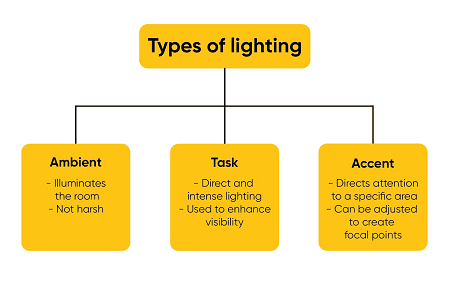
Types of lighting- Lighting can be categorized into several types based on its application and characteristics. Here are the main types:
- Ambient Lighting: Provides overall illumination to a space. It’s the general lighting that fills a room with even light, ensuring visibility and comfort. Examples include ceiling-mounted fixtures and overhead lights.
- Task Lighting: Focuses on specific areas where tasks are performed, such as reading, cooking, or working. It provides concentrated light to improve visibility and reduce eye strain. Examples include desk lamps, under-cabinet lights, and pendant lights over work areas.
- Accent Lighting: Highlights specific features or objects, adding visual interest and depth to a space. It is often used to emphasize artwork, architectural details, or plants. Examples include spotlights, track lighting, and wall-mounted fixtures.
- Decorative Lighting: Primarily used for its aesthetic value rather than for illumination. It adds to the design of the space and can be a focal point. Examples include chandeliers, decorative pendant lights, and string lights.
- Natural Lighting: Uses sunlight to illuminate a space. It is the most energy-efficient form of lighting and can be enhanced with skylights, large windows, or light tubes.
- Task and Ambient Lighting Combination: A blend of ambient and task lighting to provide general illumination while also focusing on specific work areas. This approach ensures that a room is well-lit for both general and specific needs.
Different lighting types can be combined to create a well-lit, functional, and aesthetically pleasing environment.
What is Required Types of lighting
The required types of lighting depend on the specific needs of a space and its intended use. Here are some common scenarios and the types of lighting typically required:
- Residential Spaces:
- Ambient Lighting: Essential for overall illumination in rooms such as living areas, bedrooms, and hallways.
- Task Lighting: Important in areas where specific tasks are performed, such as kitchens (under-cabinet lighting) and workspaces (desk lamps).
- Accent Lighting: Used to highlight decorative elements like artwork or architectural features.
- Offices:
- Ambient Lighting: Provides general illumination throughout the office.
- Task Lighting: Ensures adequate lighting on desks and work areas to reduce eye strain.
- Accent Lighting: Used sparingly to highlight key features or add visual interest.
- Retail Stores:
- Ambient Lighting: Provides overall illumination for the shopping area.
- Task Lighting: Focused on specific display areas or counters.
- Accent Lighting: Highlights products or promotional displays to attract customer attention.
- Educational Facilities:
- Ambient Lighting: Ensures overall visibility in classrooms and common areas.
- Task Lighting: Provides focused light on desks and reading areas.
- Accent Lighting: Used to highlight important information or features.
- Hospitality (Hotels, Restaurants):
- Ambient Lighting: Creates a welcoming atmosphere in lobbies, dining areas, and guest rooms.
- Task Lighting: Provides focused light for tasks such as reading menus or working.
- Accent Lighting: Enhances the aesthetic appeal of the space and highlights architectural details.
- Industrial/Commercial Spaces:
- Ambient Lighting: Provides uniform light for work areas and common spaces.
- Task Lighting: Ensures adequate illumination for specific tasks, such as assembly lines or detailed work.
- Accent Lighting: May be used for safety or to highlight specific areas.
Each type of lighting plays a crucial role in creating a functional, comfortable, and visually appealing environment, tailored to the specific needs and activities of the space.
Who is Required Types of lighting
The term “required types of lighting” refers to the different types of lighting necessary to meet specific needs or requirements for various spaces or applications. Here’s a breakdown of who might require specific types of lighting:
- Homeowners:
- Ambient Lighting: Needed for general illumination in living spaces, bedrooms, and hallways.
- Task Lighting: Important in areas like kitchens and home offices for specific activities.
- Accent Lighting: Used to highlight decorative features or artwork.
- Office Workers:
- Ambient Lighting: Provides general lighting throughout the workspace.
- Task Lighting: Essential for individual work areas to reduce eye strain and improve productivity.
- Accent Lighting: Used for design and aesthetic purposes in office interiors.
