LinkedIn, Twitter, and Facebook for branding, marketing, and customer engagement.
- Blogs: Informal written communication for sharing insights and updates.
- Forums and Discussion Boards: Online platforms for discussions and knowledge-sharing.
- Intranet: Internal networks for sharing information within an organization.
- Formal Communication:
- Contracts and Legal Documents: Formal documents used for agreements, contracts, and legal obligations.
- Company Policies and Procedures: Documents outlining organizational rules, guidelines, and procedures.
- Official Announcements: Formal communications to the organization about significant events or changes.
- Informal Communication:
- Watercooler Conversations: Casual discussions among colleagues.
- Gossip: Informal sharing of information, rumors, and personal anecdotes.
- Texting and Personal Messaging: Informal text-based communication, often outside of the workplace.
- Interpersonal Communication:
- Negotiations: Discussions aimed at reaching agreements or compromises.
- Conflict Resolution: Addressing and resolving conflicts within the organization.
- Feedback: Providing and receiving constructive feedback.
- Cross-Cultural Communication:
- Communication Across Cultures: Adapting communication styles for different cultural contexts when dealing with international partners or clients.
Understanding and effectively utilizing these types of business communication is crucial for organizations to function efficiently, maintain positive relationships with stakeholders, and achieve their goals. The choice of communication type often depends on the specific context, audience, and purpose of the communication.
Who is Required Types Business Communication
Various individuals and roles within an organization require different types of business communication to perform their duties effectively and ensure the smooth operation of the business. Here are some key roles and individuals who typically require various types of business communication:
- Management:
- Vertical Communication: Managers need to communicate with their teams to delegate tasks, provide instructions, and set expectations.
- Horizontal Communication: Managers often need to collaborate with other departments, share information, and coordinate efforts.
- Employees:
- Vertical Communication: Employees receive instructions, feedback, and updates from their managers.
- Horizontal Communication: Co-workers share information, collaborate on projects, and coordinate tasks.
- Sales and Marketing Teams:
- Customer Communication: Sales representatives and marketers communicate with customers to understand their needs, provide information, and promote products or services.
- Marketing Communication: These teams use various channels, including advertising, social media, and content marketing, to reach potential customers.
- Customer Service Representatives:
- Customer Communication: Customer service teams interact with customers to address inquiries, complaints, and support requests, often via phone, email, or live chat.
- Procurement and Supply Chain Specialists:
- Supplier Communication: These individuals communicate with suppliers and vendors to manage orders, deliveries, and negotiate terms.
- Human Resources:
- Employee Communication: HR professionals handle internal communication regarding HR policies, benefits, and employee issues.
- Recruitment Communication: HR communicates with potential candidates during the hiring process.
- Financial and Legal Teams:
- Contracts and Legal Documents: Legal and financial experts deal with contracts, agreements, and other legal and financial documents.
- Executives and Leadership:
- Investor Communication: Executives communicate with shareholders and potential investors through reports, meetings, and financial updates.
- Leadership Communication: Top management communicates with the entire organization about strategic directions, goals, and significant changes.
- Public Relations and Marketing Professionals:
- Public Relations (PR): PR specialists manage the organization’s image and reputation through media relations, press releases, and events.
- IT and Technical Teams:
- Email and Digital Communication: IT professionals often rely on email and digital tools for technical support and updates.
- Technical Reports: They may create reports to explain technical issues and solutions to non-technical stakeholders.
- Project Managers:
- Meetings and Presentations: Project managers conduct meetings and presentations to update stakeholders on project progress, issues, and goals.
- Email and Written Communication: They use emails and written reports to provide detailed project information.
- Cross-Cultural Teams:
- Communication Across Cultures: Teams dealing with international clients or partners adapt their communication styles to suit different cultural contexts.
- Sales Representatives and Account Managers:
- Negotiations: These roles involve negotiations with clients and partners to reach agreements and close deals.
- Legal and Compliance Teams:
- Official Announcements: Legal and compliance teams often issue formal announcements regarding regulatory compliance, changes in policies, or legal matters.
In summary, effective business communication is essential for various roles and departments within an organization to fulfill their responsibilities, collaborate with colleagues, serve customers, and maintain relationships with stakeholders. The specific types of communication required depend on the role and its functions within the organization.
When is Required Types Business Communication
Business communication is required in a wide range of situations and contexts within an organization. Here are some common scenarios and situations where different types of business communication are necessary:
- Daily Operations:
- Internal Communication: To delegate tasks, share updates, and maintain workflow.