- Retail Business Owners:
- Ambient Lighting: Ensures overall visibility in the store.
- Task Lighting: Highlights specific product displays or checkout areas.
- Accent Lighting: Draws attention to featured products or promotions.
- Educators and Students:
- Ambient Lighting: Ensures overall visibility in classrooms and study areas.
- Task Lighting: Provides focused light for reading, writing, and other tasks.
- Accent Lighting: Can be used to highlight educational displays or key information.
- Hospitality Industry Professionals (Hotels, Restaurants):
- Ambient Lighting: Creates a welcoming atmosphere in lobbies, dining areas, and guest rooms.
- Task Lighting: Provides focused lighting for dining tables, work areas, and guest tasks.
- Accent Lighting: Enhances the aesthetic appeal and highlights key features or architectural elements.
- Industrial/Commercial Facility Managers:
- Ambient Lighting: Ensures uniform illumination in work areas and common spaces.
- Task Lighting: Provides specific lighting for detailed work or production areas.
- Accent Lighting: May be used for safety purposes or to highlight specific zones within the facility.
In essence, the required types of lighting depend on the specific needs and functions of the space or activity. Proper lighting design ensures that each area is effectively illuminated to support its intended use.
When is Required Types of lighting
The requirement for different types of lighting arises based on various factors such as the function of the space, the time of day, and specific tasks being performed. Here’s when each type of lighting is typically required:
- Ambient Lighting:
- When: At all times to provide general illumination and ensure visibility throughout a space.
- Purpose: Creates a base level of light that fills a room and supports everyday activities without causing glare or shadows.
- Task Lighting:
- When: When specific activities or tasks are being performed that require focused light, such as reading, cooking, or working.
- Purpose: Provides concentrated light to enhance visibility and reduce eye strain for tasks requiring precision or detail.
- Accent Lighting:
- When: To highlight specific features, objects, or areas, such as artwork, architectural details, or plants. Often used during events, gatherings, or to enhance the aesthetic appeal of a space.
- Purpose: Adds visual interest, depth, and emphasis to particular elements within a room or area.
- Decorative Lighting:
- When: Primarily for aesthetic or design purposes, often used during special occasions, events, or to enhance the overall ambiance of a space.
- Purpose: Serves as a design element rather than for functional illumination, creating a focal point or visual interest.
- Natural Lighting:
- When: During daylight hours to provide illumination from the sun. Can be enhanced with architectural features like skylights or large windows.
- Purpose: Offers the most energy-efficient lighting and can improve mood and productivity, making use of daylight to reduce reliance on artificial lighting.
Each type of lighting is required based on the specific needs of the space and activities being conducted. For example, task lighting is critical during work or study hours, while ambient lighting is necessary at all times to ensure a well-lit environment.
Where is Required Types of lighting

The required types of lighting are needed in various locations and contexts based on their specific purposes. Here’s a breakdown of where each type is typically required:
- Ambient Lighting:
- Where: In virtually every room and space, including living rooms, bedrooms, kitchens, hallways, offices, and commercial areas.
- Purpose: To provide general illumination that makes the space functional and comfortable for everyday use.
- Task Lighting:
- Where: In areas where specific activities are performed, such as:
- Kitchens: Under-cabinet lights for countertops.
- Offices: Desk lamps for workspaces.
- Bathrooms: Vanity lights for grooming tasks.
- Reading Nooks: Floor or table lamps for reading.
- Purpose: To offer focused light that enhances visibility and reduces strain during tasks requiring precision.
- Where: In areas where specific activities are performed, such as:
- Accent Lighting:
- Where: Used to highlight specific features or objects, including:
- Art Galleries: To spotlight artwork.
- Living Rooms: To accentuate architectural features or decorative elements.
- Retail Stores: To draw attention to product displays.
- Purpose: To add visual interest and highlight particular elements or features in a space.
- Where: Used to highlight specific features or objects, including:
- Decorative Lighting:
- Where: Used in areas where aesthetics are important, such as:
- Dining Rooms: Chandeliers or pendant lights.
- Event Spaces: String lights or decorative fixtures.
- Holiday Decorations: Seasonal lights.
- Purpose: To enhance the visual appeal and create a specific ambiance or focal point.
- Where: Used in areas where aesthetics are important, such as:
- Natural Lighting:
- Where: In spaces with access to daylight, such as:
- Residential Buildings: Through windows, skylights, or light tubes.
- Offices: Large windows to bring in natural light.
- Educational Facilities: Classrooms with windows for daylight.
- Purpose: To provide energy-efficient lighting and improve mood and productivity by making use of sunlight.
- Where: In spaces with access to daylight, such as:
Each type of lighting serves a specific function and is strategically placed to meet the needs of the space and activities performed within it.
How is Required Types of lighting
The “required types of lighting” are designed and implemented based on their specific functions and the needs of the space. Here’s how each type is typically achieved:
- Ambient Lighting:
- How: Achieved using fixtures that provide broad, even light throughout a space. Common sources include ceiling-mounted lights, recessed lighting, chandeliers, and pendant lights.
- Design Considerations: Should evenly distribute light to avoid dark spots and shadows. Often uses fixtures with diffusers to soften the light.
- Task Lighting:
- How: Utilizes focused lighting to illuminate specific areas where tasks are performed. Examples include desk lamps, under-cabinet lights, adjustable reading lamps, and track lighting aimed at work areas.
- Design Considerations: Should be positioned to reduce shadows and glare on the work surface. The light intensity should be sufficient for the task being performed.
- Accent Lighting:
- How: Used to highlight particular features or objects. This can be achieved with spotlights, track lighting, wall-mounted sconces, or LED strips. The light is directed to emphasize artwork, architectural elements, or decorative pieces.
- Design Considerations: Requires careful positioning and intensity to ensure the highlighted feature stands out without overwhelming the space.
- Decorative Lighting:
- How: Focuses on visual appeal and can include a variety of styles, such as chandeliers, pendant lights, string lights, and decorative lamps. Often designed to be a focal point or add aesthetic value.
- Design Considerations: Should complement the overall design of the space. The lighting may also be integrated with other types of lighting to balance aesthetics and functionality.
- Natural Lighting:
- How: Utilizes daylight to illuminate spaces. Achieved through architectural features like windows, skylights, and light tubes. Can be enhanced with light-filtering window treatments to control the amount of light entering the space.
- Design Considerations: Should maximize daylight while minimizing glare and heat. The placement of windows and other openings should be optimized to provide consistent and efficient natural light throughout the day.
Each type of lighting is implemented through specific fixtures and design strategies to meet the functional and aesthetic requirements of the space. Proper planning and integration of these lighting types help create a well-lit, comfortable, and visually appealing environment.
Case Study on Types of lighting

Lighting Design for “Tech Innovators Inc.” Office Space
Background
“Tech Innovators Inc.” is a growing technology company that recently moved into a new office space. The company wanted to create a modern, efficient, and welcoming work environment for its employees. They engaged a lighting designer to develop a lighting plan that would enhance productivity, comfort, and aesthetics.
Objectives
- Improve Workspace Functionality: Ensure that the lighting supports various tasks and work areas.
- Enhance Employee Well-being: Create a pleasant and visually stimulating environment.
- Highlight Design Elements: Accentuate architectural features and branding elements.
Lighting Strategy
- Ambient Lighting:
- Implementation: Recessed LED downlights were installed in open areas and corridors to provide uniform illumination throughout the office. Ceiling-mounted fixtures with dimming capabilities were used in conference rooms and break areas.
- Outcome: Ensured a well-lit environment that supports general activities and provides consistent visibility throughout the office.
- Task Lighting:
- Implementation: Adjustable desk lamps with LED bulbs were provided at each workstation to offer focused light for computer work and other tasks. Under-cabinet LED strips were installed in the kitchen and break areas for additional task lighting.
- Outcome: Enhanced productivity by reducing eye strain and improving visibility for detailed work, while also ensuring that employees had adequate lighting for their specific tasks.
- Accent Lighting:
- Implementation: LED track lighting was used to highlight artwork and branding elements in the reception area. Wall-mounted spotlights were directed at architectural features, such as exposed brick walls and modern sculptures.
- Outcome: Added visual interest and emphasized the company’s brand identity, creating a more engaging and dynamic office environment.
- Decorative Lighting:
- Implementation: A contemporary chandelier was installed in the lobby to make a strong first impression. Pendant lights with colorful glass shades were used in the café area to add a touch of personality and design flair.
- Outcome: Enhanced the aesthetic appeal of the office, creating focal points and contributing to a vibrant and welcoming atmosphere.
- Natural Lighting:
- Implementation: Large floor-to-ceiling windows were utilized to maximize daylight in work areas. Light-filtering blinds were installed to control glare while allowing ample natural light to enter.