- Email and Instant Messaging: For quick exchanges between colleagues and departments.
- Meetings:
- Verbal Communication: Meetings are held for decision-making, problem-solving, and brainstorming.
- Presentations: To share information, proposals, and project updates.
- Customer Interactions:
- Customer Communication: To address inquiries, provide support, and build relationships with customers.
- Sales and Marketing Communication: To promote products and services and close deals.
- Supplier and Vendor Management:
- Supplier Communication: To manage orders, negotiate contracts, and coordinate deliveries.
- Financial and Legal Transactions:
- Contracts and Legal Documents: For agreements, legal matters, and financial transactions.
- Financial Reports: To communicate financial performance and data.
- Recruitment and HR Processes:
- Recruitment Communication: For job postings, interviews, and onboarding.
- Employee Communication: To convey HR policies, benefits, and organizational updates.
- Leadership Communication:
- Leadership Communication: To set organizational goals, provide strategic direction, and share important updates with the entire organization.
- Investor Communication: For reporting financial results and engaging with shareholders.
- Public Relations and Marketing:
- Public Relations (PR): To manage the organization’s image, issue press releases, and engage with the media.
- Marketing Communication: To reach the target market, promote products, and build brand awareness.
- Technical and IT Issues:
- Technical Reports: To explain technical issues and solutions.
- Email and Digital Communication: For technical support and updates.
- Projects and Collaborations:
- Project Updates: To inform stakeholders about project progress, issues, and goals.
- Negotiations: For reaching agreements with project partners or contractors.
- Cross-Cultural Communication:
- Communication Across Cultures: When dealing with international clients, partners, or team members, adapting communication styles for different cultural contexts is essential.
- Policy and Procedure Changes:
- Official Announcements: To inform employees about changes in organizational policies, procedures, or regulations.
- Feedback and Conflict Resolution:
- Feedback: To provide constructive feedback to employees and colleagues.
- Conflict Resolution: To address and resolve conflicts within the organization.
In essence, business communication is a constant and integral part of the daily operations of any organization. The specific types of communication required depend on the circumstances, stakeholders involved, and the purpose of the communication. Effective communication is crucial for achieving organizational goals, maintaining relationships, and ensuring clarity and understanding among all parties.
Where is Required Types Business Communication
Business communication is required in various locations and settings, both within and outside an organization. Here are some common places and contexts where different types of business communication are necessary:
- Within the Office or Workplace:
- Meetings: In conference rooms, boardrooms, or designated meeting spaces.
- Cubicles and Workstations: Colleagues communicate verbally or through digital channels at their desks.
- Breakrooms and Common Areas: Informal conversations and discussions among employees.
- Managers’ Offices: For one-on-one discussions and updates.
- Digital and Online Environments:
- Email: Used on computers and mobile devices for written communication.
- Instant Messaging Platforms: Such as Slack, Microsoft Teams, or other team collaboration tools.
- Intranet: Internal networks where employees access company news, policies, and resources.
- Video Conferencing: Virtual meetings held from various locations.
- Client and Customer Locations:
- Client Meetings: At the client’s office, a neutral location, or virtually.
- Retail Stores and Service Centers: Face-to-face interactions with customers.
- Customer Service Centers: Phone and email support for customers.
- Supplier and Vendor Locations:
- Supplier Negotiations: Often at the supplier’s place of business.
- Vendor Expos and Trade Shows: Industry events where vendors and suppliers communicate with potential clients.
- Legal and Financial Institutions:
- Legal Offices: For legal consultations, negotiations, and signings.
- Financial Institutions: For banking, loans, and financial transactions.
- Public Relations and Media Outlets:
- Media Interviews: At TV and radio studios or in-person for press conferences.
- Public Relations Events: Conferences, product launches, and public relations campaigns.
- Recruitment and HR Agencies:
- Job Interviews: At the company’s office or recruitment agencies.
- HR Departments: For employee onboarding, training, and discussions.
- Boardrooms and Executive Offices:
- Board Meetings: Where executives and board members gather to make strategic decisions.
- Executive Offices: For high-level discussions and negotiations.
- Project Sites and Construction Areas:
- Construction Sites: Project managers, contractors, and team members communicate on-site.
- Field Offices: Temporary offices set up at project sites.
- Retail and E-commerce:
- Online Retail Websites: For customer interactions and sales.
- Brick-and-Mortar Stores: Face-to-face customer interactions in physical retail locations.