- Outcome: Improved employee well-being and reduced reliance on artificial lighting during daylight hours, creating a healthier and more energizing work environment.
Results
- Employee Feedback: Employees reported higher satisfaction with their work environment, citing improved visibility and a more pleasant atmosphere.
- Productivity: The combination of ambient, task, and natural lighting contributed to increased productivity and comfort.
- Aesthetic Impact: The office’s modern and vibrant design was successfully highlighted through strategic use of accent and decorative lighting.
Conclusion
The lighting design for “Tech Innovators Inc.” effectively utilized a combination of ambient, task, accent, decorative, and natural lighting to create a functional, comfortable, and aesthetically pleasing office environment. The tailored lighting strategy addressed the specific needs of different areas, enhancing both the practicality and visual appeal of the workspace.
White paper on Types of lighting
Here’s an outline for a white paper on “Types of Lighting,” which provides an in-depth exploration of the various lighting types, their applications, and benefits. This document is designed for professionals involved in interior design, architecture, or facility management.
Executive Summary
This white paper explores the fundamental types of lighting used in various environments, detailing their applications, benefits, and design considerations. It aims to provide insights for professionals in interior design, architecture, and facility management to optimize lighting strategies for functionality, aesthetics, and energy efficiency.
1. Introduction
- Purpose: To provide a comprehensive understanding of different lighting types and their impact on various environments.
- Scope: Covers ambient, task, accent, decorative, and natural lighting.
2. Ambient Lighting
- Definition: General illumination that fills a space uniformly.
- Types of Fixtures: Recessed lights, ceiling-mounted fixtures, chandeliers.
- Applications: Residential living areas, offices, commercial spaces.
- Benefits:
- Provides overall visibility and comfort.
- Reduces glare and shadows.
- Essential for everyday activities.
3. Task Lighting
- Definition: Focused lighting that illuminates specific areas for particular tasks.
- Types of Fixtures: Desk lamps, under-cabinet lights, adjustable floor lamps.
- Applications: Workspaces, kitchens, reading areas.
- Benefits:
- Enhances visibility for detailed tasks.
- Reduces eye strain.
- Improves productivity and comfort.
4. Accent Lighting
- Definition: Lighting used to highlight specific features or objects.
- Types of Fixtures: Spotlights, track lighting, wall-mounted sconces.
- Applications: Art galleries, retail displays, architectural features.
- Benefits:
- Adds visual interest and depth.
- Emphasizes focal points and design elements.
- Enhances aesthetic appeal.
5. Decorative Lighting
- Definition: Lighting primarily used for aesthetic purposes rather than functionality.
- Types of Fixtures: Chandeliers, pendant lights, decorative lamps.
- Applications: Dining rooms, event spaces, holiday decorations.
- Benefits:
- Creates visual impact and focal points.
- Enhances the overall design and ambiance.
- Serves as a design statement.
6. Natural Lighting
- Definition: Illumination provided by sunlight.
- Types of Fixtures: Windows, skylights, light tubes.
- Applications: Residential and commercial buildings, educational facilities.
- Benefits:
- Energy-efficient and reduces reliance on artificial lighting.
- Improves mood and productivity.
- Provides dynamic lighting that changes with the time of day.
7. Design Considerations
- Integration: Combining different lighting types to achieve optimal results.
- Energy Efficiency: Selecting fixtures and technologies that reduce energy consumption.
- Control Systems: Implementing dimmers, sensors, and smart controls for flexibility.
- Aesthetics: Ensuring that lighting complements the overall design and purpose of the space.
8. Case Studies
- Commercial Office: Example of effective lighting design in an office environment, demonstrating the use of ambient, task, and accent lighting.
- Retail Store: Case study showing how task and accent lighting enhance product displays and customer experience.
- Residential Home: Overview of a lighting design approach that integrates ambient, task, and natural lighting for comfort and functionality.
9. Future Trends
- Advancements in LED Technology: Emerging trends and innovations in LED lighting.
- Smart Lighting Solutions: The impact of IoT and smart technology on lighting design.
- Sustainability: Increasing focus on environmentally friendly and energy-efficient lighting solutions.
10. Conclusion
- Summary: Recap of the importance of understanding and implementing various types of lighting.
- Recommendations: Best practices for selecting and integrating lighting types based on specific needs and goals.