- Telecommuting and Remote Work Environments:
- Home Offices: Many employees work from home and communicate with their colleagues, managers, and clients online.
- Public and Social Events:
- Networking Events and Conferences: Opportunities to network and communicate with industry professionals.
- Trade Shows: Exhibiting products and services and engaging with potential clients.
- Cross-Cultural and International Settings:
- Communication may occur in diverse locations, such as international offices, embassies, or during overseas business trips.
The specific locations where business communication takes place depend on the nature of the communication, the parties involved, and the purpose of the interaction. Effective communication is essential regardless of the location to ensure that messages are conveyed clearly and accurately.
How is Required Types Business Communication
The effectiveness of different types of business communication is crucial for achieving organizational goals, maintaining relationships, and ensuring clarity and understanding among stakeholders. How these types of business communication are implemented and executed varies based on several factors, including the context, the audience, and the purpose of the communication. Here’s how various types of business communication are typically used effectively:
- Clear and Concise Language:
- Use clear and straightforward language to avoid misunderstandings.
- Keep messages concise, focusing on key points.
- Audience Understanding:
- Know your audience and tailor your communication to their needs and preferences.
- Consider the background, knowledge, and expectations of the recipients.
- Appropriate Tone:
- Choose a tone that matches the purpose of the communication.
- Adapt your tone to the formality of the situation and the audience.
- Active Listening:
- In verbal communication, actively listen to others to understand their viewpoints.
- Encourage feedback and questions to ensure comprehension.
- Feedback Mechanisms:
- Establish feedback loops to allow recipients to ask questions and seek clarification.
- Provide avenues for stakeholders to respond or provide input.
- Consistency:
- Maintain consistency in messaging and branding across different communication channels.
- Avoid contradictory messages that can lead to confusion.
- Professionalism:
- Maintain professionalism in all communication, whether written or verbal.
- Use proper etiquette, especially in formal written communication like business letters.
- Use of Visual Aids:
- Utilize visuals like charts, graphs, and images to enhance understanding during presentations and reports.
- Ensure that visual aids are clear and support the key points.
- Adaptation to Technology:
- Embrace digital tools and technology for efficient communication, including email, instant messaging, and video conferencing.
- Ensure data security and privacy when using digital communication channels.
- Time Management:
- Be mindful of time in meetings and presentations to keep them productive.
- Avoid overloading people with excessive information.
- Cultural Sensitivity:
- When communicating across cultures, be aware of cultural norms and practices.
- Adapt your communication style to be respectful of cultural differences.
- Conflict Resolution Skills:
- Develop skills for resolving conflicts constructively, such as active listening and compromise.
- Engage in open, respectful dialogue to reach solutions.
- Regular Updates and Reporting:
- Maintain a regular schedule for reporting and updates to keep stakeholders informed.
- Ensure reports are accurate and timely.
- Training and Development:
- Invest in training programs for employees to improve their communication skills.
- Stay up to date with the latest communication trends and technologies.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations:
- Ensure that all communication complies with legal and ethical standards.
- Protect sensitive data and confidential information.
- Adaptability:
- Be ready to adapt communication methods to suit changing circumstances.
- Respond to feedback and make improvements as necessary.
In summary, the effectiveness of different types of business communication is achieved through clear and targeted messaging, a deep understanding of the audience, proper etiquette, and the use of appropriate channels and technology. Adaptation, professionalism, and cultural awareness are key components of successful business communication.
Case Study on Types Business Communication
Improving Business Communication in a Multinational Corporation
Background: XYZ Corporation is a global company with offices in multiple countries. Due to its complex organizational structure and diverse workforce, the company faced various challenges related to business communication.
Problem: XYZ Corporation’s leadership identified several key issues in their communication processes:
- Inefficient Cross-Cultural Communication: The company’s diverse workforce often struggled with cross-cultural communication, leading to misunderstandings and misinterpretations.
- Silos and Lack of Collaboration: Different departments tended to operate in silos, which hindered information sharing and collaboration.
- Overload of Emails: Employees were overwhelmed by the volume of emails, leading to important messages being missed or ignored.
- Ineffective Meetings: Meetings were often disorganized, lacked clear objectives, and failed to achieve meaningful outcomes.
Solution: To address these communication challenges, XYZ Corporation implemented several strategies:
- Cross-Cultural Communication Training:
- The company offered cross-cultural communication training to employees working in international teams. This training included cultural awareness, communication styles, and etiquette to improve interactions.