11. References
- Sources: Citing industry standards, research papers, and expert opinions.
Appendices
- Glossary: Definitions of key terms related to lighting.
- Lighting Diagrams: Visual representations of different lighting types and their applications.
This white paper provides a detailed examination of lighting types, helping professionals make informed decisions about lighting design and implementation.
Industrial Application of Types of lighting

In industrial settings, lighting plays a crucial role in enhancing safety, productivity, and efficiency. Here’s a detailed look at the industrial applications of different types of lighting:
1. Ambient Lighting
Definition: General lighting that provides uniform illumination throughout an industrial space.
Applications:
- Factories: Overhead fixtures, such as high-bay or low-bay lights, are used to ensure consistent lighting across large production areas.
- Warehouses: Ceiling-mounted lights or LED high-bays provide uniform light to facilitate movement and operations.
Benefits:
- Safety: Reduces the risk of accidents by minimizing shadows and dark spots.
- Visibility: Ensures that all areas are adequately lit, improving overall operational efficiency.
- Comfort: Creates a well-lit environment that supports workers’ visibility and reduces eye strain.
2. Task Lighting
Definition: Focused lighting that illuminates specific areas where detailed work or tasks are performed.
Applications:
- Assembly Lines: Adjustable task lights or workbench lights provide focused illumination for precise tasks.
- Inspection Areas: Specialized lighting, such as LED task lamps, is used to ensure accurate inspections of parts and products.
Benefits:
- Accuracy: Enhances visibility for detailed work, improving precision and quality.
- Productivity: Reduces eye strain and fatigue, allowing workers to perform tasks more efficiently.
- Flexibility: Task lights can be adjusted to meet the needs of different tasks and workstations.
3. Accent Lighting
Definition: Lighting used to highlight specific features or areas.
Applications:
- Safety Markings: Highlighting floor markings, emergency exits, and safety equipment to improve visibility and safety.
- Equipment Highlights: Spotlights or focused lighting used to draw attention to critical machinery or controls.
Benefits:
- Safety: Enhances visibility of important safety features and equipment.
- Operational Efficiency: Helps in quickly locating critical machinery or control panels.
4. Decorative Lighting
Definition: Lighting primarily used for aesthetic purposes rather than functionality.
Applications:
- Corporate Offices: Decorative fixtures in administrative areas or break rooms to enhance the work environment.
- Reception Areas: Stylish lighting in entrance areas to create a welcoming atmosphere for visitors and clients.
Benefits:
- Brand Image: Enhances the company’s image and creates a positive impression on visitors and clients.
- Work Environment: Contributes to a more pleasant and motivating workspace for employees.
5. Natural Lighting
Definition: Illumination provided by sunlight, integrated into industrial environments.
Applications:
- Skylights: Used in large manufacturing facilities and warehouses to bring in natural light.
- Windows: Large windows or light tubes in offices or administrative areas to maximize daylight.
Benefits:
- Energy Savings: Reduces the need for artificial lighting, lowering energy costs.
- Employee Well-being: Improves mood and productivity by providing a connection to the outside environment.
- Sustainability: Contributes to environmentally friendly practices by utilizing natural light.
6. Specialized Industrial Lighting
Definition: Lighting designed to meet the specific needs of industrial environments.
Applications:
- Explosion-Proof Lighting: Used in hazardous environments like chemical plants to prevent igniting flammable substances.
- High-Temperature Lighting: Fixtures designed to withstand high temperatures in industries like metallurgy and glass manufacturing.
Benefits:
- Safety: Ensures safe operation in hazardous or extreme conditions.
- Durability: Provides long-lasting and reliable performance in challenging environments.
Design Considerations for Industrial Lighting
- Brightness and Uniformity: Ensure sufficient illumination levels and even distribution to minimize shadows and enhance visibility.
- Energy Efficiency: Select energy-efficient lighting solutions to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
- Maintenance: Choose durable fixtures that require minimal maintenance and are easy to clean, especially in environments with dust or debris.
- Compliance: Adhere to industry standards and regulations related to lighting in industrial settings to ensure safety and efficiency.
Conclusion
In industrial applications, the effective use of ambient, task, accent, decorative, and natural lighting is essential for optimizing safety, productivity, and operational efficiency. By carefully selecting and implementing the appropriate types of lighting, industrial environments can enhance both functionality and worker comfort, contributing to overall success and sustainability.