- Interdepartmental Workshops:
- To foster collaboration, the company organized interdepartmental workshops and team-building activities. This encouraged employees from different areas to work together and share insights.
- Email Management Tools:
- The company introduced email management tools that prioritized and categorized emails. This reduced email overload and helped employees focus on critical messages.
- Meeting Guidelines:
- XYZ Corporation developed clear meeting guidelines that emphasized setting agendas, defining objectives, and assigning responsibilities. Employees were encouraged to schedule meetings only when necessary and to use video conferencing for remote participants.
Results: The implementation of these solutions had a positive impact on the organization:
- Improved Cross-Cultural Communication:
- Employees reported feeling more confident in cross-cultural interactions, resulting in better relationships with international clients and colleagues.
- Increased Collaboration:
- Interdepartmental workshops and team-building activities led to improved collaboration and the sharing of innovative ideas among departments.
- Reduced Email Overload:
- Email management tools reduced the volume of non-essential emails, allowing employees to focus on critical communication.
- More Effective Meetings:
- Meetings became more efficient, with clear objectives and structured agendas, leading to better decision-making and outcomes.
Lessons Learned: XYZ Corporation’s case study highlights the importance of recognizing and addressing communication challenges within a multinational organization. By investing in training, promoting collaboration, managing email overload, and improving meeting practices, the company was able to enhance communication and productivity. The case underscores the value of adaptability and continuous improvement in business communication processes to meet the needs of a diverse and dynamic workforce.
White paper on Types Business Communication
“Strategies for Effective Interactions in the Modern Workplace”
Abstract: Effective communication is the cornerstone of success in the business world. In today’s dynamic and diverse corporate landscape, understanding and applying various types of business communication is essential for organizations to achieve their goals, foster collaboration, and maintain strong relationships with stakeholders. This white paper explores the diverse landscape of business communication, its significance, and strategies for leveraging different types of communication effectively.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- The Role of Communication in Business
- The Evolution of Business Communication
- Verbal Communication
- Face-to-Face Meetings
- Phone Calls and Conference Calls
- Video Conferencing
- Effective Strategies for Verbal Communication
- Written Communication
- Email and Digital Correspondence
- Memos, Letters, and Reports
- Proposals and Business Plans
- Strategies for Effective Written Communication
- Digital Communication
- Instant Messaging and Collaboration Tools
- Social Media and Online Presence
- Blogs, Forums, and Intranet
- Maximizing Digital Communication Efficiency
- Non-Verbal Communication
- Body Language and Visual Cues
- Effective Use of Symbols and Icons
- Enhancing Non-Verbal Communication in the Digital Age
- Formal Communication
- Contracts and Legal Documents
- Company Policies and Procedures
- Leadership and Official Announcements
- Navigating Formal Communication Channels
- Informal Communication
- Watercooler Conversations
- Gossip and Word-of-Mouth
- Texting and Personal Messaging
- Balancing Informal Communication with Professionalism
- Interpersonal Communication
- Negotiations and Conflict Resolution
- Feedback and Constructive Communication
- Building Strong Interpersonal Relationships
- Cross-Cultural Communication
- The Importance of Cultural Awareness
- Adapting Communication Styles
- Best Practices for Cross-Cultural Interactions
- Mass Communication
- Public Relations and Reputation Management
- Advertising and Marketing Strategies
- Engaging with a Broad Audience
- Internal vs. External Communication
- Navigating Communication within and outside the Organization
- Strategies for Effective Internal and External Communication
- Conclusion
- The Future of Business Communication
- The Ongoing Evolution of Communication Strategies
Executive Summary:
Effective business communication is a multifaceted process, encompassing various types and strategies that are essential for success in the modern workplace. This white paper provides an in-depth exploration of the diverse landscape of business communication, covering verbal and written communication, digital tools, non-verbal cues, formal and informal channels, interpersonal interactions, cross-cultural considerations, mass communication, and the distinction between internal and external communication.
The paper emphasizes the importance of understanding the specific requirements and nuances of each communication type to adapt and achieve desired outcomes. Successful business communication fosters collaboration, enhances decision-making, and strengthens relationships with customers, partners, and employees.
In an ever-evolving corporate environment, organizations that master the art of effective business communication are better positioned to thrive and adapt to changing circumstances. This white paper offers insights and practical strategies to help businesses enhance their communication capabilities, ultimately driving success and growth in a rapidly evolving global marketplace.





